Extraction method of phytic acid in rice bran
An extraction method and rice bran technology are applied in the field of phytic acid extraction from rice bran, and can solve the problems of poor color, long extraction time, and low final phytic acid extraction rate.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
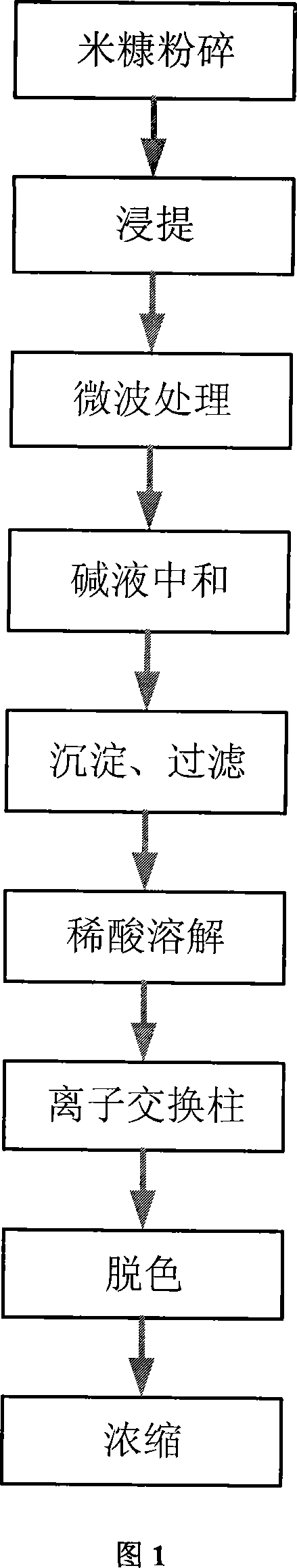
[0021] Using rice bran as raw material, crush it through a 150-mesh sieve, weigh 5g of rice bran, add 0.1mol / L hydrochloric acid solution, and control the ratio of solid to liquid to 1:5, 1:6, 1:7, 1:8, 1:9 , 1:10, control the pH to 3.0, leaching for 3 hours, and microwave the sample under the condition of medium heat (about 1000W) for 3 minutes. Then use 1mol / L sodium hydroxide solution to adjust the pH range to 3.0, and then stand and stir for 3h. Filtrate to obtain a beige suspension liquid, first adjust the pH to 4.0 with 10% calcium hydroxide emulsion, and then use 1mol / L sodium hydroxide solution to adjust the pH>7.0 to obtain a beige turbidity with white precipitates. After stirring evenly, let it stand for 2 hours to make the precipitation complete. After filtering, a gray to yellow-brown intermediate calcium phytate slurry was obtained. Calculate the amount and purity of the intermediate product calcium phytate, and see Table 1 for the effect of the solid-liquid rati...
Embodiment 2
[0025] Use rice bran as raw material to crush it through a 150-mesh sieve, weigh 5g of rice bran, add 0.1mol / L hydrochloric acid solution, control the ratio of solid to liquid to 1:7, control the pH to 3.0, extract for 3 hours, and use a power of 500W or 700W , 1000W, 1200W microwave treatment samples, time is 3min. Then use 1mol / L sodium hydroxide solution to adjust the pH range to 3.0, and then stand and stir for 3h. Filtrate to obtain a beige suspension liquid, first adjust the pH to 4.0 with 10% calcium hydroxide emulsion, and then use 1mol / L sodium hydroxide solution to adjust the pH>7.0 to obtain a beige turbidity with white precipitates. After stirring evenly, let it stand for 2 hours to make the precipitation complete. After filtering, a gray to yellowish-brown calcium phytate slurry was obtained. The amount and yield of the intermediate product calcium phytate were calculated, and the effect of microwave power on the yield of the intermediate product calcium phytate ...
Embodiment 3
[0030] Use rice bran as raw material to crush it through a 150-mesh sieve, weigh 5g of rice bran, add 0.1mol / L hydrochloric acid solution, control the ratio of solid to liquid to 1:7, control the pH to 3.0, extract for 3 hours, and use a power of 500W or 700W , 1000W, 1200W microwave treatment samples, time is 3min. Then use 1mol / L sodium hydroxide solution to adjust the pH range to 3.0, and then stand and stir for 3h. Filtrate to obtain a beige suspension liquid, first adjust the pH to 4.0 with 10% calcium hydroxide emulsion, and then use 1mol / L sodium hydroxide solution to adjust the pH>7.0 to obtain a beige turbidity with white precipitates. After stirring evenly, let it stand for 2 hours to make the precipitation complete. After filtering, a gray to yellow-brown intermediate calcium phytate slurry was obtained. Calculate the amount and yield of the intermediate product calcium phytate, and see Table 3 for the effect of microwave treatment time on the yield of the intermed...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com