Cylindrical secondary battery and preparation method thereof
A secondary battery, cylindrical technology, applied in the field of cylindrical secondary battery and its preparation, can solve problems such as unsatisfactory safety, safety problems caused by cylindrical batteries, and undiscovered related technologies, and achieve major production Practical significance, improving market application prospects, and ensuring the effect of testing safety
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0037] In order to prepare the cylindrical secondary battery provided by the present invention, the present invention also provides a method for preparing a cylindrical secondary battery, the method comprising the following steps:
[0038] The first step is to coat the gel-like polymer material on the surface of the separator in the electrolyte layer of the battery and dry it;
[0039] The second step is to wind the battery’s positive electrode sheet, negative electrode sheet, and the above-mentioned separator coated with polymer materials into a battery cell, and assemble it in sequence according to the order of rolling groove, liquid injection, and sealing to form a cylindrical battery;
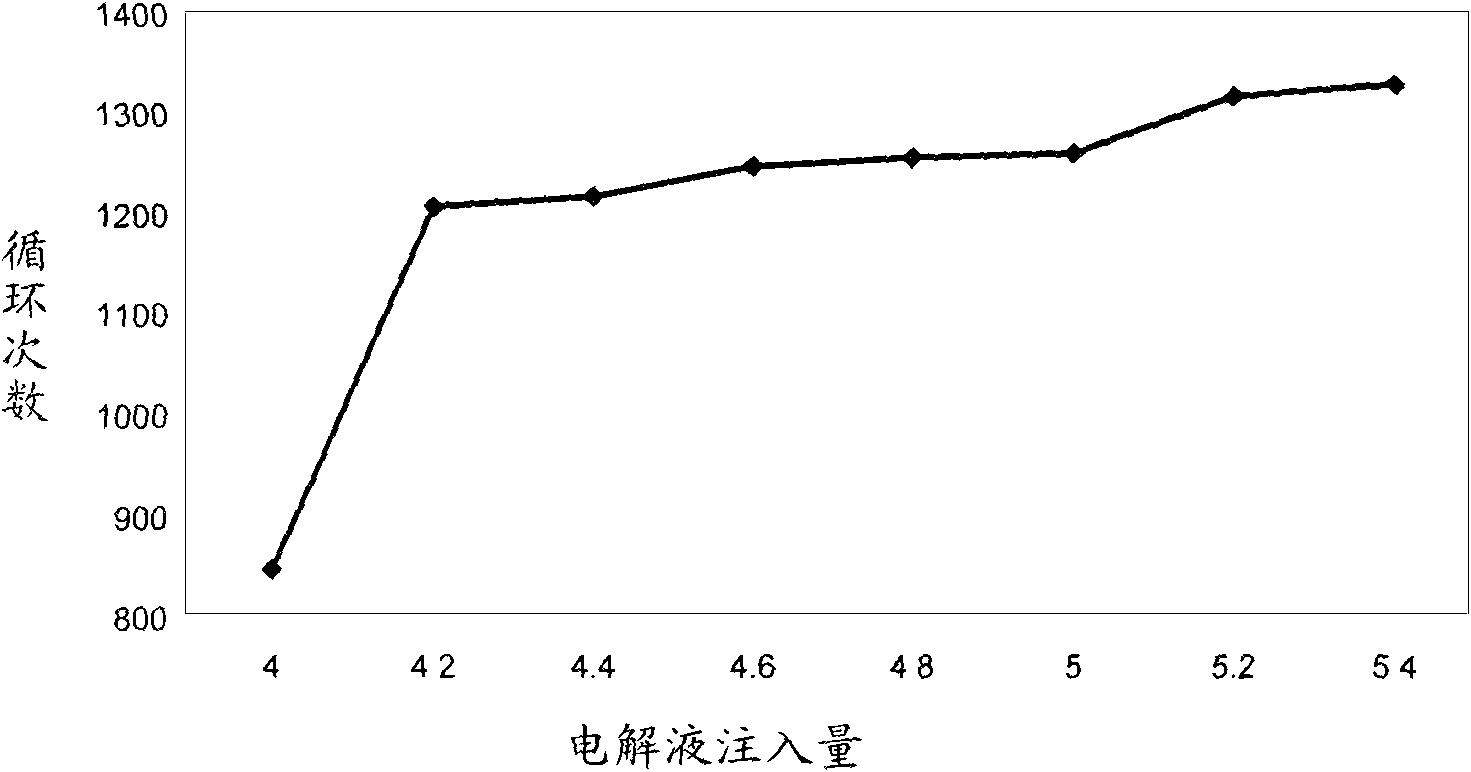
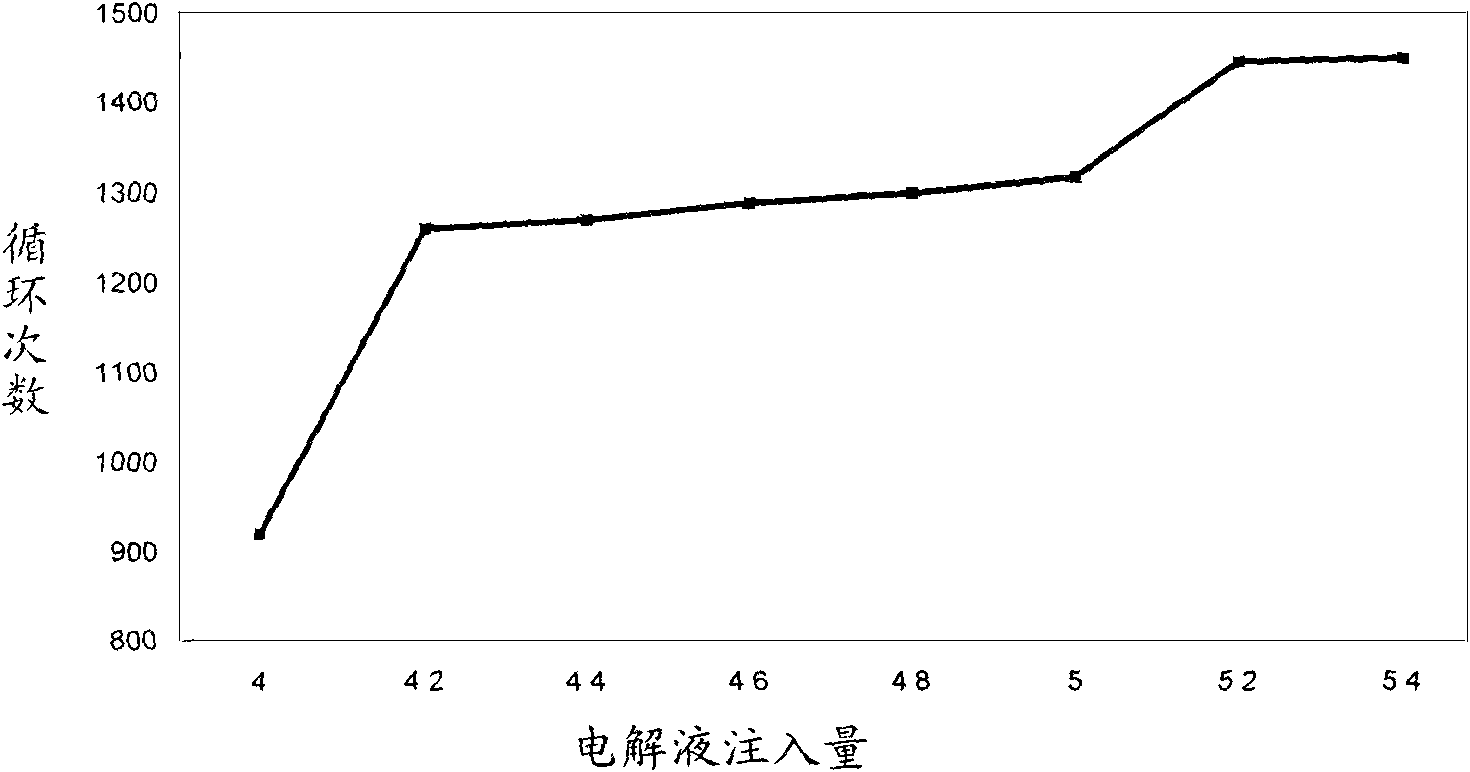
[0040] The third step is to inject the non-aqueous electro-liquid into the casing of the cylindrical battery, and place the battery in a nitrogen-filled negative pressure environment with a temperature of 80-120 ° C, so that the non-aqueous electro-liquid and the polymer material form a gel ...
Embodiment 1
[0052] Preparation of the battery positive plate: 93% lithium iron phosphate LiFePO4, 4% conductive carbon black and 3% polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) are mixed in N-methylpyrrolidone (NMP), and evenly coated on the aluminum current collector, Finally, it is dried and compacted at a temperature of 120°C, and the positive electrode sheet is obtained after cutting;
[0053] Preparation of battery negative plate: 90% mesocarbon microspheres (MCMB), 4% conductive carbon black and 3% polyvinylidene fluoride PVDF were mixed in N-methylpyrrolidone NMP, uniformly coated on the copper current collector, Finally, it is dried and compacted at a temperature of 120°C, and the negative electrode sheet is obtained after cutting;
[0054] Preparation of diaphragm: Mix vinylidene fluoride and hexafluoropropylene PVDF-HFP copolymer with an average molecular weight of 500,000 in N-methylpyrrolidone NMP and evenly coat it on a polypropylene (PP) diaphragm with a thickness of 16 μm. 2 μm, then dr...
Embodiment 2
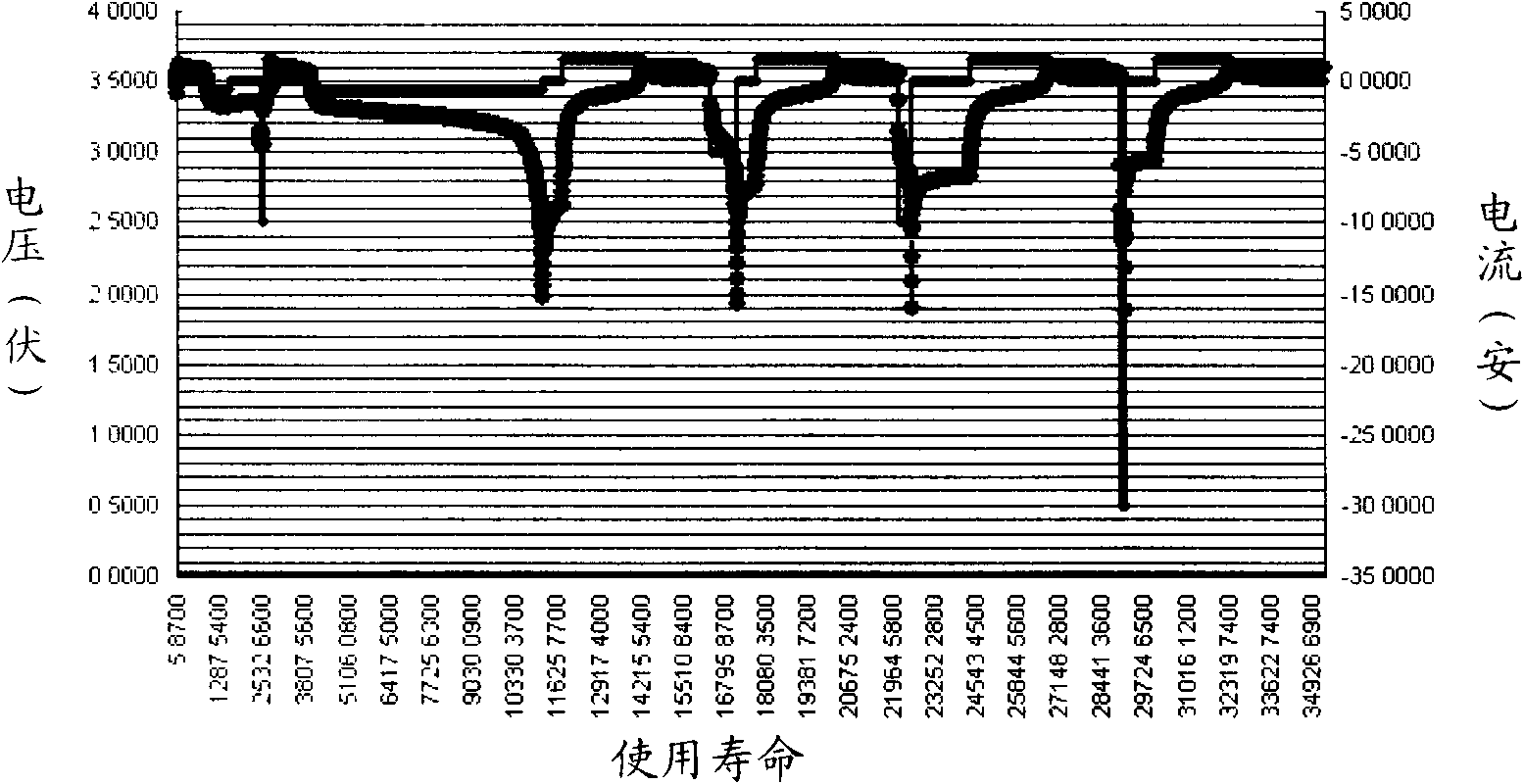
[0058] By adding conductive carbon black and ultra-long nano-carbon fiber (VGCF) to the negative electrode sheet of the battery, the structure and manufacturing method of the specific part are the same as in Example 1, and finally the low-temperature performance of the battery is greatly improved.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com