Method for detecting total number of bacterial colonies in activated lactobacillus drink
A technology of active lactic acid bacteria and detection methods, which is applied in the direction of biochemical equipment and methods, microbial measurement/inspection, etc., and can solve problems such as cumbersome operations, complicated effects, and reduced accuracy of results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0012] Embodiment 1: TTC nutrient agar preparation
[0013] Weigh 33g of nutrient agar, add 1 liter of distilled water or deionized water, divide into Erlenmeyer flasks, stir, heat and boil to dissolve, and autoclave at 121°C for 15min. After sterilization, when the culture medium is cooled to about 45°C, add sterile TTC to make the concentration of TTC reach 2.5mg / 100ml, mix well, and pour onto the plate.
Embodiment 2
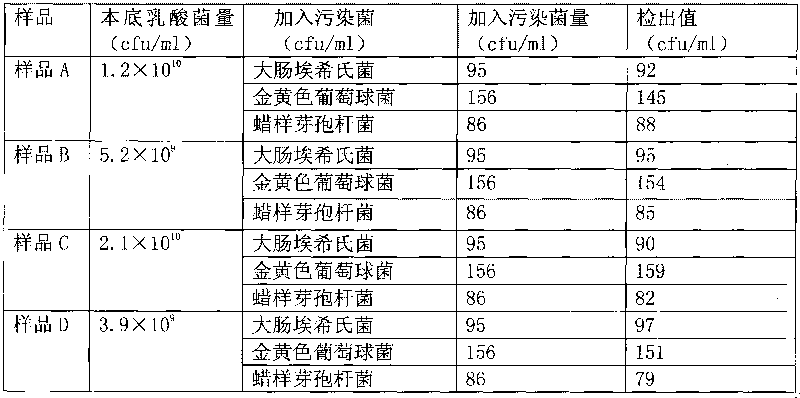
[0014] Embodiment 2: Detection of the total number of bacterial colonies in artificially polluted samples
[0015] Take fresh cultures of Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, and Bacillus cereus, dilute them with sterile saline to a concentration of 0.5 McFarland turbidimetric tubes, and then serially dilute them 10 times. Add the solution to sterile samples A, B, C, and D respectively, so that the concentration of each contaminating bacteria in the sample reaches about 1000cfu / ml. Take 1ml of the bacterium-added sample and mix it with 9ml sterile normal saline to make a 10-fold dilution, take 1ml of the diluted solution and mix it with an appropriate amount (25ml) of sterile normal saline, filter it through a 0.45μm filter membrane, and then use 25ml Rinse the filter membrane with physiological saline, and stick it on the TTC nutrient agar plate described in Example 1 with the filter side up after rinsing. 37 ℃, 48 ± 2h inverted culture. Its count is as follows:
[001...
Embodiment 3
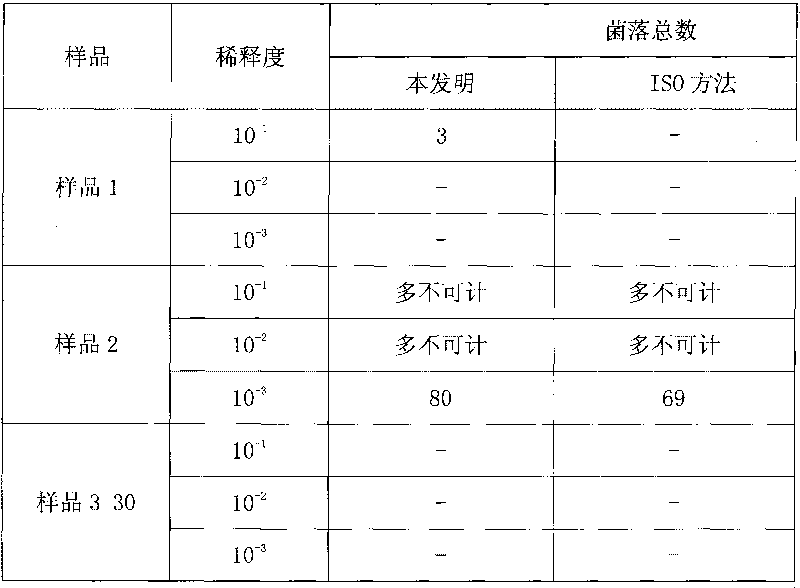
[0018] Embodiment 3: Comparison between the present invention and ISO 13559:2002 (E) "Butter, fermented milk products and fresh cheese. Enumeration of contaminating microorganisms. Colony counting method at 30°C"
[0019] 30 kinds of yoghurt samples were purchased in the market, and the method of the present invention and ISO 13559: 2002 (E) "Butter, fermented milk products and fresh cheese. Counting of contaminating microorganisms. Colony counting method at 30°C" was adopted respectively to check the total number of colonies .
[0020] The present invention detects that 2 samples are positive for the total number of colonies, and the ISO method detects 1 sample. In the present invention, at 10 times dilution concentration, 28 samples have no colony growth on the filter membrane, and sample 1 grows 3 colonies. After identification, none of them are lactic acid bacteria, which can be included in the total number of colonies. The total number of colonies in sample 1 is 30cfu / ml....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com