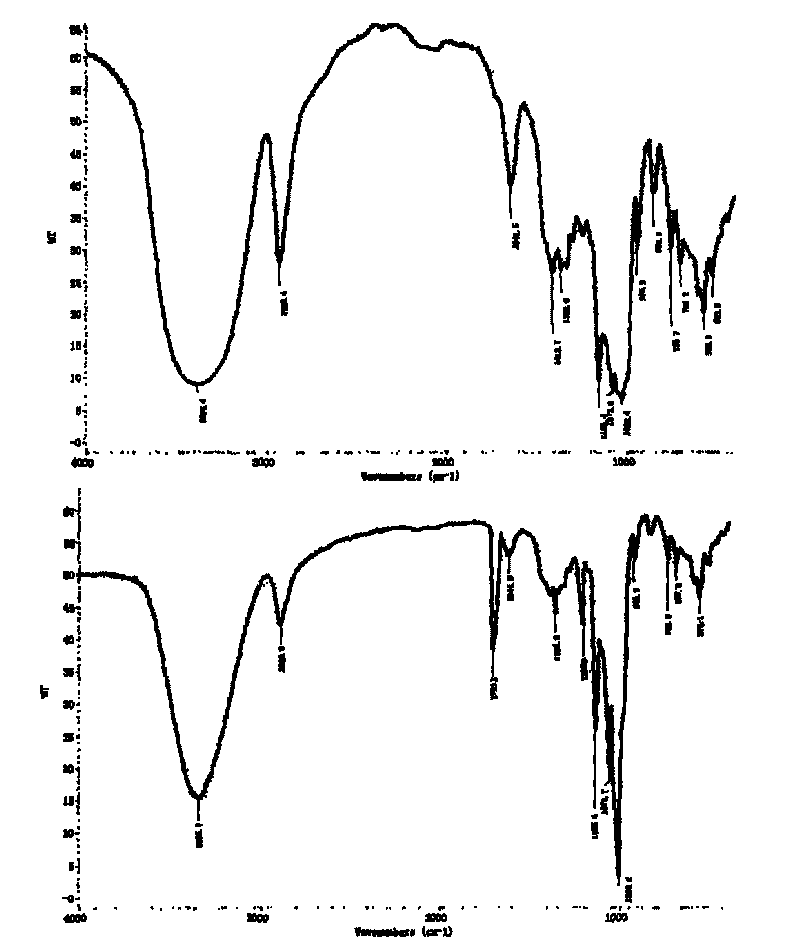
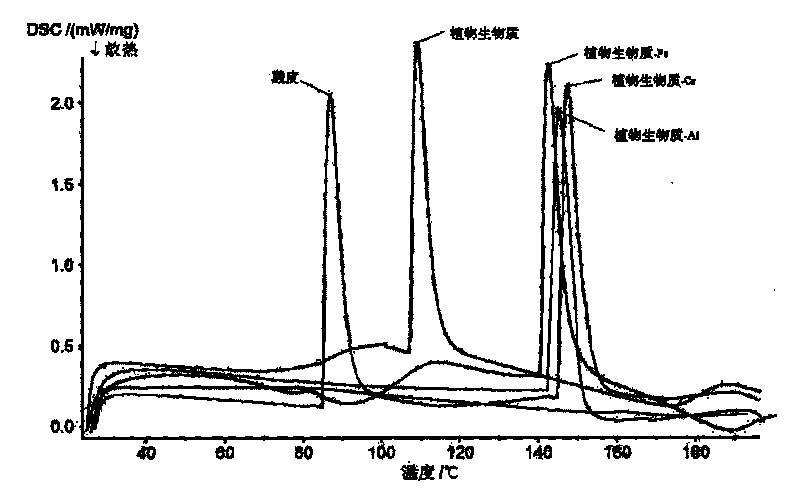
Plant biomass-metal in-situ leather combining-tanning method
A plant biomass combined tanning technology, which is applied in the field of plant biomass-metal in-situ combined tanning of leather, can solve the problems of molecular size collagen binding force affecting penetration, difficult mechanism and other problems, and achieves stable framework structure, simple synthesis technology, The effect of raising the shrinkage temperature of finished leather
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
[0022] 50.0 g of the original polysaccharide substance (starch, cellulose, sucrose, etc.) is formulated into a 40% paste liquid, and the pH of the solution is adjusted to 3.0 with 3% sulfuric acid, and 1.5 g of cerium ammonium nitrate is added, and the mixture is stirred at 48° C. Reflux for 4 hours, the obtained precipitate was separated and purified by centrifugation, dried in an oven at 45°C, and then the plant biomass was mixed with ferrous chloride (FeCl 2 ) in a molar ratio of 1:1 to 2:1 to prepare solutions with a molar concentration of 0.05 to 0.20 mol / L, add them to a reactor with a stirrer, and mix them thoroughly under stirring. The fraction is 3% HCl solution to adjust the pH of the reaction solution to 2.0-4.0, react at room temperature for 2-6 hours, and centrifuge and purify the generated precipitate, dry it at a temperature of 40-60°C and a vacuum of 0.04MPa, and then place it in an oven at a temperature of 50°C drying.
Embodiment approach 2
[0024] 50.0 g of the original polysaccharide substance (starch, cellulose, sucrose, etc.) is formulated into a 40% paste liquid, and the pH of the solution is adjusted to 3.0 with 3% sulfuric acid, and 1.5 g of cerium ammonium nitrate is added, and the mixture is stirred at 48° C. Reflux for 4 hours, the obtained precipitate was separated and purified by centrifugation, dried in an oven at 45°C, and then the plant biomass was mixed with chromium chloride (CrCl 3 ) in a molar ratio of 1:1 to 2:1 to prepare solutions with a molar concentration of 0.05 to 0.20 mol / L, add them to a reactor with a stirrer, and mix them thoroughly under stirring. The fraction is 3% HCl solution to adjust the pH of the reaction solution to 2.0-4.0, react at room temperature for 2-6 hours, and centrifuge and purify the generated precipitate, dry it at a temperature of 40-60°C and a vacuum of 0.04MPa, and then place it in an oven at a temperature of 50°C drying.
Embodiment approach 3
[0026] 50.0 g of the original polysaccharide substance (starch, cellulose, sucrose, etc.) is formulated into a 40% paste liquid, and the pH of the solution is adjusted to 3.0 with 3% sulfuric acid, and 1.5 g of cerium ammonium nitrate is added, and the mixture is stirred at 48° C. Reflux for 4 hours, the obtained precipitate was separated and purified by centrifugation, dried in an oven at 45°C, and then the plant biomass was mixed with aluminum chloride (AlCl 3 ) in a molar ratio of 1:1 to 2:1 to prepare solutions with a molar concentration of 0.05 to 0.20 mol / L, add them to a reactor with a stirrer, and mix them thoroughly under stirring. The fraction is 3% HCl solution to adjust the pH of the reaction solution to 2.0-4.0, react at room temperature for 2-6 hours, and centrifuge and purify the generated precipitate, dry it at a temperature of 40-60°C and a vacuum of 0.04MPa, and then place it in an oven at a temperature of 50°C drying.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com