Method for preparing heparin derivatives by using biological enzyme to selectively modify heparin structure
A heparin derivative and selective technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of reducing the content of 2-O-sulfate group and 6-O-sulfate group, and achieve a wide range of indications, great social value and economic value, Effects of Dosage and Toxicity Reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0020] Product I was synthesized using heparan sulfate 3-OH sulfotransferase. The usual sulfation reaction conditions are 1mg heparin in 20ml reaction liquid and shake (300rpm) at room temperature for 6h. The reaction solution contains 50mM Tris-HCl (pH7.2), 1% Triton X-100, 1% BSA, 1mM MgCl 2 , 1mM MnCl 2 , 1 mM PNPS, 40 μM PAP, 8 mg 3-OST-1 (or 3-OST-5) and 4 mg AST-IV. The reaction product was separated by DEAE resin, dialyzed and freeze-dried to obtain the synthetic product I. Use mixed heparin degrading enzymes to completely degrade heparin and synthetic product I into disaccharides, and use C 18 The composition and content of disaccharides were analyzed by reversed-phase column HPLC. The results are shown in figure 1 , indicating that the 3-O-sulfate disaccharide content of product I is about 3 times that of heparin, revealing that the number of anticoagulant active centers has increased by 3 times.
example 2
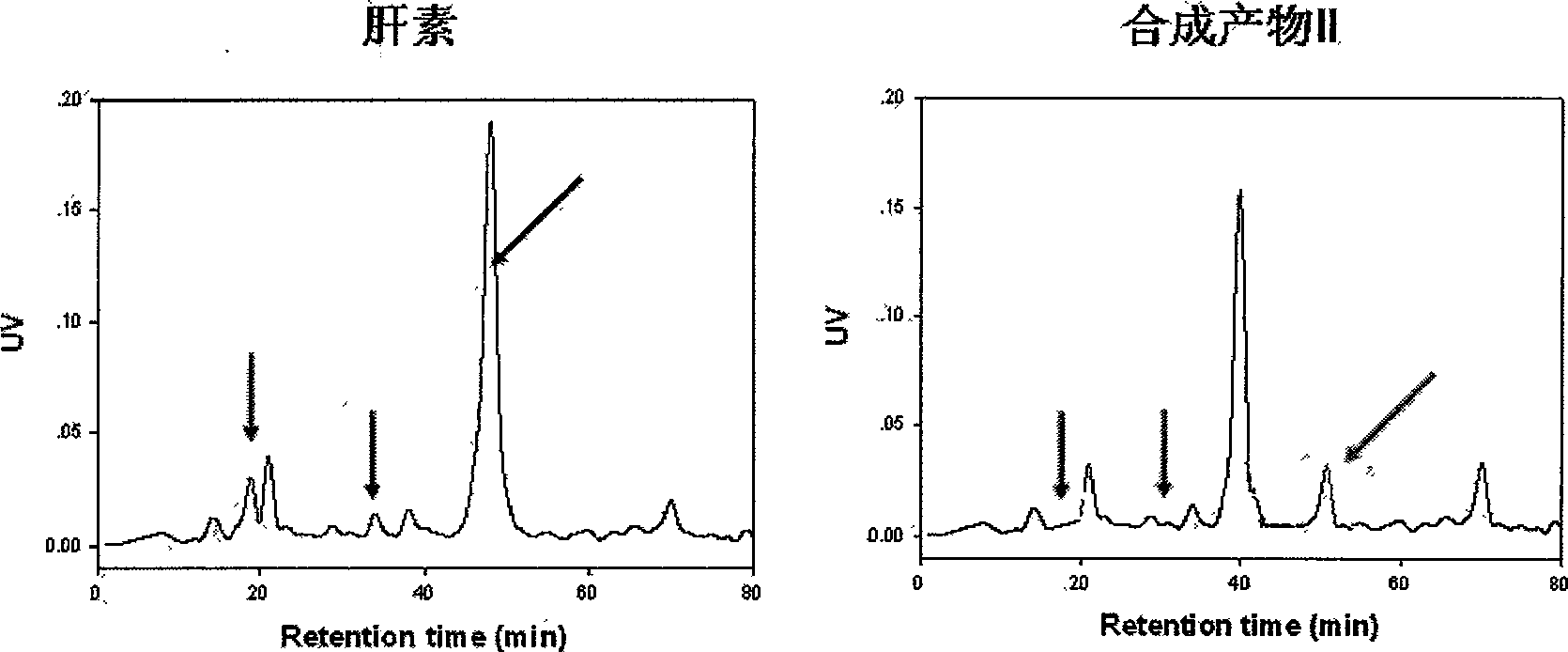
[0022] Product II was synthesized using heparan sulfate 2-O desulfatase. The usual desulfation reaction condition is that the product I is reacted in 20ml of reaction solution at room temperature with shaking (300rpm) for 6h. The reaction solution contains 50mM Tris-HCl (pH7.2), 1% Triton X-100, 1% BSA, 1mM MgCl 2 , 1mM MnCl 2 , 1mM CaCl 2 , 5mg 2-O-sulfatase. The reaction product was separated by DEAE resin, dialyzed and freeze-dried to obtain the synthetic product II. Heparin and synthetic product II were completely degraded into disaccharides with mixed heparin-degrading enzymes, and C 18 The composition and content of disaccharides were analyzed by reversed-phase column HPLC. The results are shown in figure 2 , indicating that the 2-O-sulfate disaccharide content of product II is about 20% of that of heparin.
example 3
[0024] Using heparan sulfate 6-O desulfatase, product III was synthesized. The usual desulfation reaction conditions are product II in 20ml of reaction solution at room temperature shaking (300rpm) reaction for 6h. The reaction solution contains 50mM Tris-HCl (pH7.2), 1% Triton X-100, 1% BSA, 1mM MgCl 2 , 1mM MnCl 2 , 1mM CaCl 2 , 5mg 6-O-sulfatase. The reaction product was separated by DEAE resin, dialyzed and freeze-dried to obtain the synthetic product III. Heparin and synthetic product III were completely degraded into disaccharides with mixed heparin-degrading enzymes, and C 18 The composition and content of disaccharides were analyzed by reversed-phase column HPLC. The results are shown in image 3 , indicating that the 6-O-sulfate disaccharide content of product III is about 20% of that of heparin.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com