Geopolymer composites and structures formed therefrom
A technology of mineral polymers and composite materials, applied in the direction of loose filter material filters, other household appliances, hydraulically coagulable material layered products, etc., which can solve environmental and health hazards and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
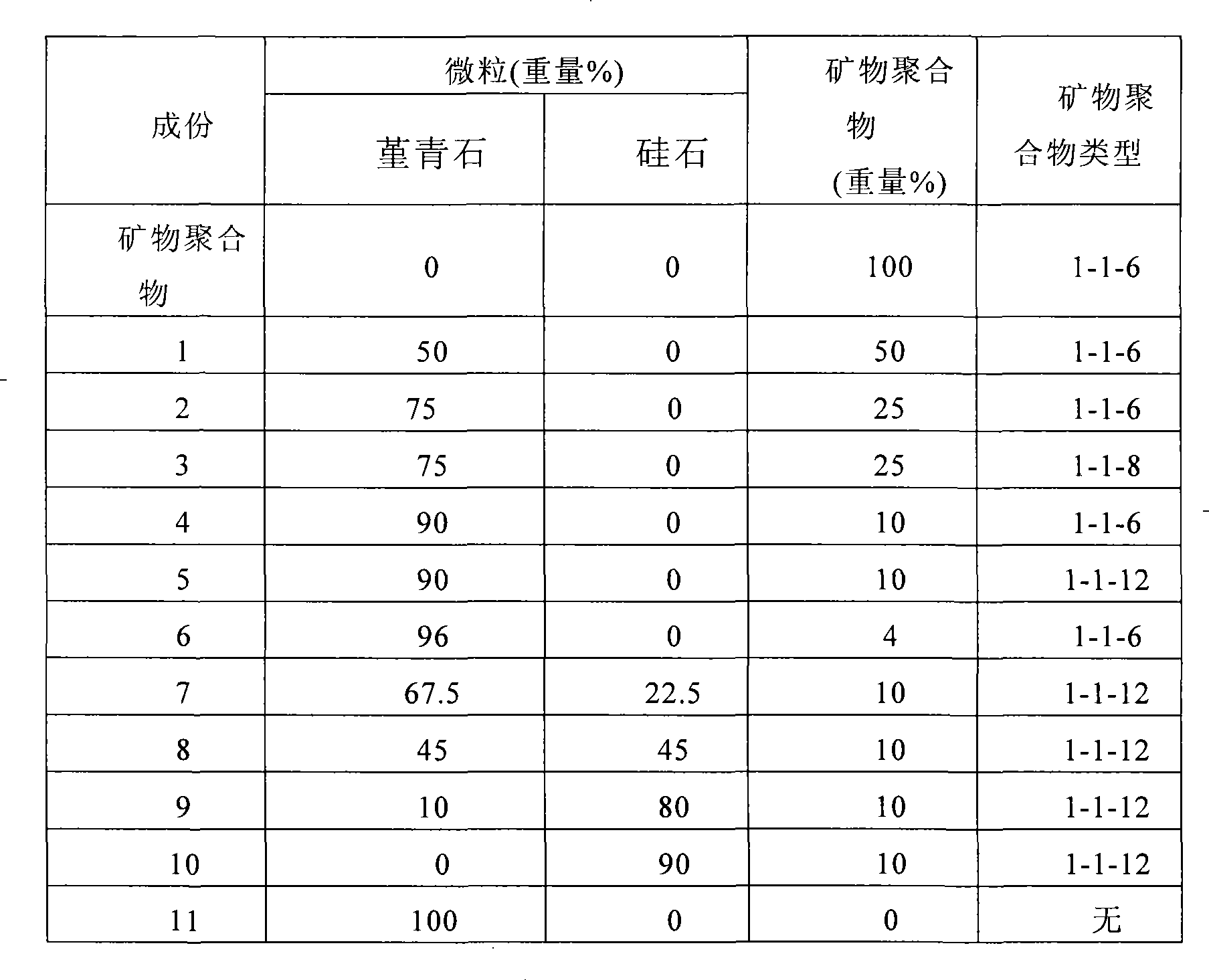
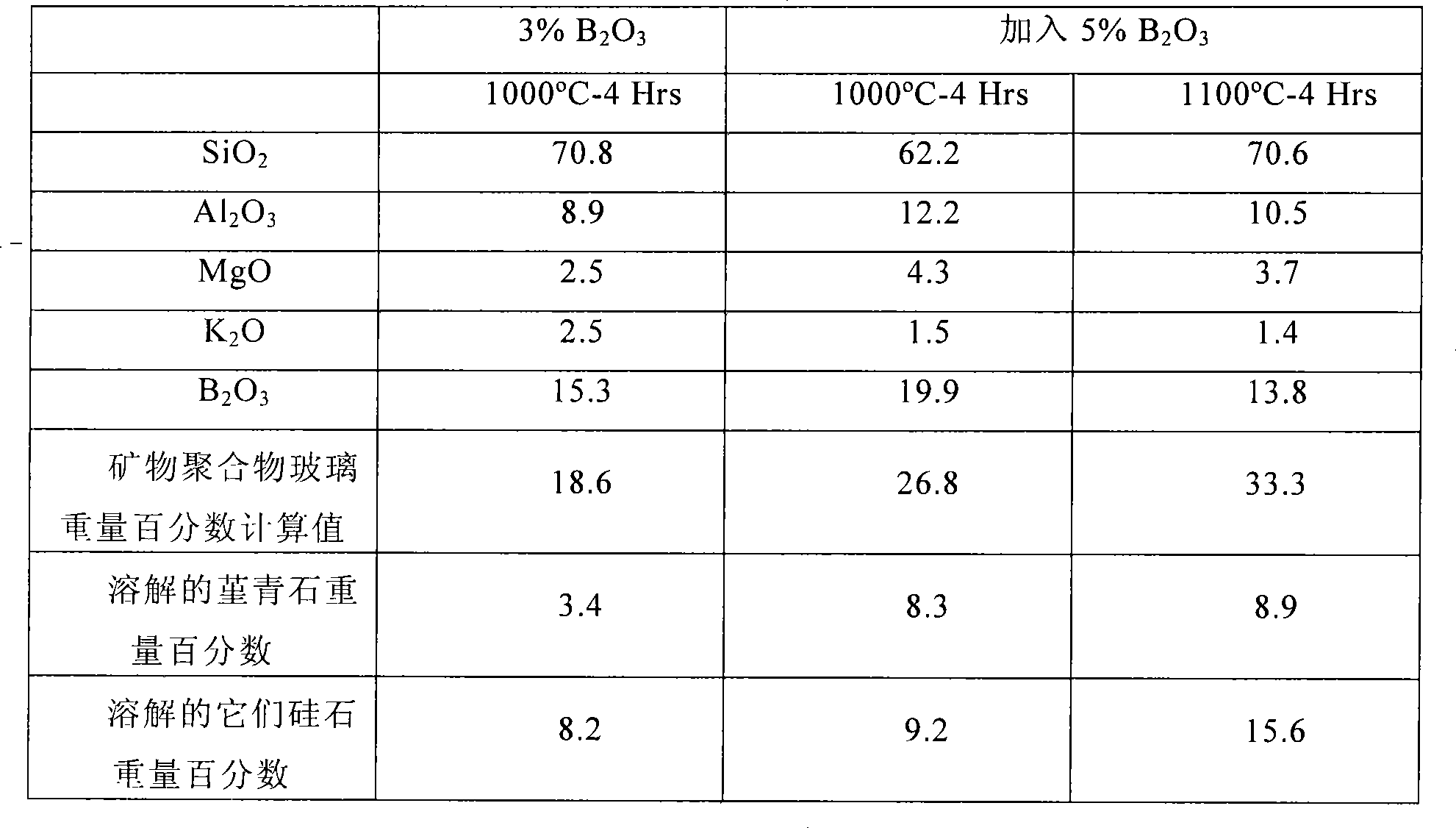
[0030] Composition 4 is 90% by weight cordierite bound with 10% by weight potassium aluminosilicate mineral polymer and added 5% by weight B 2 o 3 (Percentage of total formulation) Modified ceramics prepared as follows: 2.07g Glomax LL, 186.4g cordierite and 1g CMC (AqualonR Cellulose Gum) binder were mixed for 3 minutes; 8.27g Ludox and 10.36g were added to 100g water g boron oxide (B 2 o 3 ), heated until the boron oxide was dissolved, then added to the dry mixture and mixed; 10.34 g of Kasil-1 was added to the mixed ingredients and mixed thoroughly to form a solution. This solution is then added to the dry ingredients and mixed thoroughly to form a geopolymer bound wet mix. The furnish was dried and heated to 800° C. to produce a dry composition of approximately 94.7 wt. % cordierite and 5.3 wt. % potassium boroaluminosilicate glass (assuming no cordierite decomposition). The CTE of Example 1 is about 17.5×10 -7 / °C (25 to 800°C).
Embodiment 2
[0032] Composition 10, containing 90% by weight of transparent silica bound with 10% by weight of potassium aluminosilicate mineral polymer, and with an excess of 3% by weight of B 2 o 3 Additive-modified ceramics were prepared as follows: 559.2 g of crushed vitreous silica, 31 g of Kasil-1, 6.28 g of Glomax LL, 24.8 g of Ludox and 18.66 g boron oxide. Upon drying and heating to 800°C, the batch yielded a dry composition containing approximately 92.8% by weight silica and 7.2% by weight potassium boroaluminosilicate glass (assuming no decomposition of the silica particles upon heating). The CTE of Example 2 is about 11×10 -7 / °C (25 to 800°C).
Embodiment 3
[0034] Composition 9, containing 80% by weight transparent silica, 10% by weight cordierite bound with 10% by weight potassium aluminosilicate mineral polymer, and with an excess of 3% by weight B 2 o 3 Additive-modified ceramics, prepared as follows: 31 g Kasil-1, 6.28 g Glomax LL, 24.8 g Ludox, 18.66 g boron oxide, 503.24 g of Fused silica and 55.92 g of ground cordierite. Upon drying and heating to 800° C., the batch produced a glass containing approximately 83.6 wt. % silica, 9.2 wt. % cordierite (assuming no cordierite decomposition), and 7.2 wt. % potassium boroaluminosilicate geopolymer glass (assuming no dry composition of silica or cordierite particle decomposition). The CTE of Example 3 is about 10.0×10 -7 / °C (25 to 800°C).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| coefficient of thermal expansion | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| coefficient of thermal expansion | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com