Zero discharge processing EBM method for dyeing waste water
A printing and dyeing wastewater and zero-discharge technology, which is applied in textile industry wastewater treatment, water/sewage treatment, oxidized water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of high water consumption, high energy consumption, low turbidity, etc., and reduce product production cost, reducing the load of purification and reuse, and solving the effects of clogging
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0030] The present invention provides an EBM method for zero discharge treatment of printing and dyeing wastewater, such as figure 2 As shown, it is an electro-biochemical membrane technology integrated system, referred to as EBM (Electricity-Biochemistry-Membrane) system, which includes the following steps:
[0031] Step 1: Implement the centrifugal spin-drying countercurrent washing process in the dyeing and rinsing process;
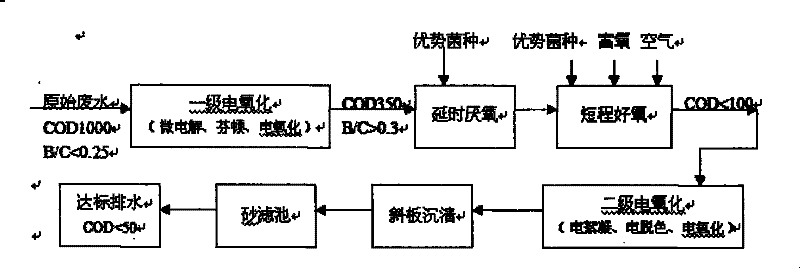
[0032] Step 2: Such as image 3 As shown, the original wastewater from printing and dyeing is treated in compliance with the standards, and the compliance discharge water is obtained;
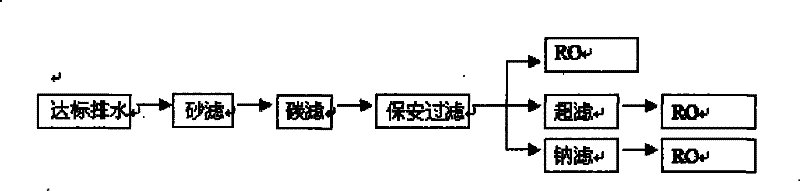
[0033] Step 3: Such as Figure 4 As shown, deep purification treatment is carried out on the discharged water that meets the standards to obtain fresh water and high-concentration water, and the fresh water is reused;
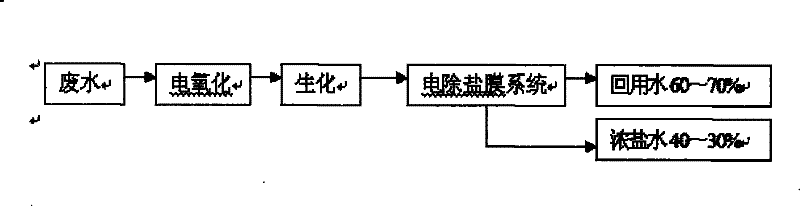
[0034] Step 4: Such as Figure 5 As shown, high-concentration water is treated.
[0035] Each step is described in detail below.
[0036] In step 1, the most comm...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com