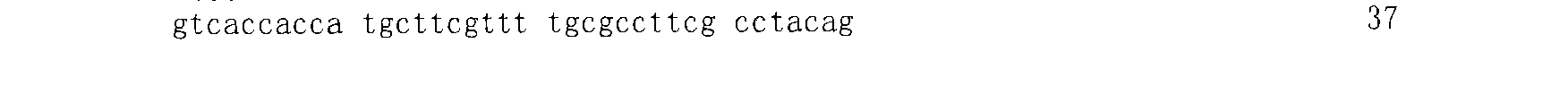A screening method for identifying new drugs
A screening method and drug technology, applied in the field of screening for identifying new drugs, can solve problems such as poor bioavailability, lack of inhibitory activity, and poor specificity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
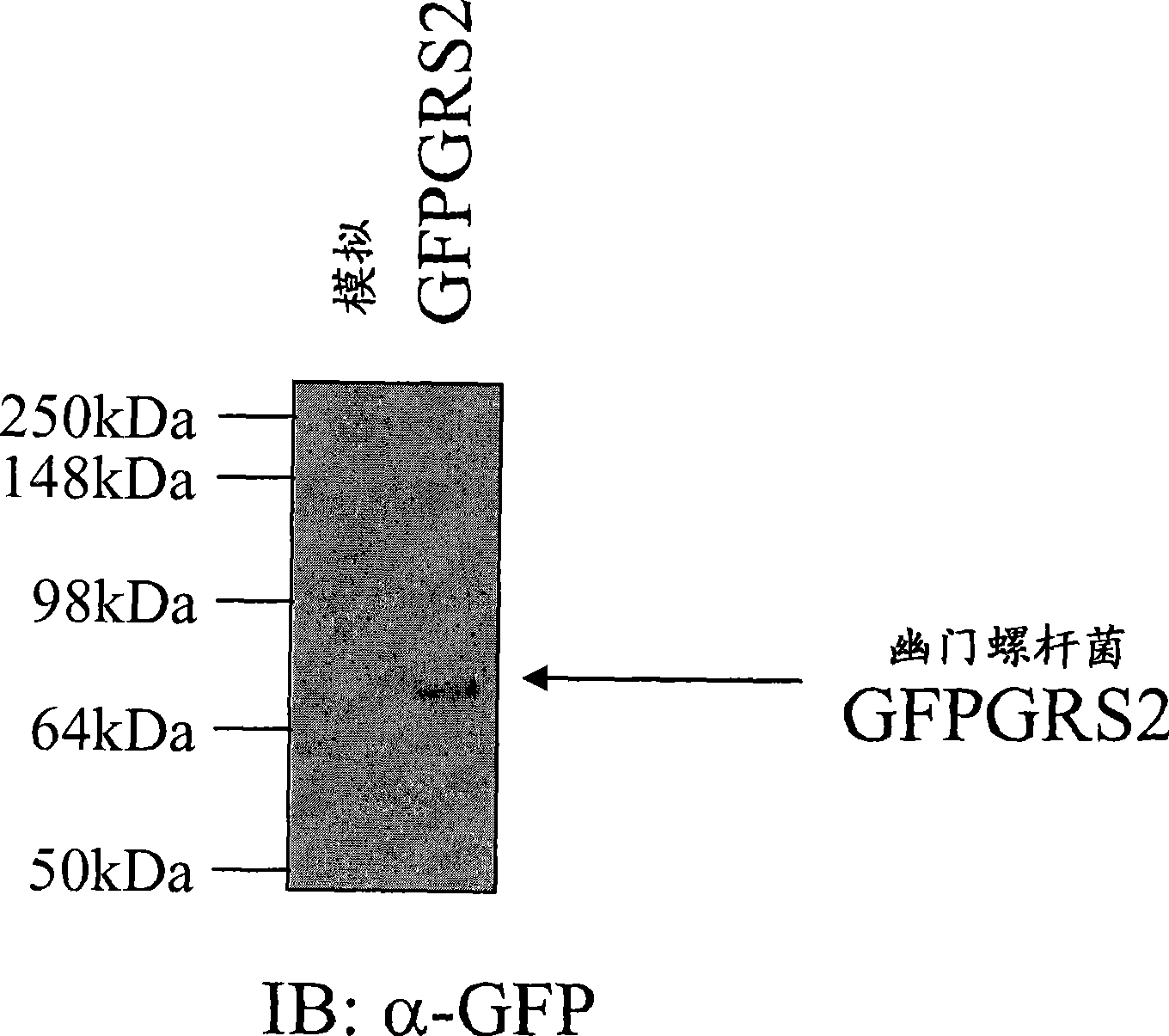
[0058] Example: Expression of Helicobacter pylori glutamyl-tRNA synthetase in HeLa cells
[0059] import :
[0060] The pathogen H. pylori utilizes two essential glutamyl-tRNA synthetases (GluRS1 and GluRS2). GluRS1 is a typical recognition GluRS (discriminating GluRS), and GluRS2 is atypical because it only corrects misacylated Glu-tRNA Gln It is necessary for the production.
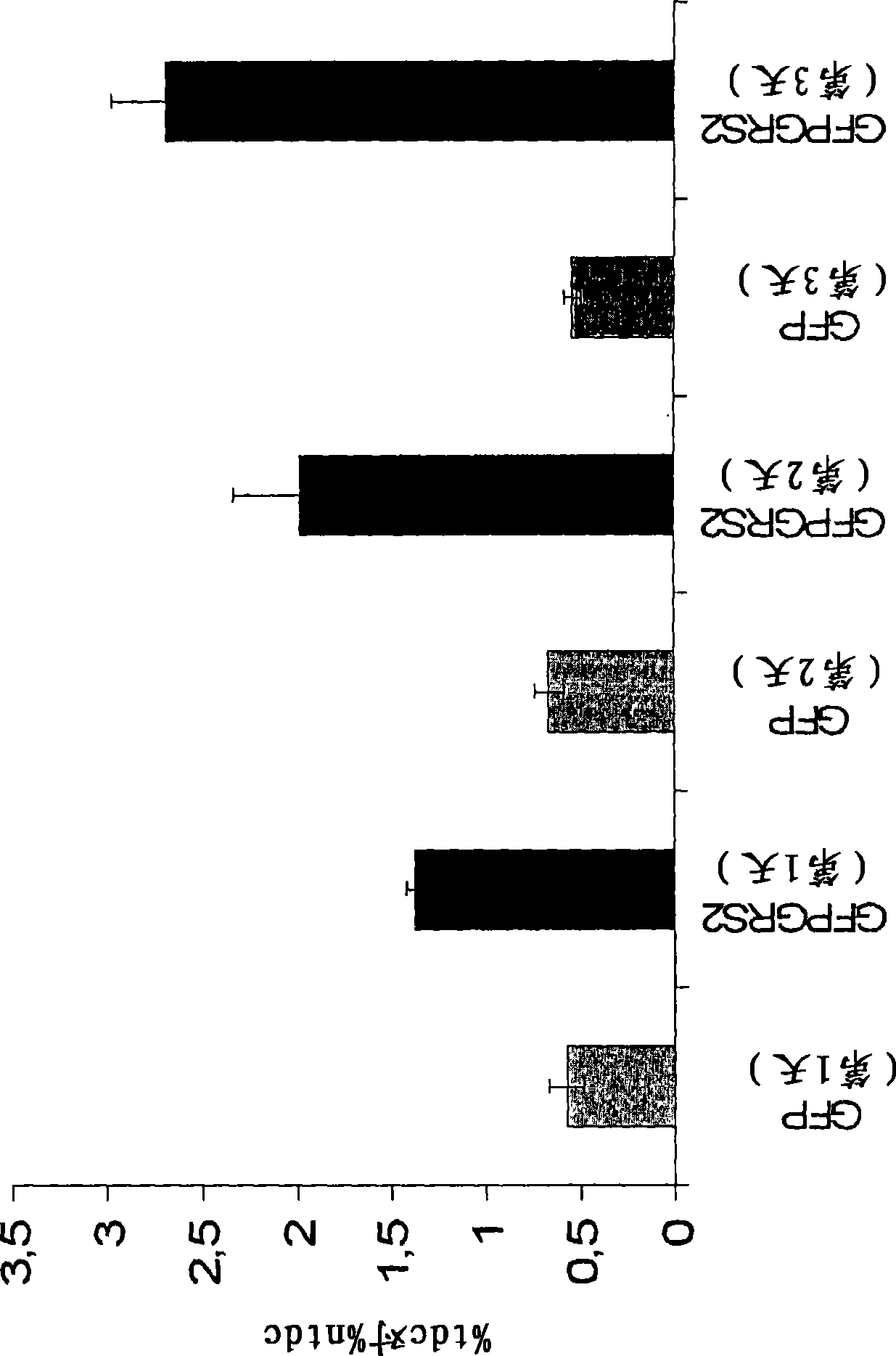
[0061] To investigate whether expression of H. pylori atypical GRS2 in mammalian systems has toxic effects and leads to cell death, H. pylori GFPGRS2 was expressed in HeLa cells, human cell lines and their putative toxic effects were examined.
[0062] get expression vector
[0063] The plasmid vector GRS2#1 (SEQ ID NO: 1)
[0064] 5'-GTCACCACCATGCTTCGTTTTGCGCCTTCGCCTACAG
[0065] and GRS2#2 (SEQ ID NO: 2)
[0066] 5'-GACTCAATGGTGATGGTGATGATGTGCTTTGAGCCTTAAAACTT
[0067] It is used to amplify GRS2 from genomic DNA from Helicobacter pylori (ATCC 700392D), and add kozak consensus ribosome bind...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com