Method for cultivating Cordyceps sinensis fungus
A cultivation method, the technology of the genus Cordyceps, applied in the direction of fungi, etc., can solve the problems of non-industrialization and efficacy gap, and achieve the effect of simple operation, low cost and high yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
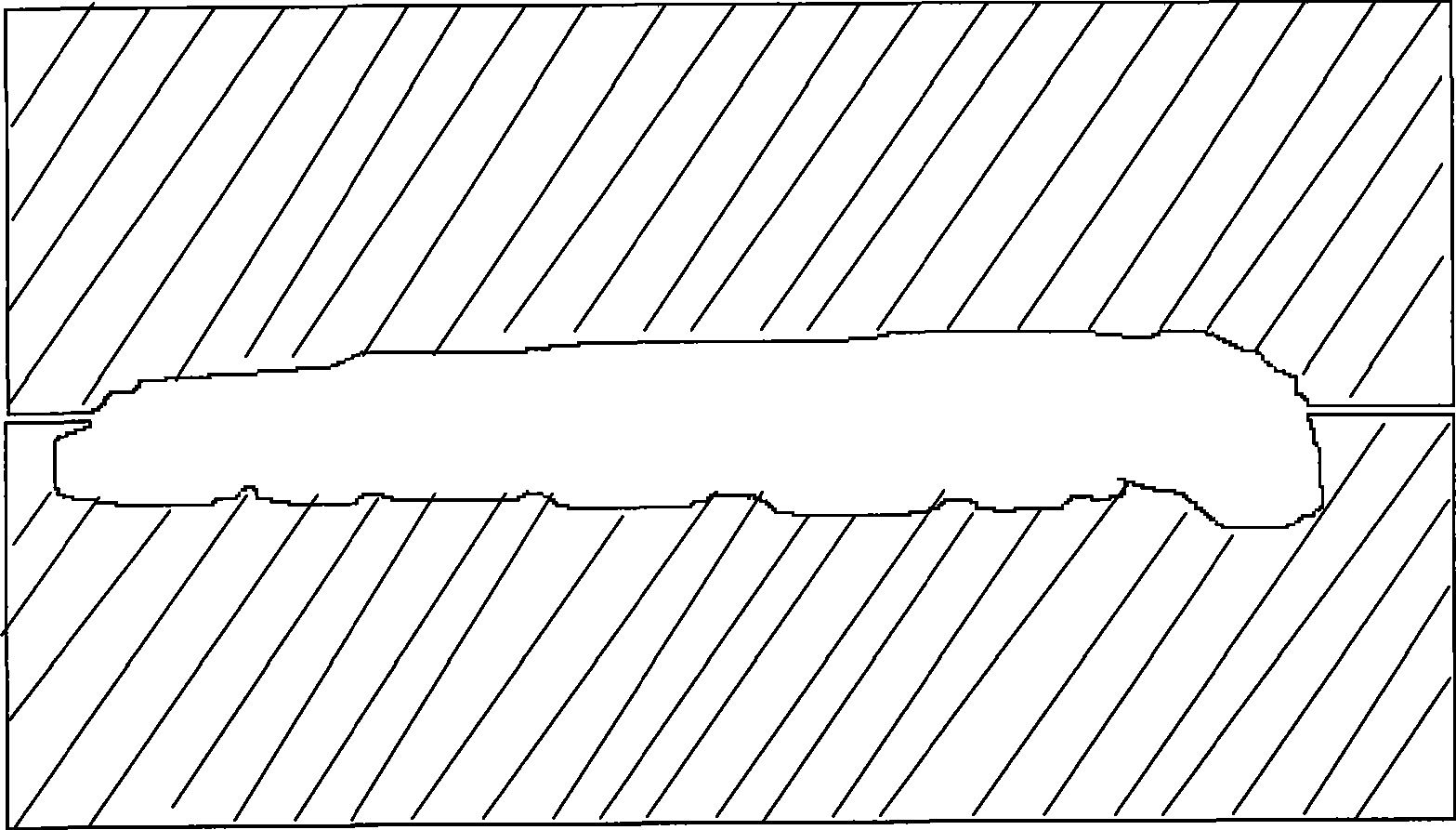
[0023] 1. Prepare a culture chamber whose interior is the shape of the host bat moth larvae of Cordyceps sinensis, such as figure 1 shown. Composed of upper and lower parts, the mold is made of transparent non-porous polyethylene material. The upper and lower parts respectively have grooves in the shape of the upper and lower parts of the bat moth larvae, which enclose the shape of the bat moth larvae after being closed and closed. The culture cavity is 30mm long, about 4mm in diameter, and has a total volume of about 0.4ml. The culture chamber provides an oxygen-free, limited growth space and an internal environment in which metabolites are enriched in the microenvironment for the cultivation of fungi.
[0024] 2. Take Cordyceps sinensis mycelia liquid fermentation liquid (prepared with reference to the method of "Cordyceps sinensis submerged culture and its polysaccharide research and application" 2005 Northwestern University master's degree thesis), and filter under asept...
Embodiment 2
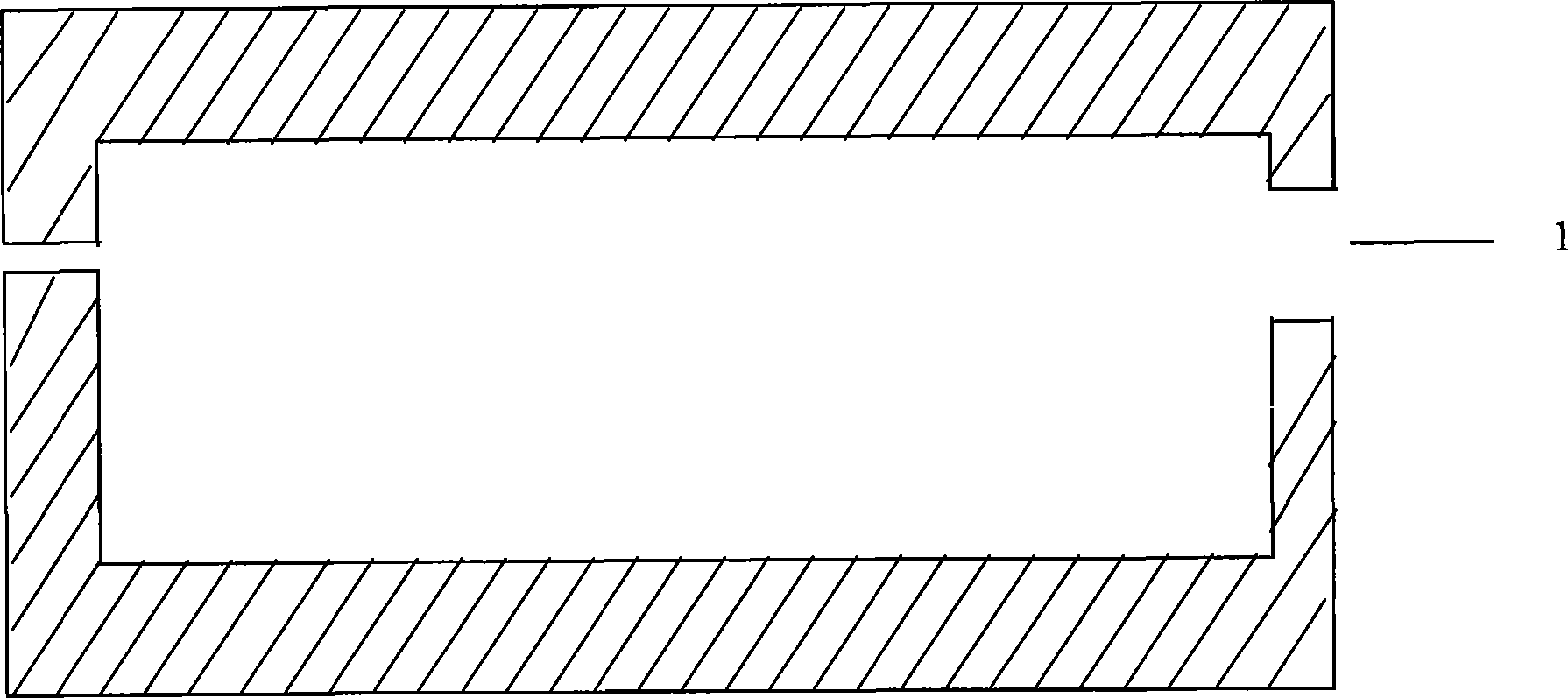
[0035] 1. Prepare a culture cavity with a rectangular parallelepiped inside, such as figure 2 shown. Composed of upper and lower parts, it is a mold made of breathable polytetrafluoroethylene material. The mold can be sintered from polytetrafluoroethylene powder under high temperature and high pressure. The inside of the mold is distributed with hydrophobic pores of about 20um, the gas can diffuse inside and outside, and the liquid and solid are trapped inside the culture chamber. The upper and lower parts of the mold have grooves in the shape of the upper and lower parts of the cuboid, which are closed and closed to form a cuboid shape. There is a circular opening at the junction of the upper and lower parts that communicates with the outside world. The diameter is 3mm. The culture cavity is 40mm long, 8mm high and wide, and has a total volume of about 2.5ml. The culture chamber provides an anoxic or low-oxygen environment for the cultivation of fungi, the growth space i...
Embodiment 3-5
[0048] Whole process is roughly the same as embodiment 2. The difference is that the culture cavity in Example 3 is 30mm*15mm*15mm, with a volume of about 7ml, the culture cavity in Example 4 is 40mm*16mm*16mm, and the volume is about 10ml, and the culture cavity in Example 5 is 46mm*18mm*18mm , the volume is about 15ml. After 20 days of cultivation, the culture cavity is covered with mycelium. Take out the mycelium block, and after breaking it, it is found that only about 15% of the mycelium block in Example 3 is not dense enough, and the mycelium is not well bonded into a whole. In the sample of Example 4, about 33% of the hyphae blocks are not dense enough inside, and the mycelium is not well bonded into a whole. And embodiment 5 has nearly half of the mycelium block compactness not enough. It shows that if the volume of the culture chamber is too large, the mycelium is not easy to grow into a dense mycelium block.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com