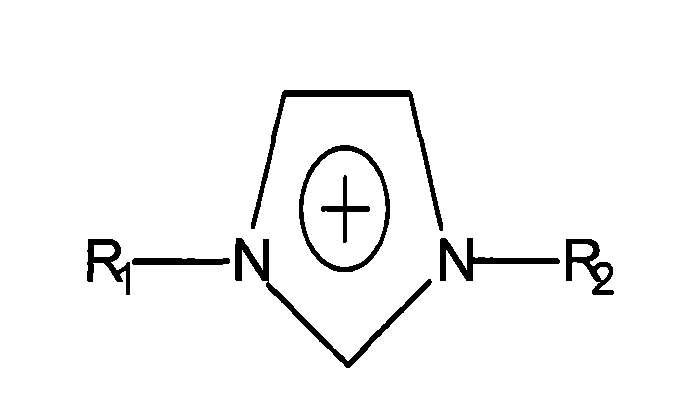
Method for separating lignin and cellulose from lignocellulose by using ionic liquid solvent
An ionic liquid solvent, lignocellulose technology, applied in the field of lignin and cellulose technology, can solve the problems of pollution, environmental pollution, poor research and development effect of lignin resources, etc., and achieves good separation effect, no environmental pollution, The effect of strong industrial application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0020] The raw materials, implementation conditions and benefits used in Examples 1 to 6 are shown in Table 1, and the specific operations are as follows: first, 2.5g pine wood powder is added to a 100ml clean and dry stainless steel reactor with a polytetrafluoroethylene liner, and a certain concentration of [Bmim][Cl] ionic liquid aqueous solution, control the temperature at 150°C, react for 60 minutes, then cool down to room temperature, filter the reacted mixture to obtain high boiling alcohol lignin solution and pulp. Add 5 times the volume of 80°C hot water to the lignin solution at room temperature and stir for 10 min. The lignin was collected by filtration, washed with water for 5 times, and then dried to obtain ionic liquid lignin powder. After the pulp was washed 5 times with hot water at 80°C, it was dried at 90°C to obtain dry pulp.
[0021] Table 1
[0022] Example
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com