Preparation of LiFePO4
A solution and iron salt technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, phosphorus compounds, inorganic chemistry, etc., can solve the problems of complex steps and high preparation costs, and achieve the effects of simple steps, excellent performance and low price
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Embodiment 1: a kind of LiFePO of this example 4 The preparation method, its step is:
[0033] a. Add phosphorus-containing compound solution, surfactant, and carbon-coated carbon source to 10ml iron salt solution for hydrothermal synthesis; the iron salt solution is FeSO 4 , the phosphorus compound is H 3 PO 4 , the surfactant is PEG, the carbon-coated carbon source is sucrose; the molar ratio of Fe atom to P atom is 1:1, the molar ratio of Fe atom to surfactant is 1:1, and sucrose is 5% of FeSO4 mass.
[0034] b. Introduce nitrogen for 10 minutes, and then discharge the air;
[0035] c. Add 10ml of lithium salt solution, the lithium salt solution is LiOH, and the molar ratio of Fe atom to Li atom is 1: 2.5;
[0036] d. Introduce nitrogen for 10 minutes, control the pH value to 9.0, heat up to 180°C for hydrothermal treatment for 360 minutes;
[0037] e. Suction filtration, washing and drying to obtain pure-phase crystals of flaky or columnar LiFePO 4 finished pr...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Embodiment 2: a kind of LiFePO of this example 4 The preparation method, except that the molar ratio of Fe atoms and P atoms in step a is 1: 1.2, the rest of the steps are the same as in Example 1.
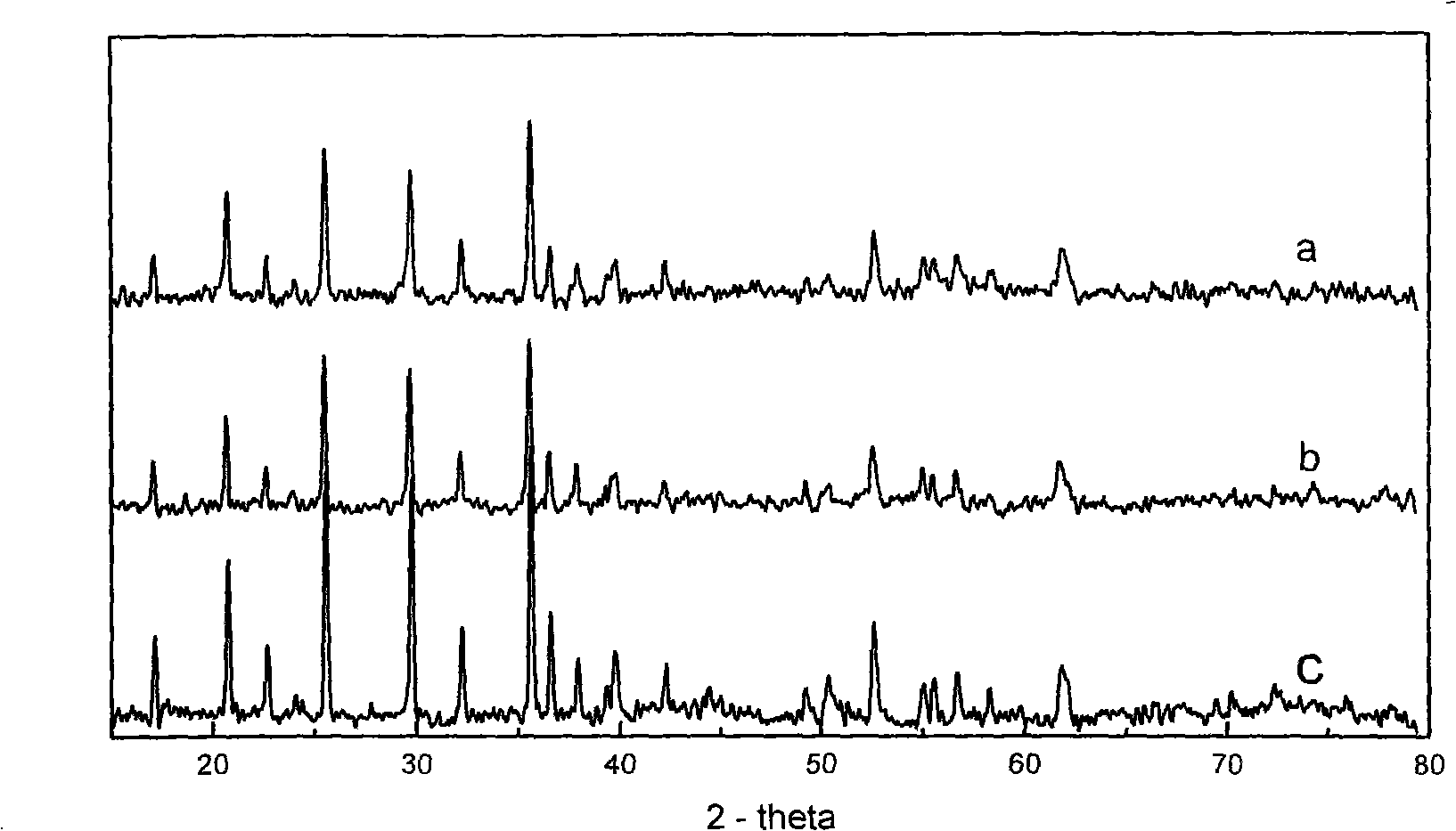
[0043] After the X-ray diffraction analysis of the obtained product, it is also LiFePO with pure phase, no impurities, and good crystallinity. 4 The sample has no change in the scanning electron microscope compared with Example 1, and its electrochemical behavior shows that its first discharge capacity increases.
[0044] The X-ray diffraction data of this embodiment product see figure 1 in b.
[0045] The first discharge curve of this embodiment is shown in Figure 5 in b.
Embodiment 3
[0046] Embodiment 3: a kind of LiFePO of this example 4 The preparation method, except that the molar ratio of Fe atoms and P atoms in step a is 1: 1.4, the remaining steps are the same as in Example 1.
[0047] The X-ray diffraction data of the obtained product is indistinguishable from that of Example 1 and Example 2. Compared with Example 1, the scanning electron microscope is obviously transformed from sheet-packed to columnar, and the electrochemical data shows that the initial discharge capacity of the product is better than that of Example 1 and Comparative Example 1. There is a noticeable attenuation.
[0048] The scanning electron microscope picture of this embodiment is shown in image 3 , is columnar, indicating that LiFePO prepared using the preparation method of the present invention 4 The sample can control the shape of the product under different conditions.
[0049] The discharge curve for the first time in this embodiment is shown in Figure 5 in c.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com