Synthetic method of pyroglutamyl small peptide
A pyroglutamine-based, synthetic method technology, applied in the field of pyroglutamine-based small peptide synthesis, to achieve the effects of avoiding yield loss, simple operation, and less by-products
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
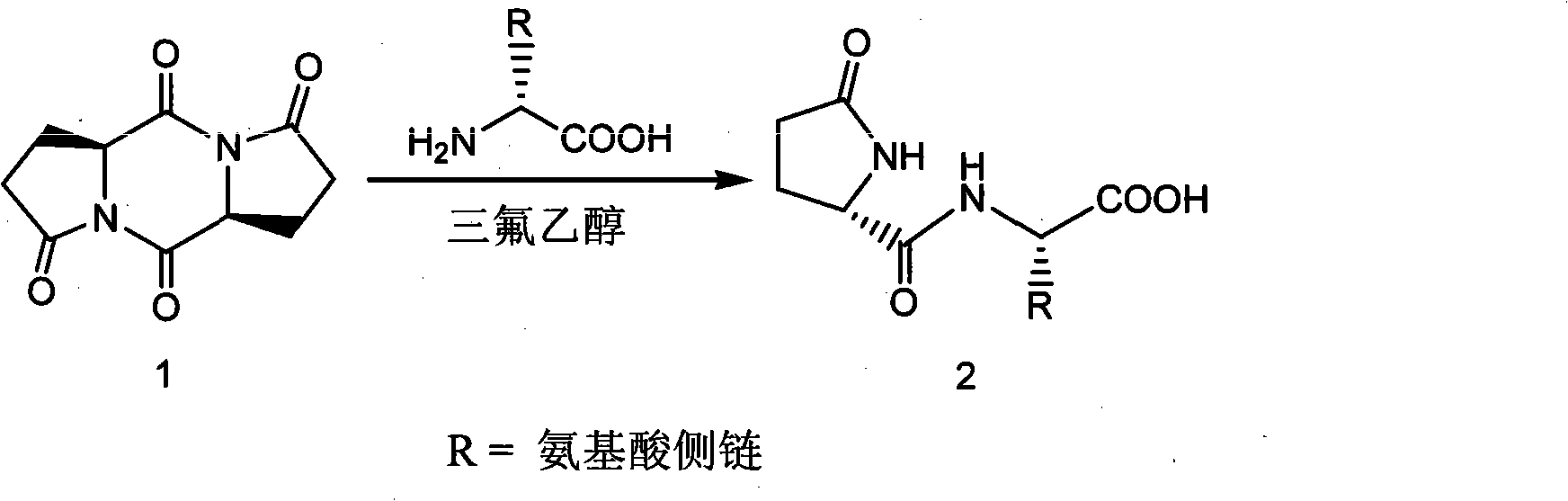
[0031] Embodiment 1: Add 1.04g (4.68mmol) pyroglutamyl cyclic bis-condensate in the 25mL round bottom flask that reflux condenser is housed, 0.75g (10mmol) glycine, 10mL trifluoroethanol and 1.38mL (10mmol) triethylamine. The mixture was heated and stirred at 70°C overnight. After concentration under reduced pressure, purification by column chromatography (eluent: isopropanol: acetonitrile: ammonia water = 10:10:1) yielded 1.48 g of white L-pyroglutamic acid-glycine dipeptide solid with a yield of 85%. 1 H NMR (D 2 O): δ (ppm) 2.06-2.15 (1H, m), 2.35-2.47 (2H, m), 2.48-2.58 (1H, m), 3.82 (2H, s), 4.35 (1H, dd, J=9.04 Hz, 5.28Hz); 13 CNMR (D 2 O): δ (ppm) 25.0, 29.2, 42.6, 57.1, 174.9, 175.6, 182.4; ESI-MS (m / z): 187 [M+H] + , 209[M+Na] + .
Embodiment 2
[0032] Example 2: L-pyroglutamic acid-β-alanine dipeptide (L-pGlu-β-Ala-OH): add 1.04g (4.68mmol) coke in a 25mL round bottom flask equipped with a reflux condenser Glutaminyl cyclic bis-condensate, 0.89 g (10 mmol) β-alanine, 7 mL trifluoroethanol and 1.74 mL (10 mmol) diisopropylethylamine. The mixture was stirred with heating at 0 °C overnight. After concentration under reduced pressure, purification by column chromatography (eluent: isopropanol: acetonitrile: ammonia water = 10:10:1) yielded 1.11 g of colorless viscous L-pyroglutamic acid-β-alanine dipeptide , yield 59%. 1 H NMR (D 2 O): δ (ppm) 1.98-2.07 (1H, m), 2.32-2.42 (2H, m), 2.44-2.54 (1H, m), 2.46 (2H, t, J=6.72Hz), 3.43 (2H, t, J = 6.32Hz), 4.26 (1H, dd, J = 9.04Hz, 5.20Hz), 4.41 (1H, dd, J = 8.24Hz, 5.00Hz); 13 C NMR (D 2 O): δ (ppm) 25.2, 29.3, 35.2, 36.1, 57.1, 174.8, 178.4, 182.3; ESI-MS (m / z): 201 [M+H] + , 223[M+Na] + .
Embodiment 3
[0033] Example 3: L-pyroglutamic acid-L-aspartic acid dipeptide (L-pGlu-L-Asp-OH): Add 1.04g (4.68mmol) in a 25mL round bottom flask equipped with a reflux condenser Pyroglutaminyl cyclic diacid, 1.33g (10mmol) aspartic acid, 20mL trifluoroethanol and 2.76g (20mmol) potassium carbonate. The mixture was stirred with heating at 40°C overnight. After concentration under reduced pressure, purification by column chromatography (eluent: isopropanol: acetonitrile: ammonia water = 5:5:1) yielded 0.75 g of white L-pyroglutamic acid-L-aspartic acid dipeptide solid, Yield 33%. 1 H NMR (D 2 O): δ (ppm) 2.01-2.09 (1H, m), 2.34-2.40 (2H, m), 2.44-2.55 (1H, m), 2.88 (1H, d, J = 17.00Hz, 7.36Hz), 2.96 (1H, d, J = 17.02Hz, 5.08Hz), 4.32 (1H, dd, J = 9.06Hz, 4.88Hz), 4.74 (1H, dd, J = 6.94Hz, 5.48Hz); 13 C NMR (D 2 O): δ (ppm) 25.1, 29.2, 35.4, 49.2, 56.8, 173.9, 174.4, 174.8, 182.3; ESI-MS (m / z): 245 [M+H] + , 267[M+Na] + .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com