Heat pressing production method of polyethylene fiber-plant fibre compound material
A polyethylene fiber and plant fiber technology, which is applied in the pretreatment of molding materials, manufacturing tools, flat products, etc., can solve the problems of poor mixing uniformity of polyethylene powder and plant fiber scraps, easy pyrolysis and carbonization of straw, and mechanical properties of plates. Low-level problems, to achieve the effect of easy melting and heat transfer, improved physical and mechanical properties, and favorable heat transfer
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
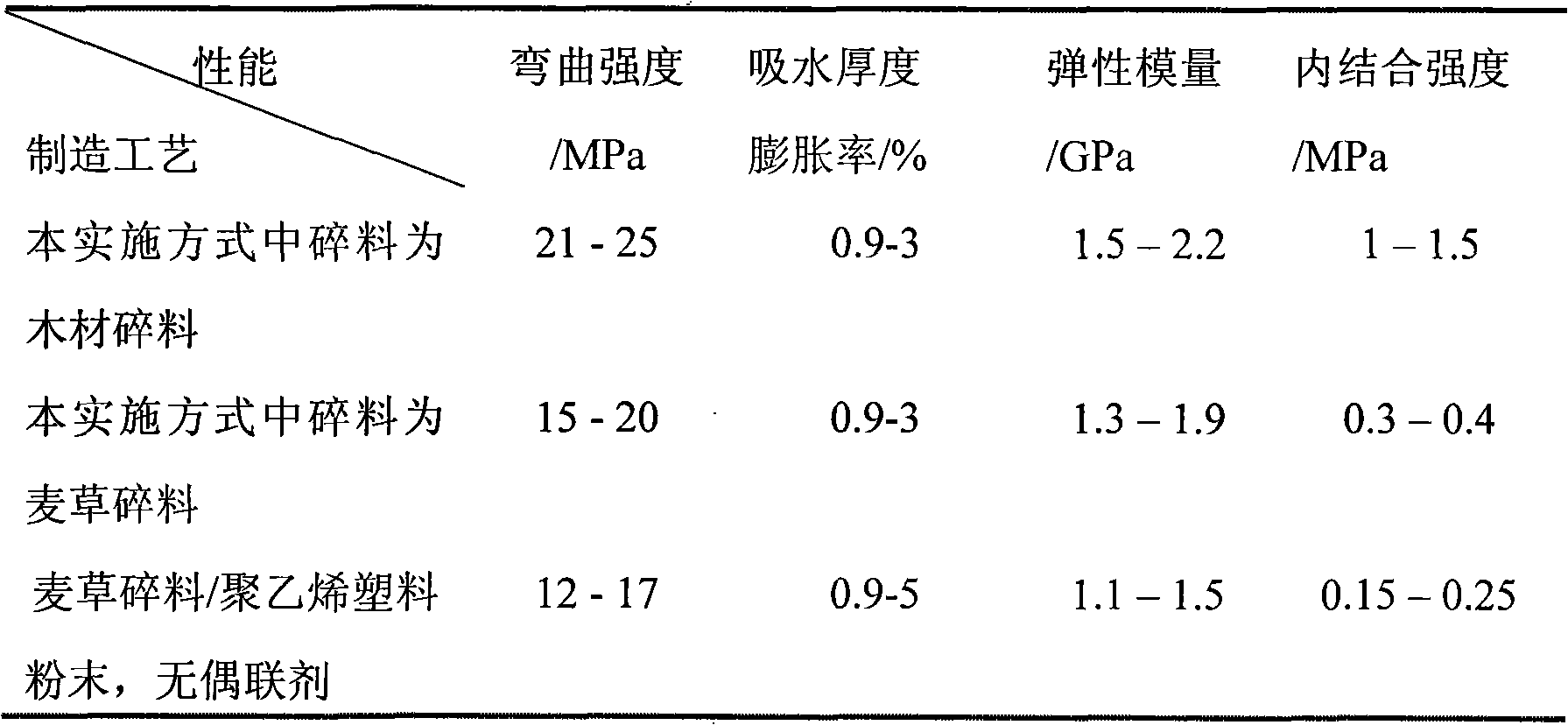
[0010] Embodiment one: the hot-pressing manufacturing method of polyethylene fiber-plant fiber composite material in the present embodiment is as follows: one, the maleic anhydride grafted polyethylene particle that accounts for polyethylene plastic particle quality 3%~6% and polyethylene Plastic particles are mixed, heated and melted at a temperature of 170-180°C, then cooled to room temperature and sawn into polyethylene plastic fibers with a length of 5mm-25mm, a width of 2mm-3.5mm, and a thickness of 0.2mm-1.5mm; 2. Mix the polyethylene plastic fiber obtained in step 1 with the plant debris with a fineness of 10 to 40 meshes to obtain the mixture; 3. Pave the mixture obtained in step 2 into a slab, and then place the slab on two Between the metal backing plates, preheat for 20 to 30 minutes at a pressure of 1 to 3 MPa and a temperature of 150 to 160 °C; 4. Place the preheated slab at a pressure of 4 to 6 MPa and a temperature of 170 to 190 ℃ for 8-15 minutes, and then cool...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0016] Embodiment 2: This embodiment differs from Embodiment 1 in that the plant debris described in step 2 is wheat straw, straw, flax, cotton stalks, straw or waste wood debris. Others are the same as in the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0017] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that in step 2, the plant debris accounts for 51% to 60% of the total weight of the mixture. Others are the same as in the first embodiment.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fineness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com