Apparatus and method for measuring two-dimensional small angle based on light beam angle drift dynamic compensation
A measurement device and dynamic compensation technology, applied in the direction of measurement devices, optical devices, instruments, etc., can solve the problems such as the angular drift of the beam is not eliminated, the angle measurement deviation, the image signal is weak, etc., to improve the stability and repeatability. , Improve the angle measurement resolution, improve the effect of anti-interference ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
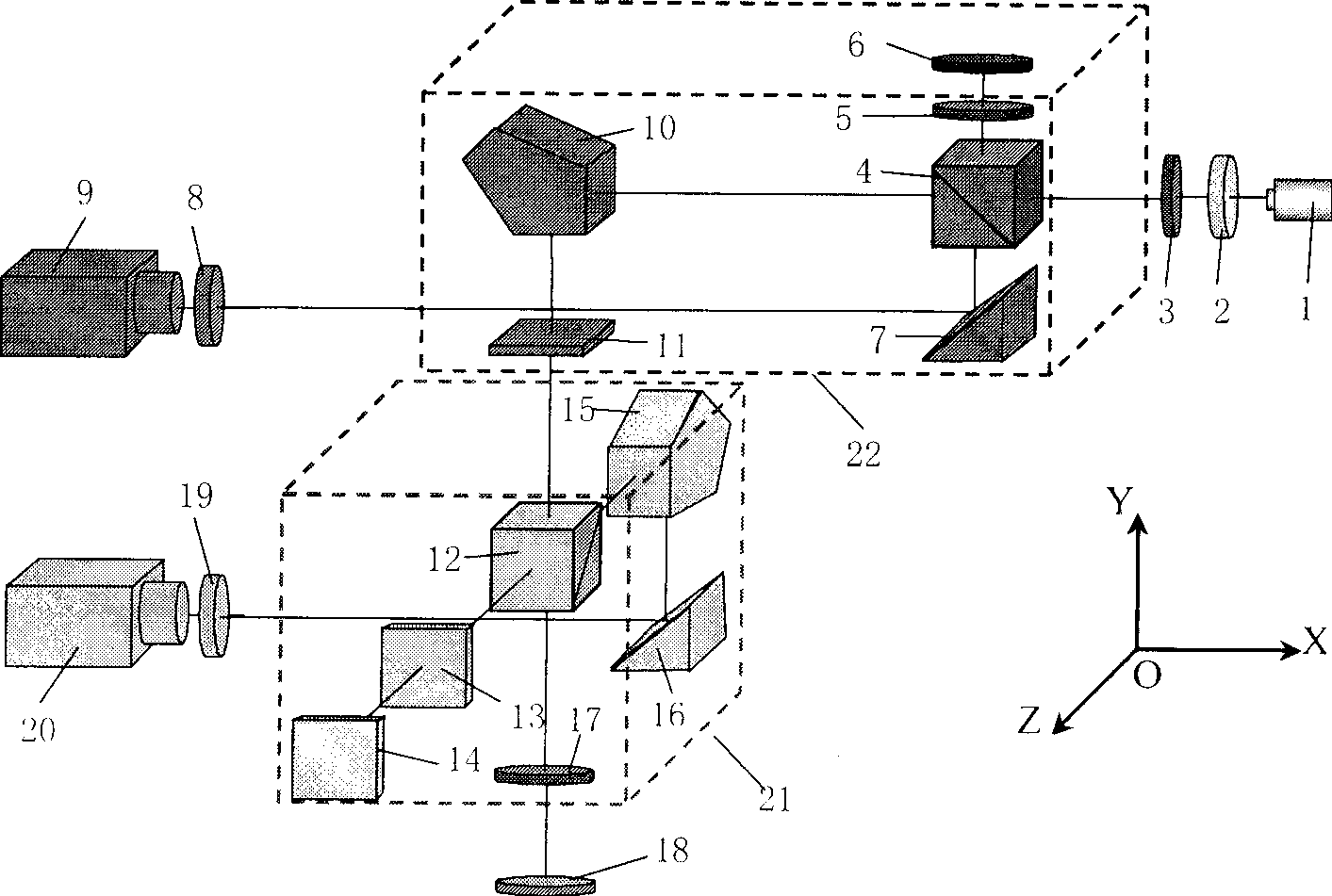
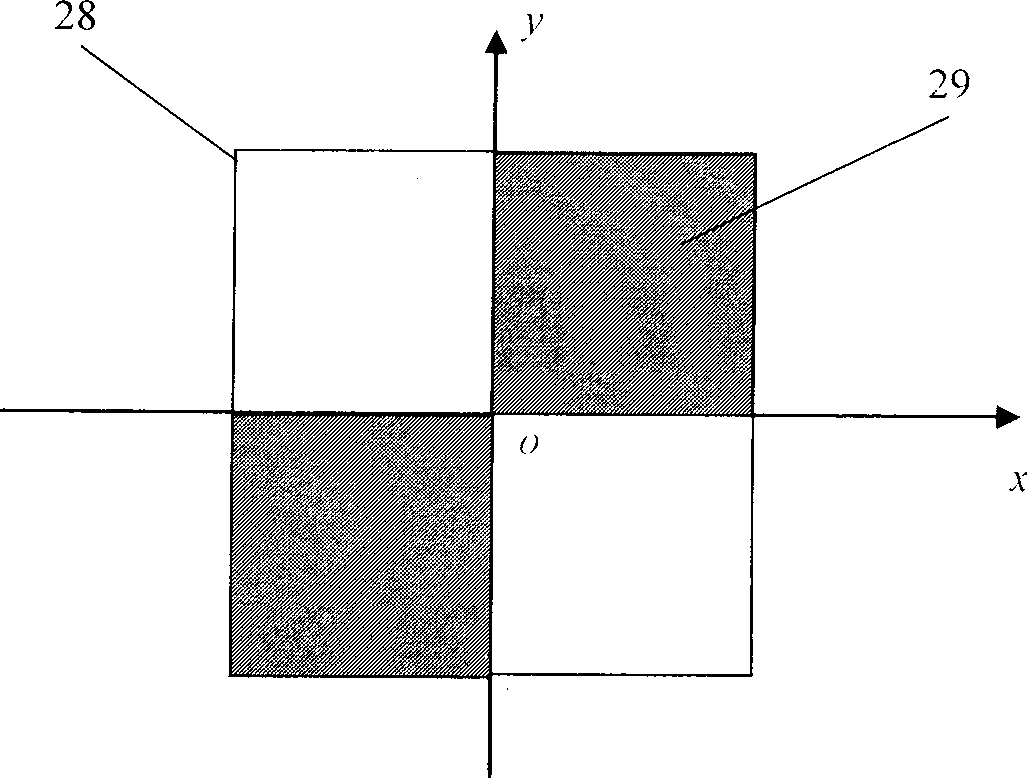
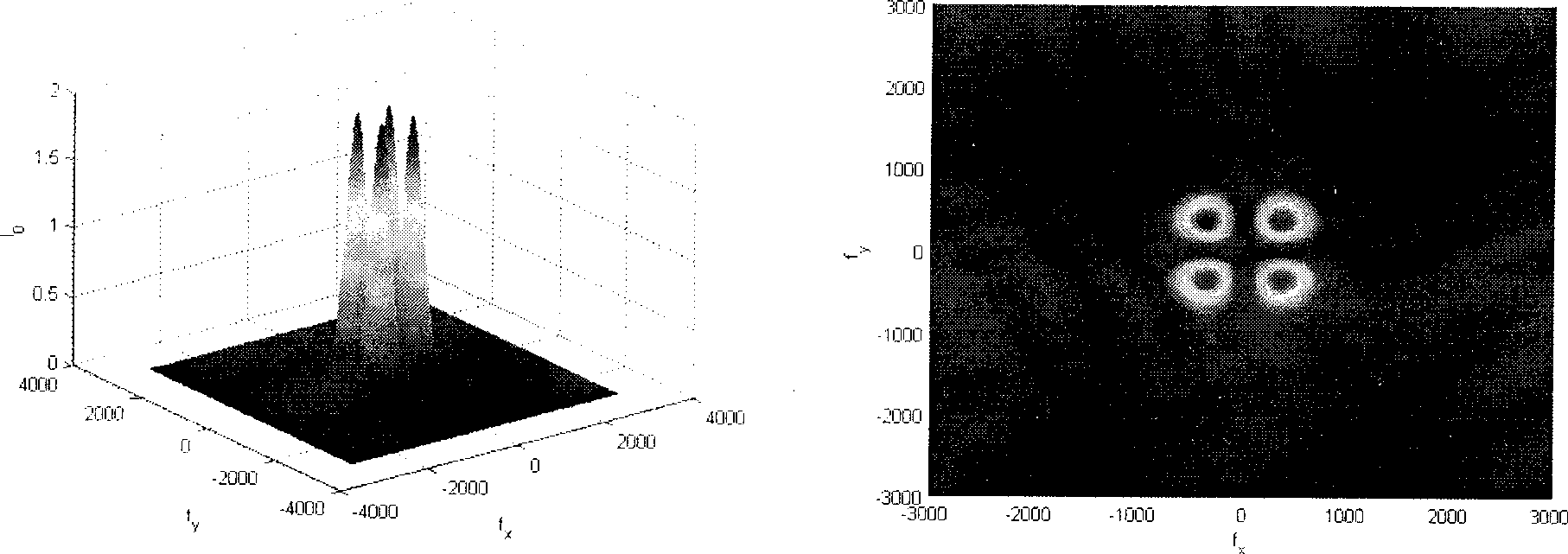
[0083] Such as figure 1 As shown, first adjust the beam splitter 4 and the polarization beam splitter 19, so that the measurement and reference light spots received by the CCD image sensors 9 and 20 are completely separated, see Fig. The light spots received by the CCD image sensor overlap and cannot be accurately positioned. After the adjustment is completed, the beam splitter 4 and the polarization beam splitter 12 should be fixed, and the two are no longer adjusted during the measurement process. The collimated beam emitted by the linearly polarized He-Ne laser 1 is vertically incident on the two-dimensional phase plate 2 to generate a diffracted collimated beam; Reflected by the reflection environment 6, it is incident on the beam splitter 4 through the linear polarizer 5 again, the transmitted light beam is reflected by the plane mirror 7, and is received by the CCD image sensor 9 after passing through the Fourier lens 8, and the minimum value coordinate of the light spot...
Embodiment 2
[0090] see Figure 7 , the plane reference mirror 6 can also adopt a right-angle prism 27, and the measurement and reference beam changes caused by angle drift in the radial angle measurement unit 22 can be found in Figure 8 , the radial angle measurement error caused by beam angle drift is a differential mode signal, and other components and working principles in this embodiment are the same as those in Embodiment 1. For radial angle measurement, the radial angle measurement error caused by angular drift can be dynamically compensated by summing the minimum displacement of the measurement spot and the reference spot, namely:
[0091] θ R =(d MR +d RR ) / (2f)
[0092] Where: θ R is the small angle change along the radial direction at the measuring point; d MR , d RR Be respectively the displacement of radial angle measurement unit 21 and reference signal reference on CCD image sensor 9, f is the equivalent focal length of Fourier lens 8; In this case, the propagation of...
Embodiment 3
[0094] Such as Figure 6 As shown, the linearly polarized He-Ne laser uses a semiconductor laser, and is incident on the two-dimensional phase plate 2 after being collimated and thinned by a single-mode fiber collimating system. The other components and working principles of this embodiment are the same as those of Embodiment 1. .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com