Passivation material for in-situ restoration of soil polluted by heavy metal, and preparation and use method thereof
A technology for in-situ remediation and polluted soil, applied in the restoration of polluted soil, etc., can solve the problem of insufficient understanding of the stability of the remediation effect of passivation materials and environmental safety, the lack of outstanding effect of multi-element composite pollution treatment, and the impact on soil physical and chemical properties. properties and other issues, to achieve good passivation repair effect, small impact on soil physicochemical properties and fertility, and easy social acceptance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Example 1: Preparation and use of passivation materials
[0029] Adjust the pH of the aqueous solution of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTMABr) to 11.0-11.3. with 25% tetramethylammonium hydroxide (TMAOH), and stir for 10 minutes. Under the conditions of continued stirring and room temperature, add ethyl orthosilicate (TEOS) to the above solution. The molar ratio of the above raw material reaction is: n(TEOS): n(TMAOH): n(CTMABr): n(H 2 O)=1.0:0.36:0.24:110. The gel formed by the reaction is placed at room temperature for 24 hours, then the upper layer solution is discarded, the solid product is filtered, washed 4 times, dried in an air stream for 2 hours (120°C), and then calcined in a muffle furnace at 550°C for 4 hours, that is The finished product can be obtained.
[0030] When the passivation material is used, according to the specific soil pollution, 0.45% to 0.9% of the dry soil weight is applied to the soil. Considering that the passivation material is in full co...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Example 2: In-situ passivation to repair alkaline contaminated soil
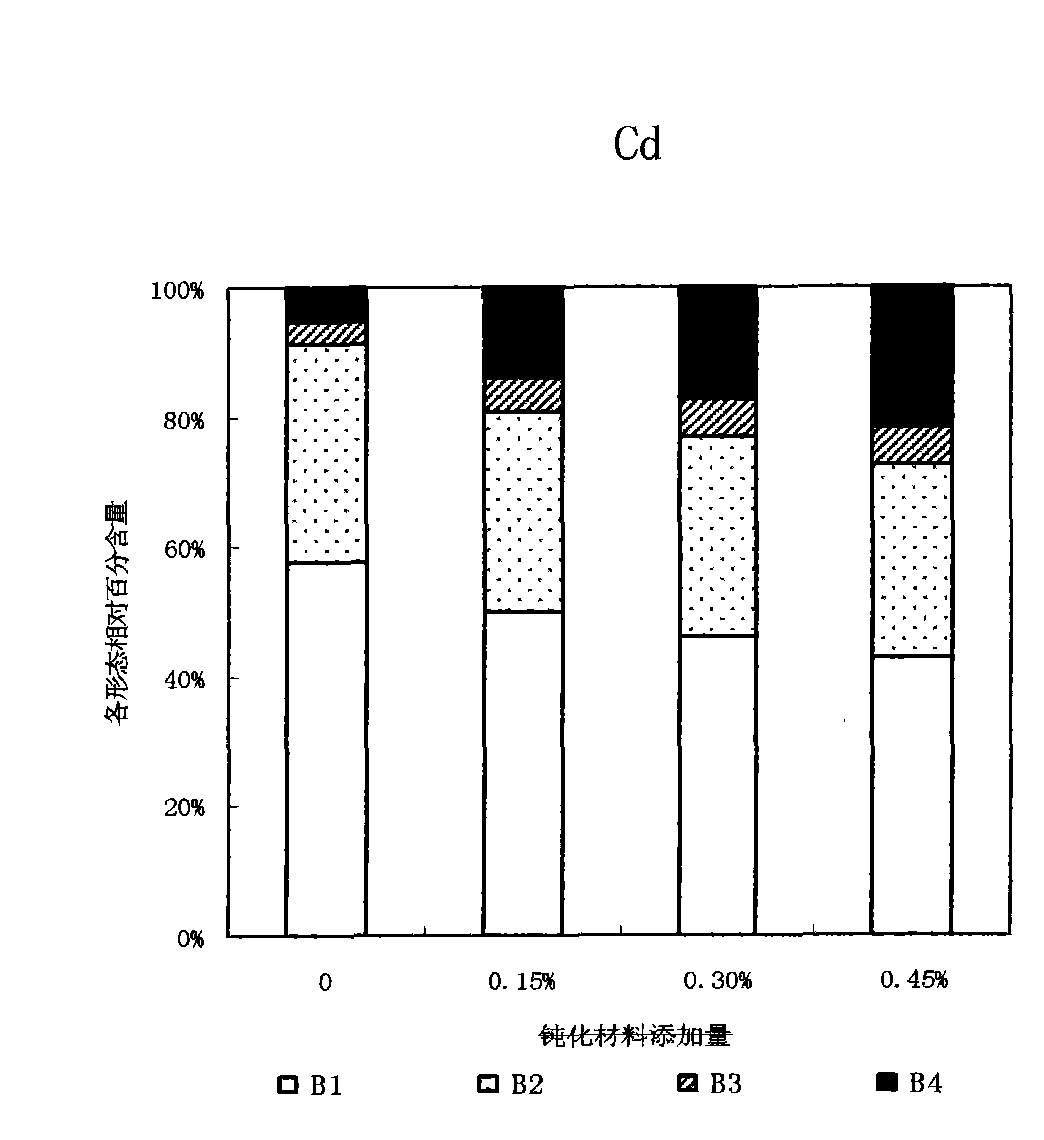
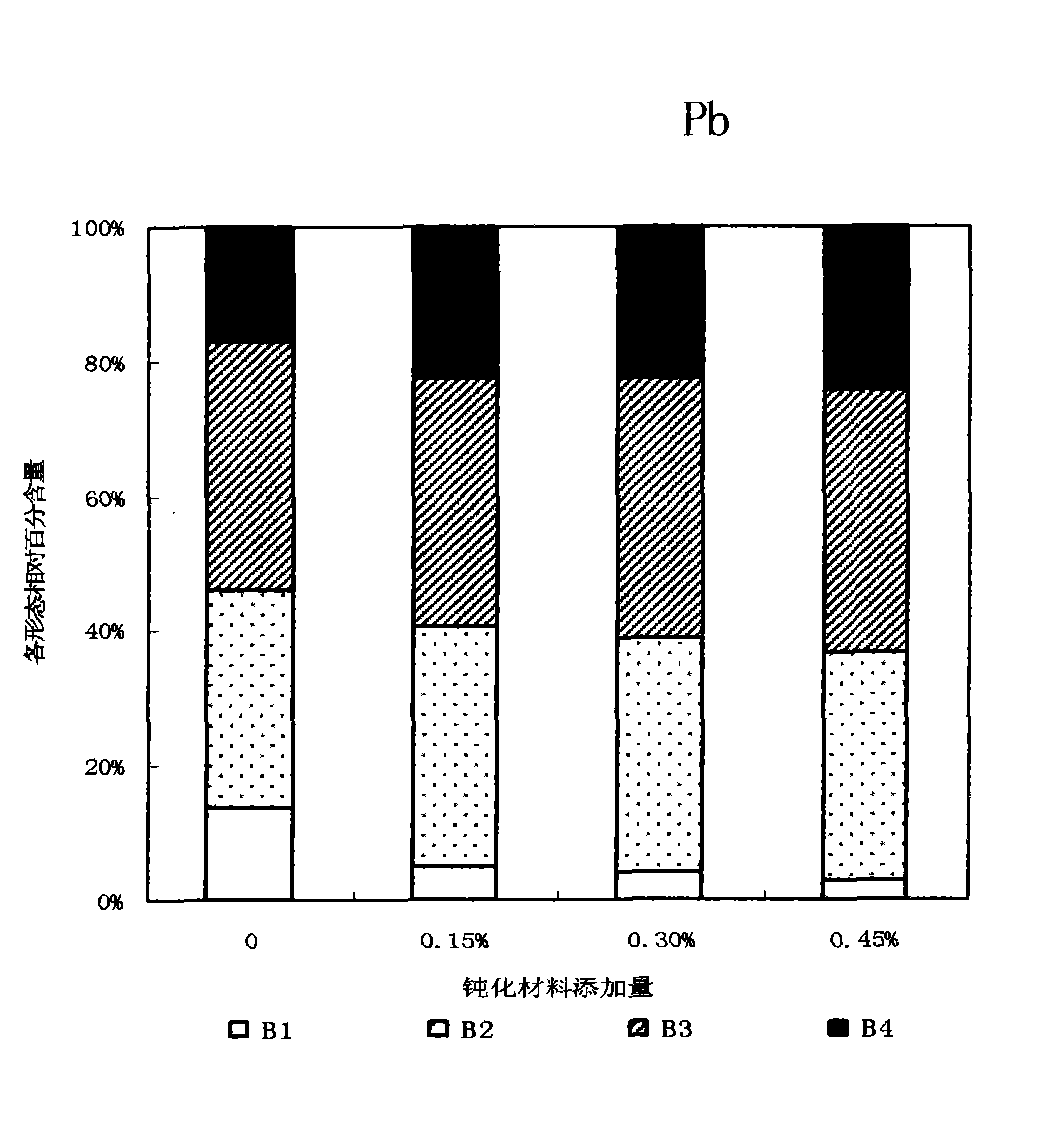
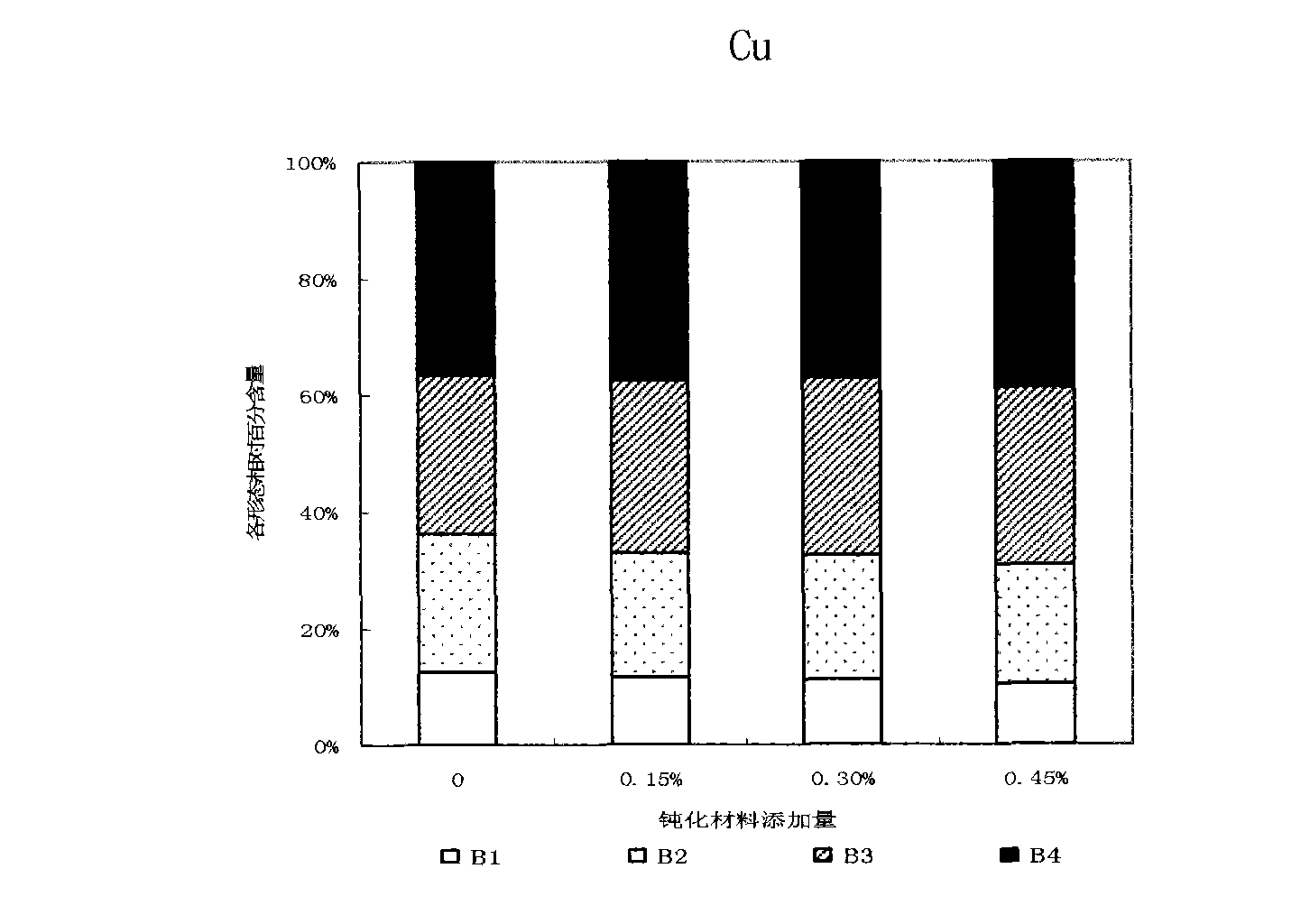
[0032] The test soil was collected from the suburbs of Tianjin, with a pH of 8.18, which was alkaline. The concentrations of exogenous heavy metals in the soil are: Cd-5mg / kg, Pb-600mg / kg, Cu-200mg / kg. Add passivation materials with mass ratios of 0, 0.15%, 0.30%, 0.45% to the soil, and add a certain amount of urea and potassium dihydrogen phosphate as base fertilizer, mix them thoroughly, and put them into plastic pots. Load 1.5 kg of soil, and repeat each treatment 3 times. Sow rapeseed after 2 weeks of aging and irrigate with deionized water daily to keep the soil moisture at about 60% of the field water holding capacity. The rapeseed was harvested and sampled after 60 days of growth, digested with nitric acid-perchloric acid, atomic absorption spectrophotometry was used to determine the content of Cd, Pb, and Cu in plant samples, and the continuous extraction analysis method (BCR) recommended by th...
Embodiment 3
[0037] Example 3: In-situ passivation to repair acid contaminated soil
[0038] The test soil was collected from Jiaxing, Zhejiang, with a pH of 6.08, which was acidic. The concentrations of exogenous heavy metals in the soil are: Cd-5mg / kg, Pb-600mg / kg, Cu-200mg / kg. Add passivation materials with mass ratios of 0, 0.15%, 0.30%, 0.45% to the soil respectively, and add 0.48g urea, 0.23g sodium dihydrogen phosphate and 0.25g potassium sulfate as base fertilizer, mix well, and load In plastic pots, each pot contains 1.5 kg of soil, and each treatment is repeated 3 times. Sow rapeseed after one month of aging and irrigate with deionized water daily to keep the soil moisture at about 60% of the field water holding capacity. Rape was harvested and sampled after 50 days of growth, digested by nitric acid-perchloric acid method, and atomic absorption spectrophotometry was used to determine the content of Cd, Pb, and Cu in plant samples.
[0039] The content of heavy metals in the shoots...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com