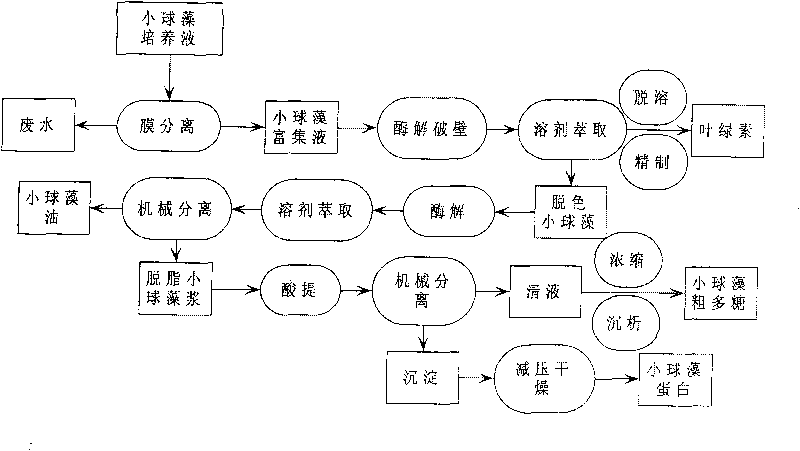
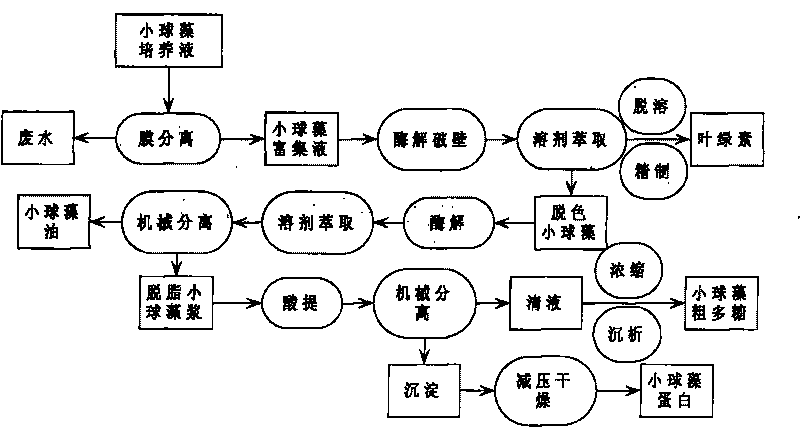
Method for continuously extracting functional components of chlorella vulgaris
A functional component, chlorella technology, applied in the preparation method of peptides, chemical instruments and methods, algae/bryopeptides, etc., can solve the problems of unclear products, long operation cycle, low yield, etc., and achieve simple operation Reliable, easy-to-maintain active effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Use a pump to introduce the chlorella culture solution into a membrane separation system with polysulfone (or ceramic or polyether) as the membrane material for microporous membrane filtration. The control membrane separation process parameters are: the cross-flow velocity is 2.4cm / s, the operating pressure The temperature is 0.02MPa, the temperature is 20°C, the chlorella is concentrated to 0.5% of the original volume, and the chlorella concentrate is obtained. Add 0.1% of cellulase, 0.1% of pectinase, and 0.1% of xylanase to the concentrated solution (the amount of enzyme added is the percentage of dry matter in the concentrated solution of Chlorella), at a temperature of 40°C, and carry out enzymatic hydrolysis for 1 hour Broken. To obtain the concentrated liquid of broken chlorella, ethanol was added to the concentrated liquid of broken chlorella to make the concentration 50%, the temperature was 50° C., and extraction was carried out for 2 hours. Then centrifuge (...
Embodiment 2
[0035]Use a pump to introduce the chlorella culture solution into a membrane separation system using polysulfone (or ceramics or polyether) as a membrane material for microporous membrane filtration. The control membrane separation process parameters are: the cross-flow velocity is 5cm / s, and the operating pressure is 0.04MPa, the temperature is 30°C, the chlorella is concentrated to 0.8% of the original volume, and the chlorella concentrate is obtained. Add 0.2% of cellulase, 0.3% of pectinase, and 0.4% of xylanase to the concentrated solution (the amount of enzyme added is the percentage of dry matter in the concentrated solution of Chlorella), at a temperature of 50°C, and carry out enzymatic hydrolysis for 2 hours The wall is broken to obtain the concentrated solution of the broken wall chlorella. Add ethanol to the concentrated solution of broken chlorella to make the concentration 60%, the temperature is 55° C., and extract for 3 hours. Then centrifuge (3000r / min) to ob...
Embodiment 3
[0037] Use a pump to introduce the chlorella culture solution into a membrane separation system using polysulfone (or ceramics or polyether) as a membrane material for microporous membrane filtration. The control membrane separation process parameters are: the cross-flow velocity is 4cm / s, and the operating pressure is 0.08MPa, the temperature is 40 ℃, the chlorella is concentrated to 1% of the original volume, and the chlorella concentrate is obtained. Add 0.3% of cellulase, 0.3% of pectinase, and 0.3% of xylanase to the concentrated solution (the amount of enzyme added is the percentage of dry matter in the concentrated solution of Chlorella), at a temperature of 60°C, and carry out enzymatic hydrolysis for 5 hours The wall is broken to obtain the concentrated solution of the broken wall chlorella. Add ethanol to the broken chlorella concentrate to make the concentration 70%, the temperature is 50°C, and extract for 6 hours. Then centrifuge (3000r / min) to obtain ethanol ext...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com