Solar house
A technology of solar energy and solar cells, applied in the field of solar houses, can solve the problems of limiting the surface area of solar cells receiving sunlight and reducing the efficiency of solar energy utilization, and achieve the effects of improving utilization efficiency, increasing area, and increasing surface area
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
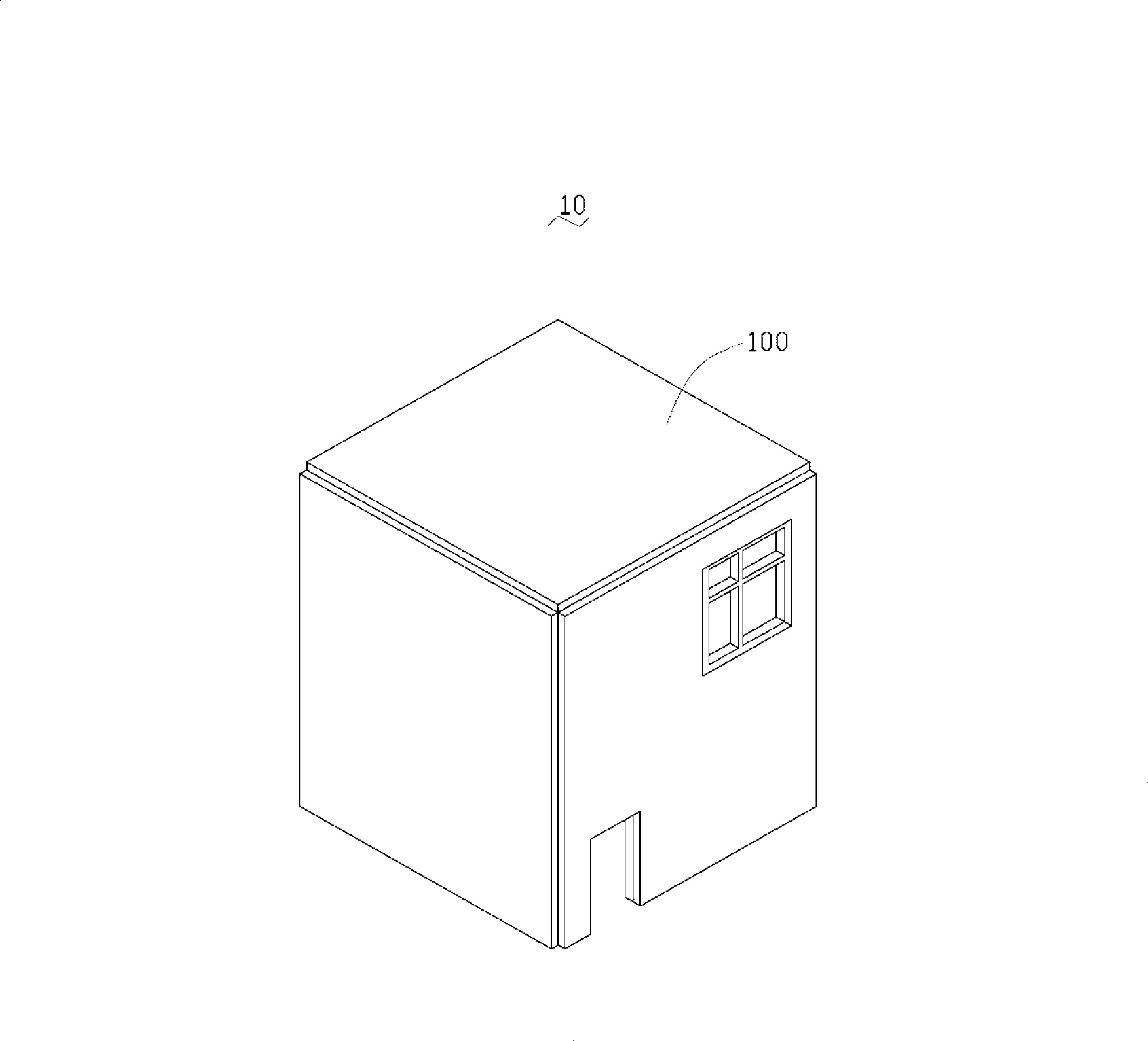
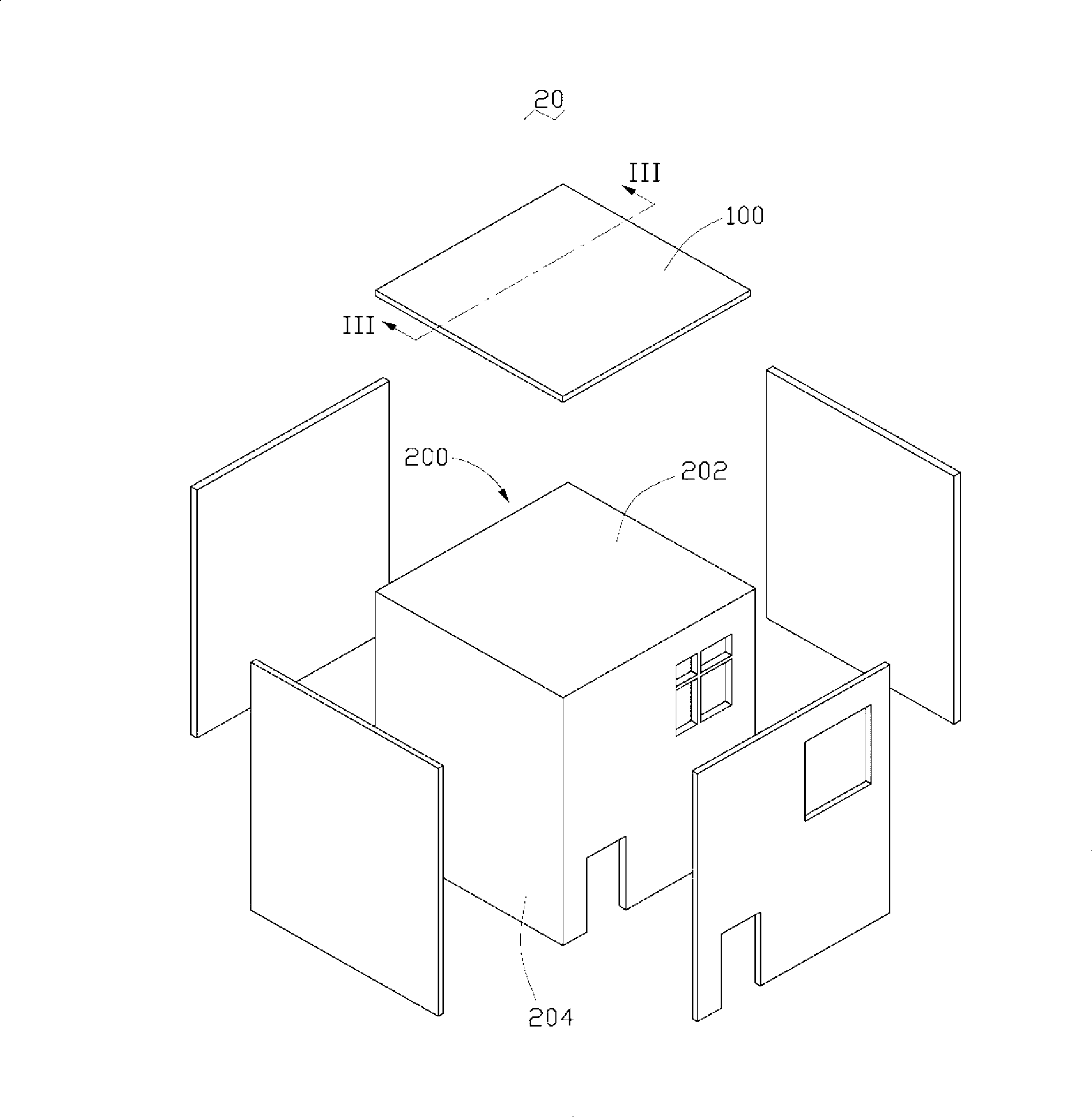
[0014] Please refer to figure 1 and figure 2 , The solar house 20 according to the first embodiment of the present invention includes a house body 200 and a plurality of solar cells 100 .
[0015] The house body 200 is substantially in the shape of a cuboid, and includes a roof 202 and four side walls 204 connected to the roof. The house body 200 can be constructed with common building materials, such as glass and bricks. In this embodiment, the house body 200 is mainly made of glass.
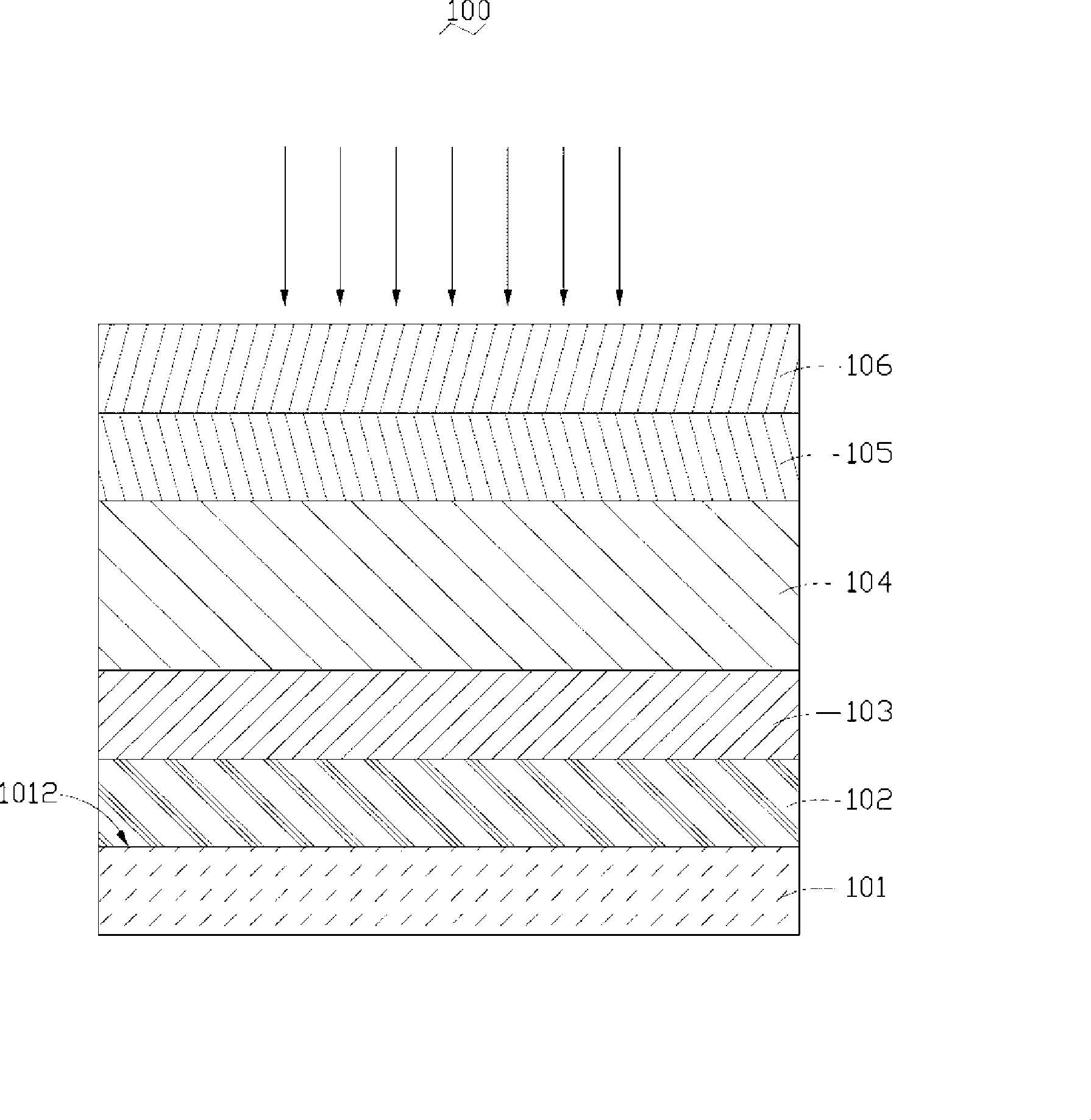
[0016] Solar cells 100 are disposed on the upper surface of the roof 202 and the outer surfaces of each side wall 204 . The solar cell 100 is fixed on the roof 202 and each side wall 204 by, for example, bonding or brackets. In this embodiment, the solar cell 100 is fixed by bonding. The solar cell 100 absorbs sunlight irradiated on the roof 202 and each side wall 204 and converts it into electrical energy. The solar battery 100 is connected to a converter or a battery (not shown) throug...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com