Assays to predict atherosclerosis and dysfunctional high-density lipoprotein
An atherosclerosis and protein technology, which can be used in biological testing, material testing, etc., and can solve the problem of not knowing the pro-inflammatory HDL protein profile.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
Detection of hemoglobin, haptoglobin, and hemopexin
[0146] ELISA methods for haptoglobin and hemopexin, and methods for preparation of HDL supernatants and apoA-I-binding immunosorbent proteins are shown below.
human hemoglobin ELISA
[0147] Table 1. Materials used for the hemoglobin ELISA
Note: Allow all reagents to come to room temperature before use.
HDL Separation Using Magnetic Bead Reagents
[0148] 1. Separate plasma or serum from the blood sample using a green top tube or a serum separation tube and centrifuge at 2300 rpm for 20 minutes at 5°C.
[0149] 2. Remove the supernatant (serum or plasma). Note: If the sample has been frozen, thaw the sample and centrifuge at 12,000 rpm in a centrifuge for 5 minutes at room temperature. This should settle any particles present in the serum or plasma that might affect the assay.
[0150] 3. Add supernatant (up to 250 μL / well) to a clear round bottom 96-well plate.
[0151] 4. Add 1 / 5 total volume of magneti...
Embodiment 2
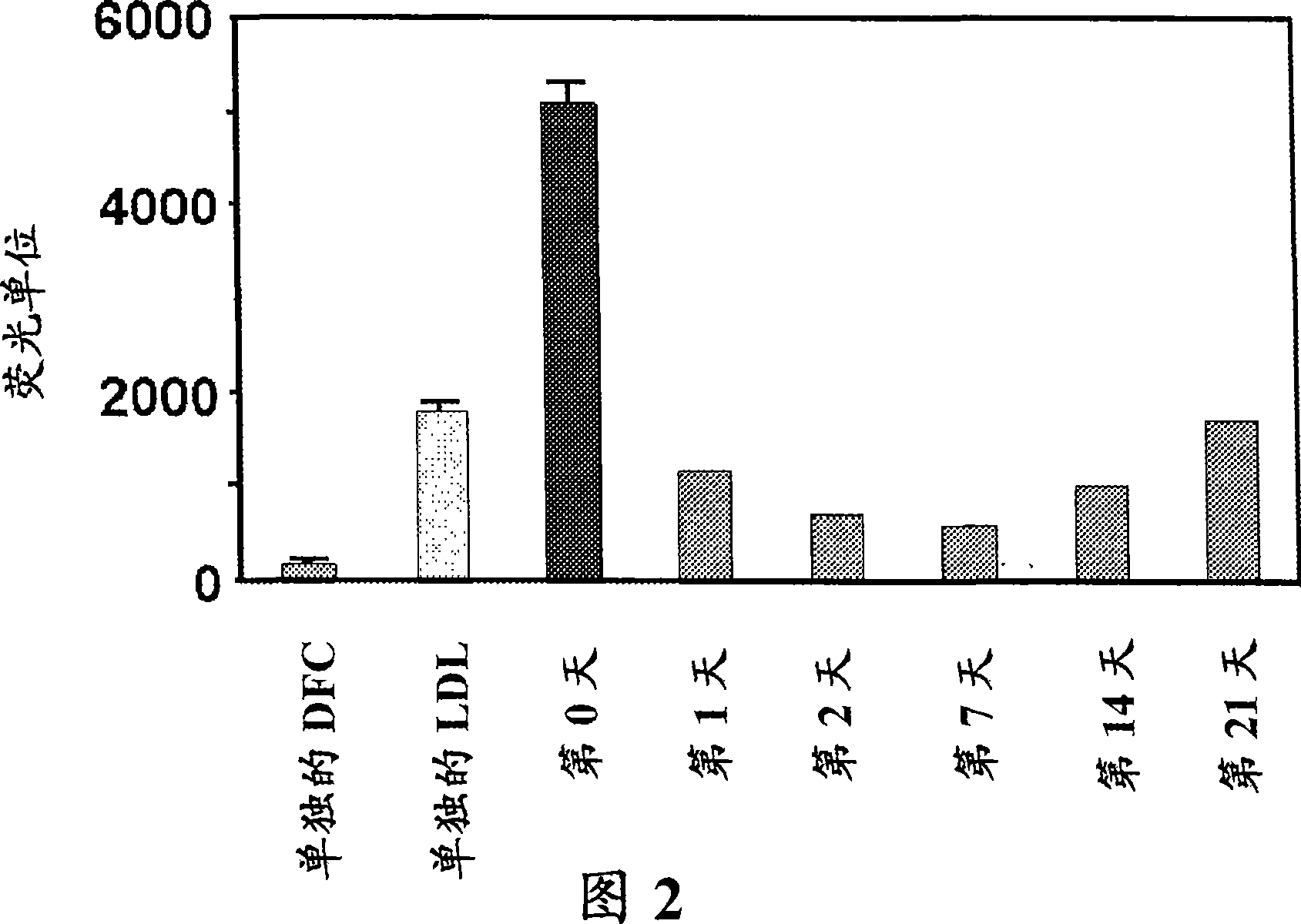
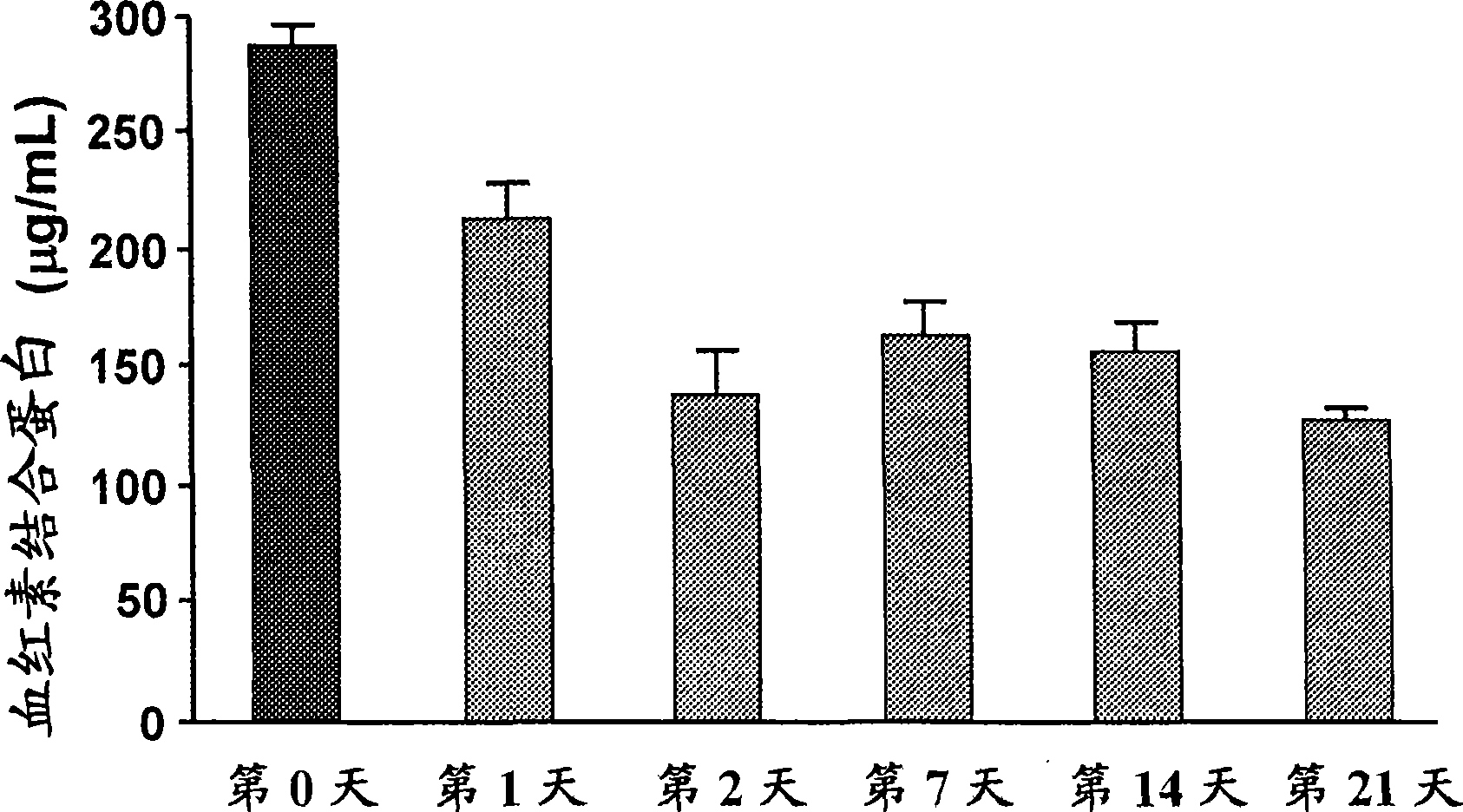
[0338] We have reported that the inflammatory properties of HDL are a more sensitive indicator of atherosclerosis than HDL-cholesterol levels in both mice and humans. In this example, we describe the use of ProteinChip technology coupled to surface-enhanced laser desorption / ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (SELDI-TOF-MS) to identify HDL that distinguishes between normal mouse HDL and mouse HDL fed an atherogenic diet specific protein fingerprints. Feeding C57BL / 6J mice an atherogenic diet for 1 week resulted in decreased HDL-cholesterol levels, decreased paraoxonase activity, increased reactive oxygen species levels, and decreased ability of HDL to promote cholesterol efflux from macrophages. When the mice were switched back to normal chow for an additional 2 weeks, the pro-atherogenic features of HDL reverted to a normal phenotype. In total, we identified 88 SELDI peaks with p<0.05 that were differentially present in proinflammatory HDL of mice fed an atherogenic ...
Embodiment 3
in the serum of mice fed an atherosclerotic / hyperlipidemic diet HDL-bound hemoglobin
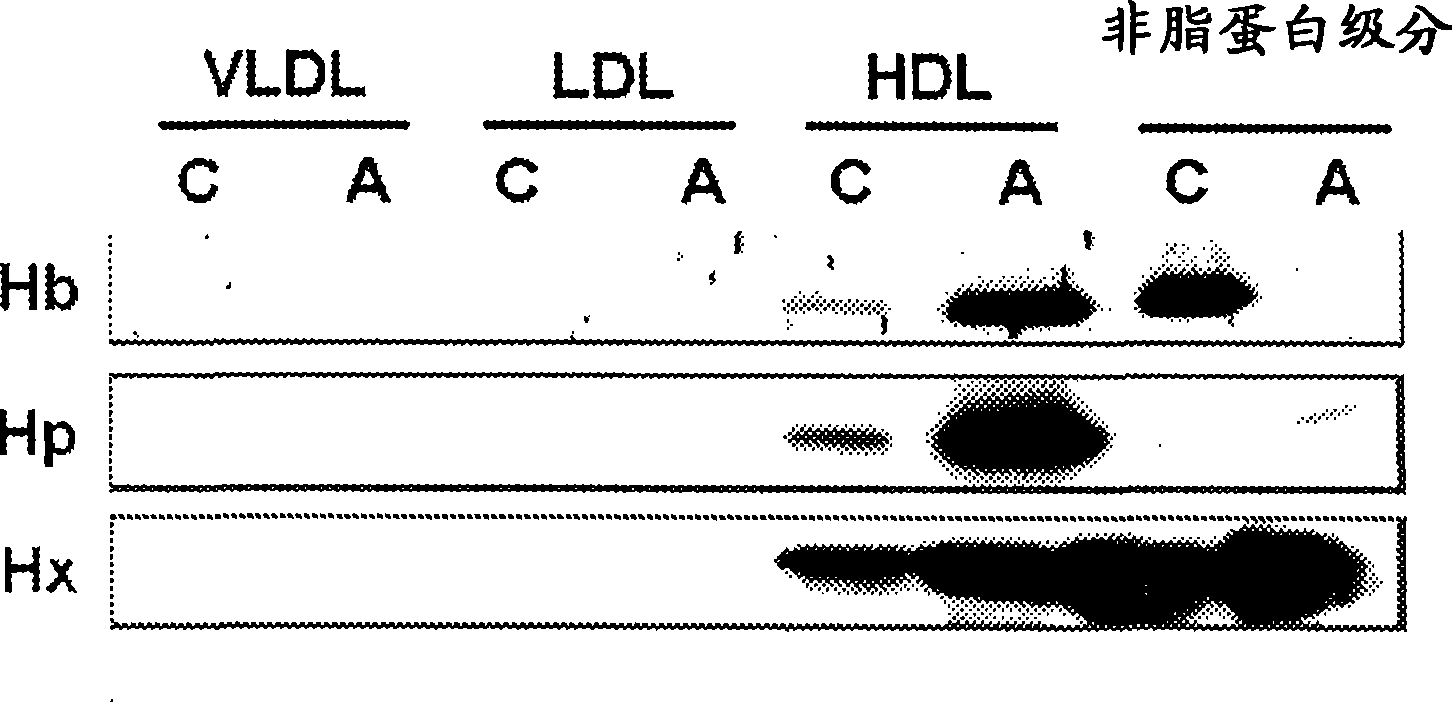
[0369] In Example 2, we identified 8 specific protein fingerprints using the strong anion-exchange SELDI ProteinChip technology that differentiates normal / anti-inflammatory HDL from pro-inflammatory HDL in a mouse model of atherosclerosis. Using microfluidics-tandem mass spectrometry, we identified the SELDI peaks representing m / z 14,900 and m / z 15,600 as mouse hemoglobin α chain (Hb-α, 14.9 kDa) and mouse hemoglobin β chain (Hb-β , 15.9 kDa). Western blot analysis confirmed differential binding of Hb to pro-inflammatory HDL when compared to normal HDL. Biochemical characterization of HDL-bound Hb further revealed that Hb bound to pro-inflammatory HDL has distinct physical and chemical properties, including reduced pI (pI4. High molecular weight complexes present in the HDL-containing fraction bind. The major form of hemoglobin found bound to HDL is oxyhemoglobin (oxyHb). Based on the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com