Booster circuit
A technology of booster circuit and comparison circuit, which is applied in the direction of conversion equipment without intermediate conversion to AC, can solve the problems of increasing current consumption, decreasing boosting efficiency, and increasing layout area, so as to suppress current consumption and improve boosting. Efficiency, the effect of suppressing the increase of the layout area
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0092] Hereinafter, a booster circuit according to an embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings.
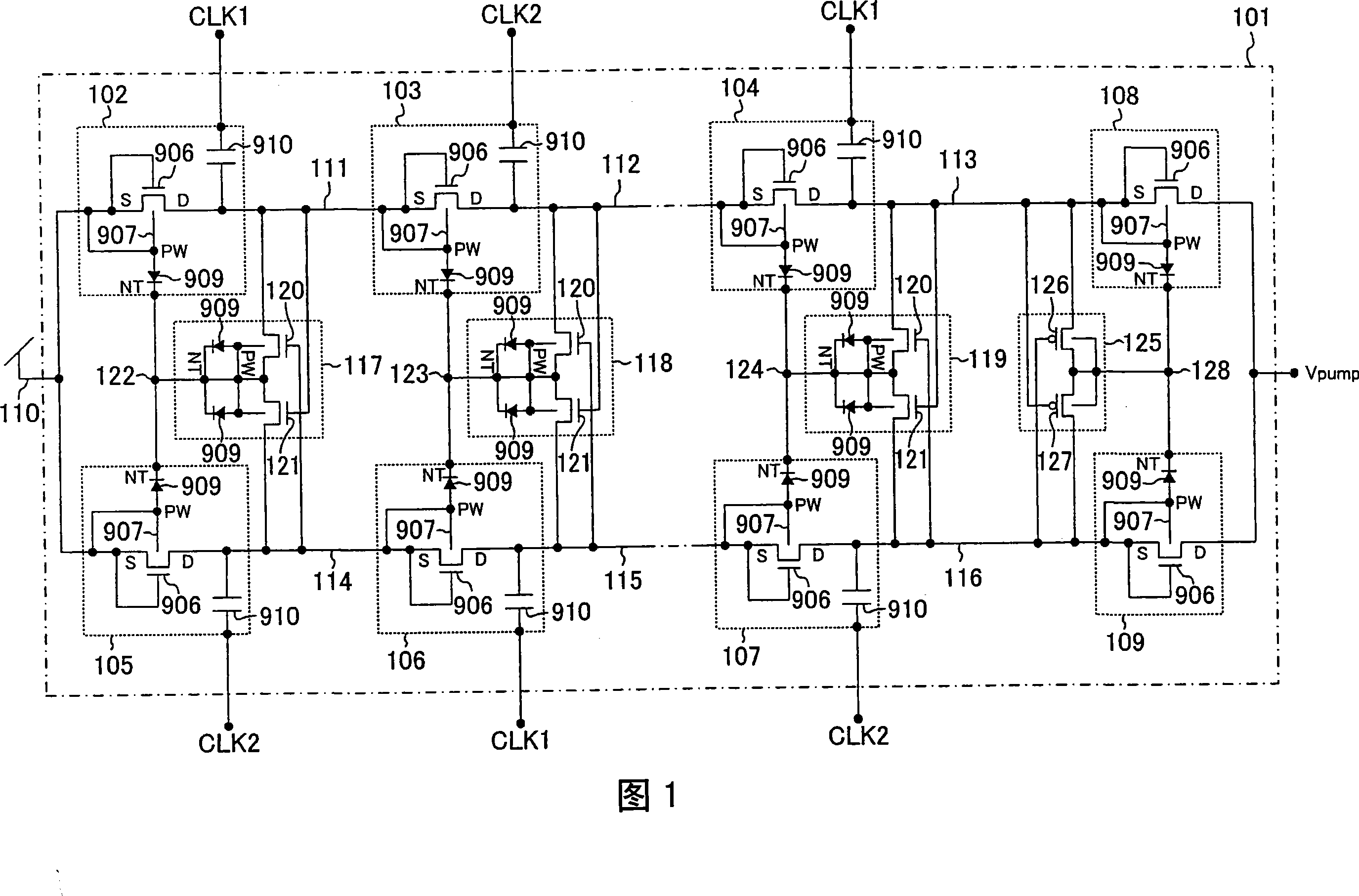
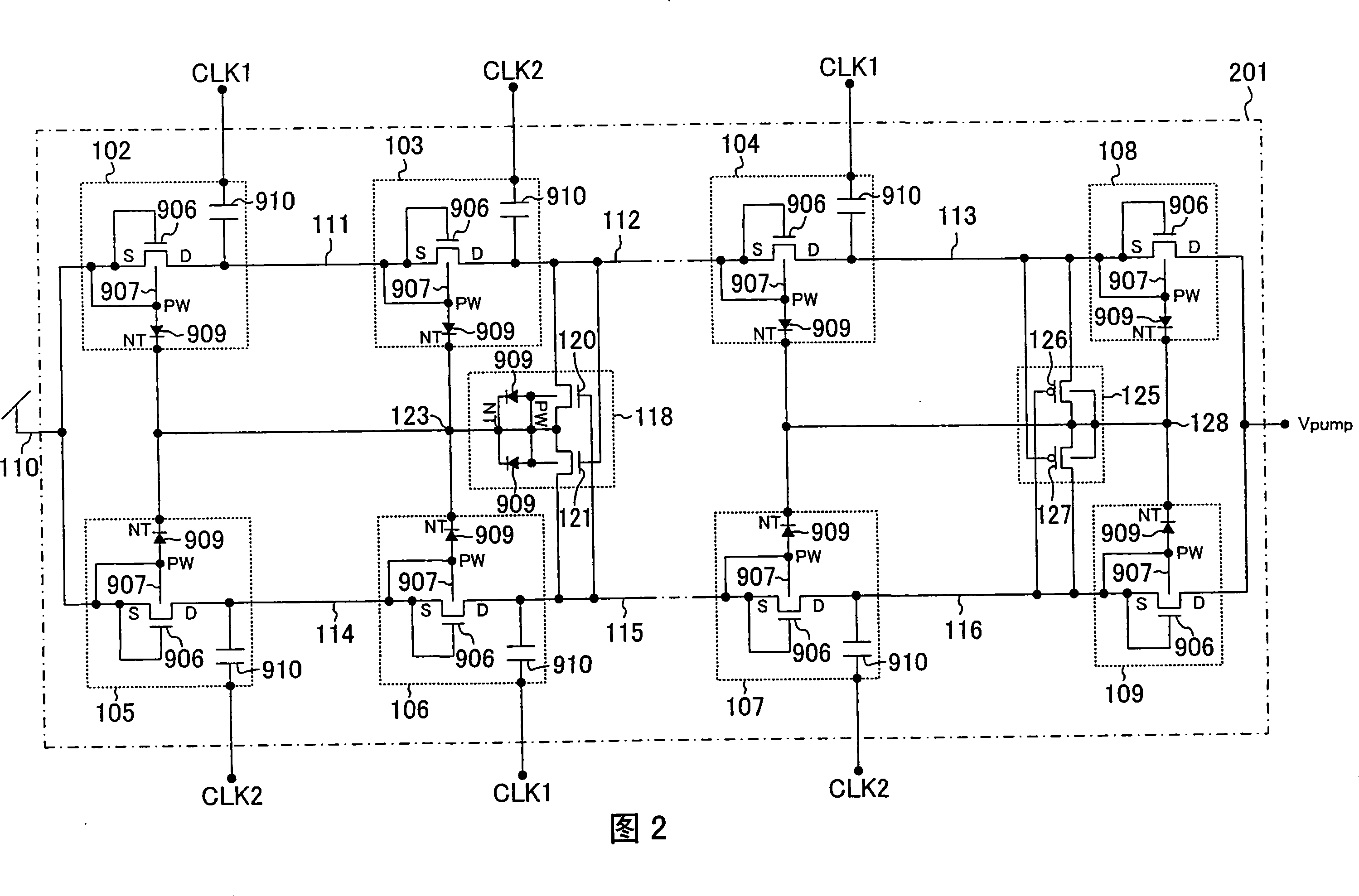
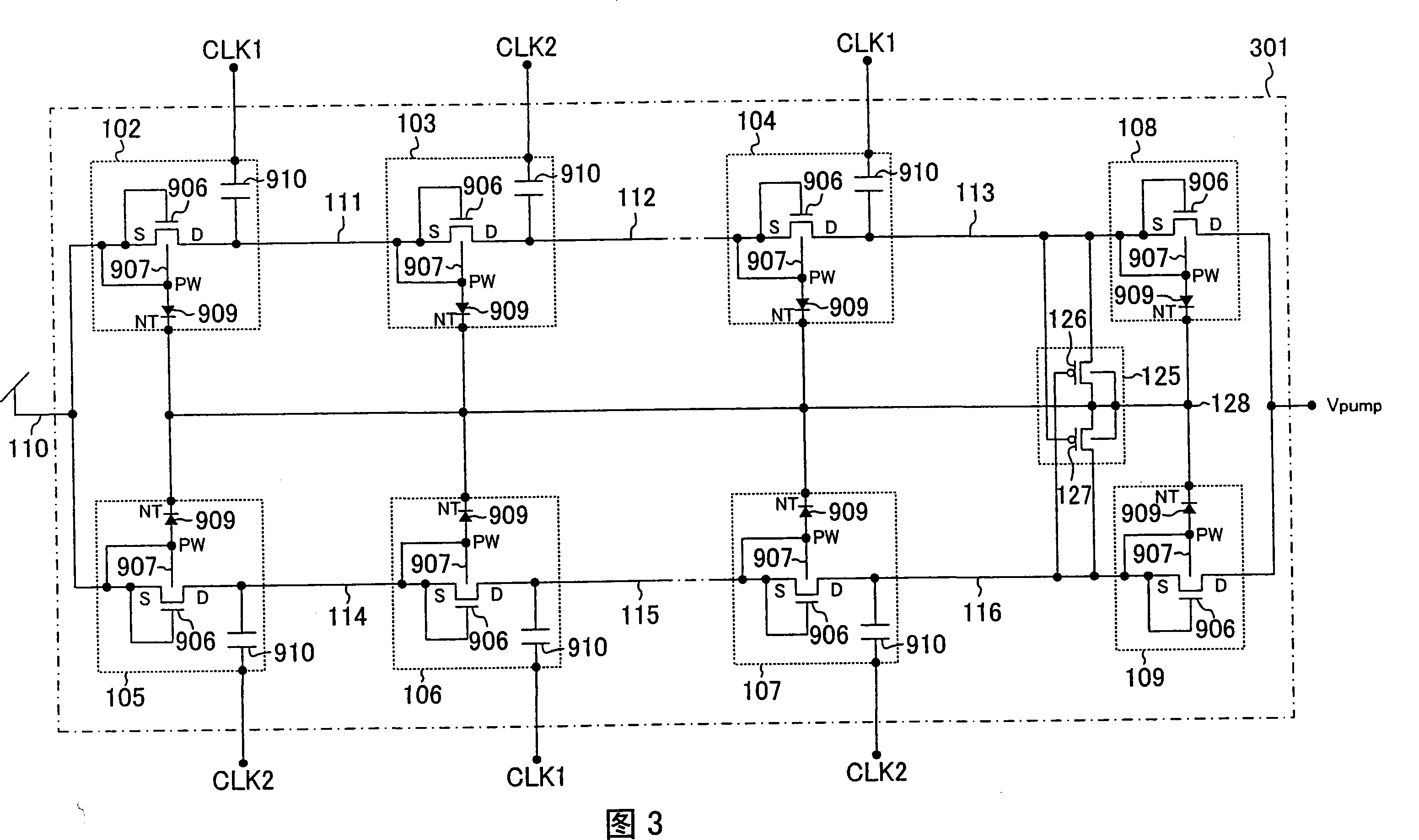
[0093] FIG. 1 shows a configuration example of a booster circuit according to the present invention. In FIG. 1 , 101 is a dual-parallel booster circuit that generates an output terminal voltage (boosted voltage) Vpump by inputting two-phase clock signals CLK1 and CLK2 to perform a boosting operation. 102, 103, 104, 105, 106, and 107 have the structure of the first column and the second column, and input CLK1 to the odd-numbered stage in the first column, input CLK2 to the even-numbered stage in the first column, and input CLK2 to the odd-numbered stage in the second column Input CLK2, input CLK1 boost unit to the even-numbered stage of the second column; 108, 109 are anti-reverse current circuits for preventing reverse current of the boost voltage Vpump, 110, 111, 112, 113, 114, 115, 116 117, 118, and 119 are the input and output termin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com