Imaging device and imaging method
A technology of a camera device and a camera element, which is applied in the direction of focusing device, measuring device, static camera, etc., can solve the problems of entering and focusing accuracy decline, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
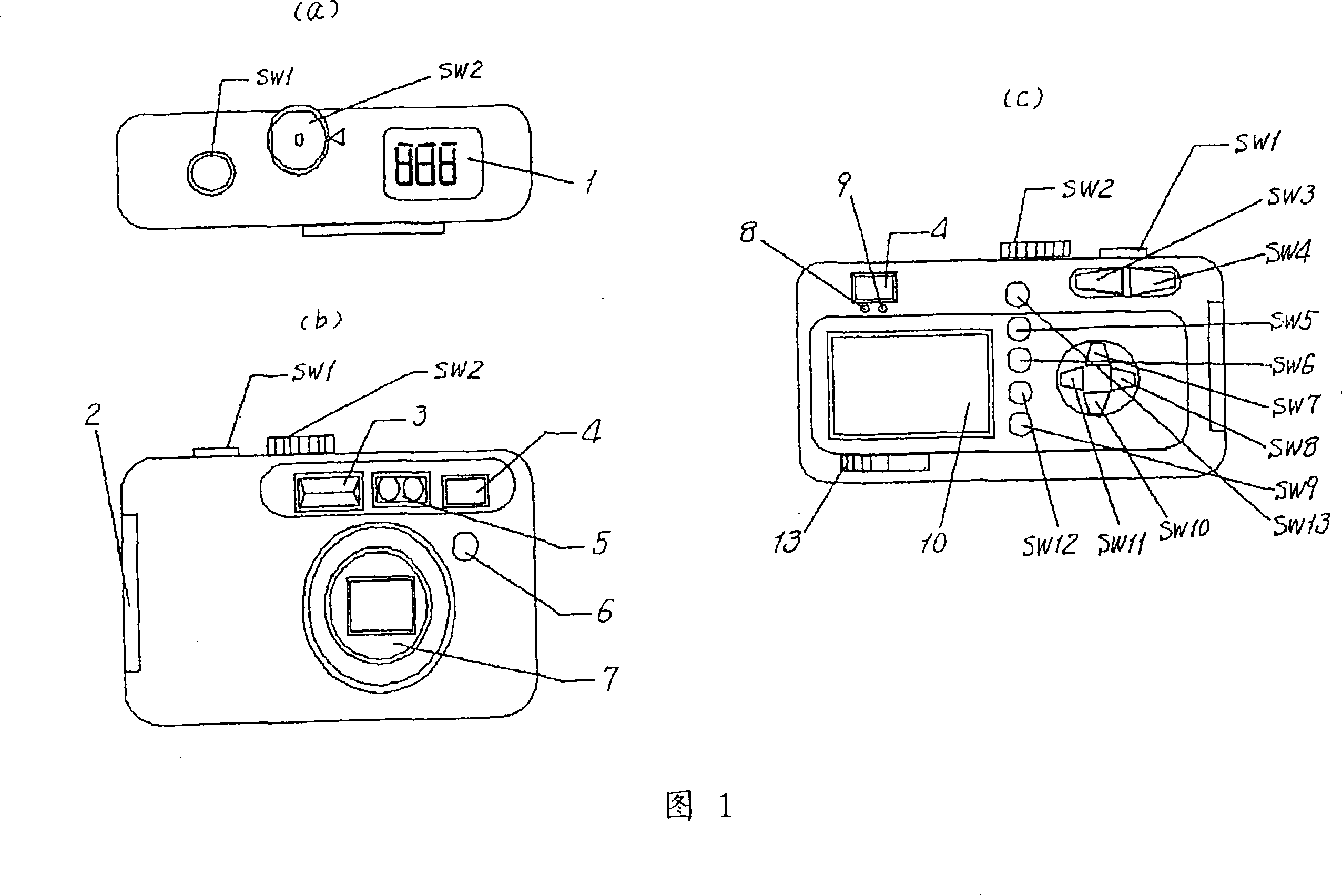
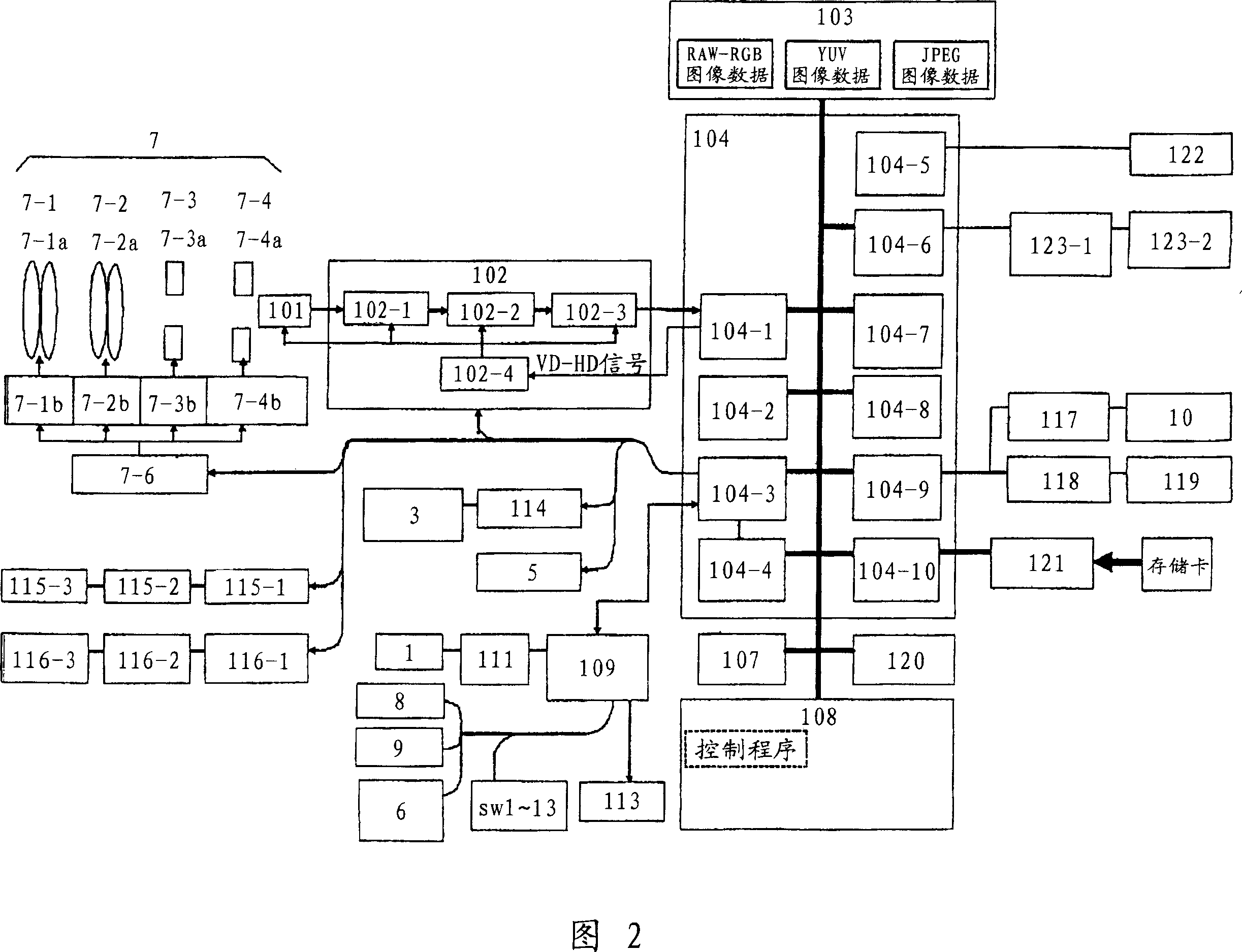
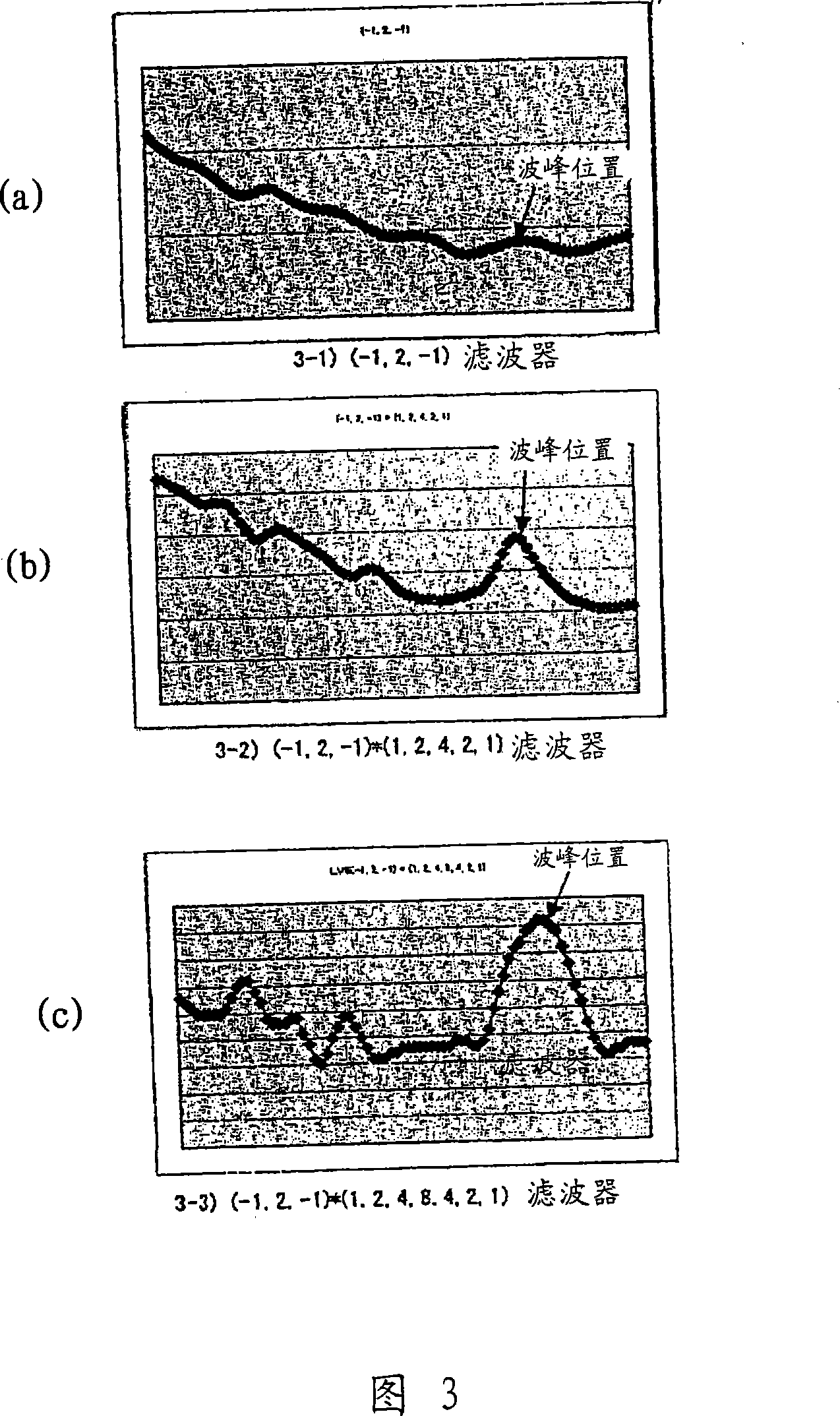
[0057] FIG. 4 shows the operation of the imaging device of the first embodiment. First, the operation is started by operating the releaser shutter button SW1 shown in FIG. 1 , and the brightness of the subject is determined based on the photometry result immediately before the releaser shutter button was pressed (4-2). Subject brightness can be measured from the output of CCD101. A process of selecting a frequency component extraction filter based on the luminance (LV value) obtained from the photometry result (4-3) is performed. In this embodiment, three filters as shown in FIG. 7 are prepared, for example, a frequency extraction filter is selected by processing according to the flowchart shown in FIG. 6 . Specifically, the structures of the three filters shown in FIG. 7 are shown as follows. The first filter is a composite filter of a high-pass filter composed of coefficients '-1', '2', '-1' and a low-pass filter composed of coefficients '1', '2', '1'. The second filter i...
Embodiment 2
[0065] Next, Embodiment 2 will be described with reference to the flowchart shown in FIG. 5 .
[0066] When the releaser shutter button SW1 shown in FIG. 1 is operated, the brightness of the subject is determined based on the photometry result immediately before the releaser shutter button was pressed (5-2). A process of selecting a frequency component extraction filter based on the luminance (LV value) obtained from the photometry result (5-3) is performed. In this embodiment, three filters as shown in FIG. 7 are prepared, and a frequency extraction filter is selected by processing such as the flow chart shown in FIG. 8 . The filter selection process first judges whether the brightness of the subject is less than LV6 (10-1), and if it is not less than LV6, that is, greater than or equal to LV6, it is judged whether it was not selected during the last scan (10-2), if If there is no selection, then select the first filter (10-3), if it was selected during the last scan, then p...
Embodiment 3
[0072] Next, Embodiment 3 will be described centering on the flowchart shown in FIG. 9 . When the releaser shutter button SW1 shown in FIG. 1 is operated, the brightness of the subject is determined based on the photometry result before the releaser button is pressed (11-2). Next, the focus lens is moved to the focus start position (11-3), and pixel data is acquired (11-4). This pixel data is a digital RGB signal taken into the CCD I / F block of the digital signal processing IC. After the acquisition of the pixel data, it is judged whether or not scanning has been completed to the end of the focus position (11-5). If the end point of the focus position is not completed, the focus position is moved sequentially (11-6), the end point is scanned, and the same process is performed until the end (11-5).
[0073] Next, a frequency component extraction filter is selected based on the luminance (LV value) obtained from the photometry result (11-7). In this embodiment, three filters ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com