Pulsed X-ray for continuous detector correction
A detector and X-ray technology, applied in the field of diagnostic imaging, can solve the problems of large changes in time, unstable photoconductor gain and offset, and achieve the effect of preventing artifacts and reducing thickness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
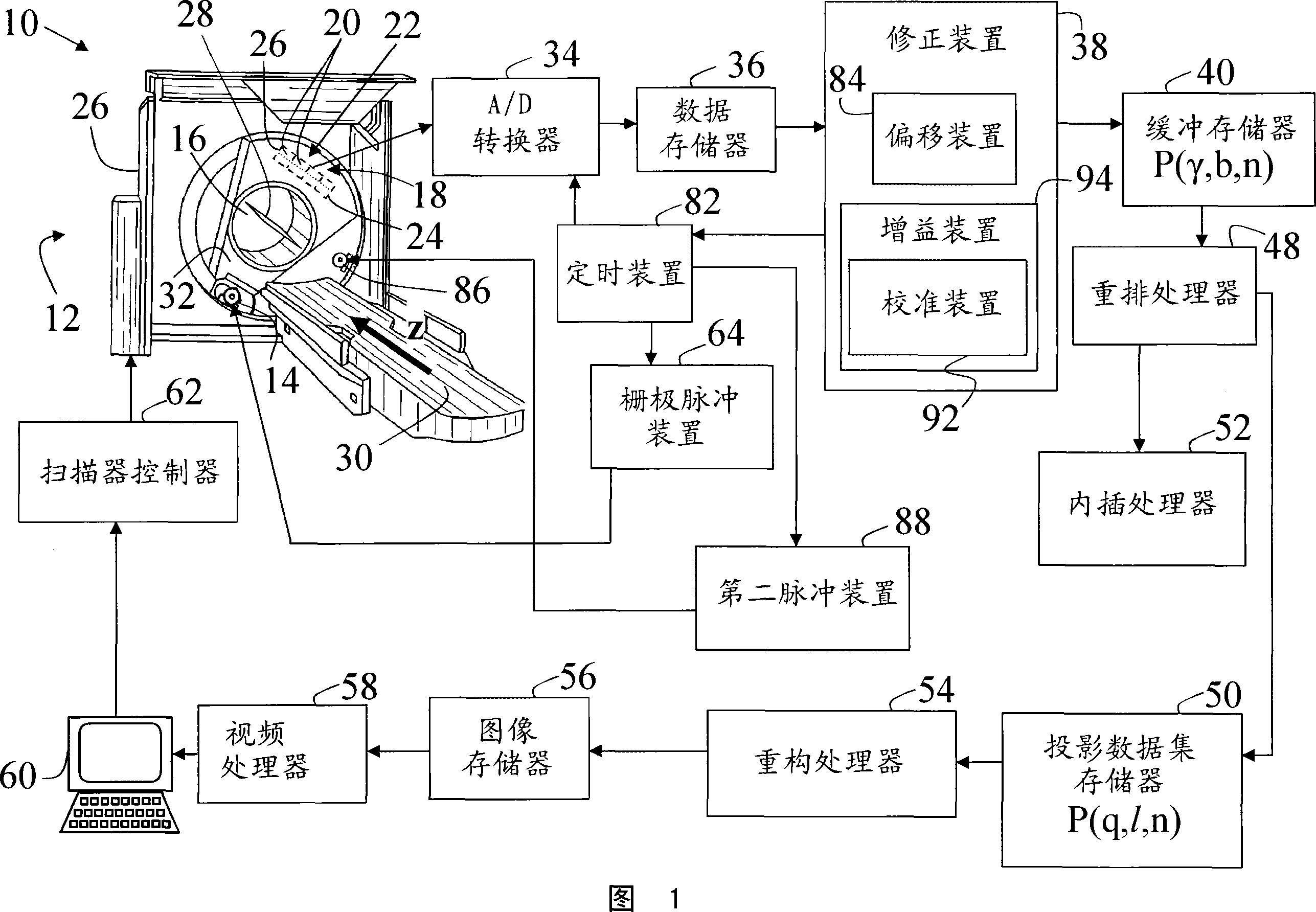
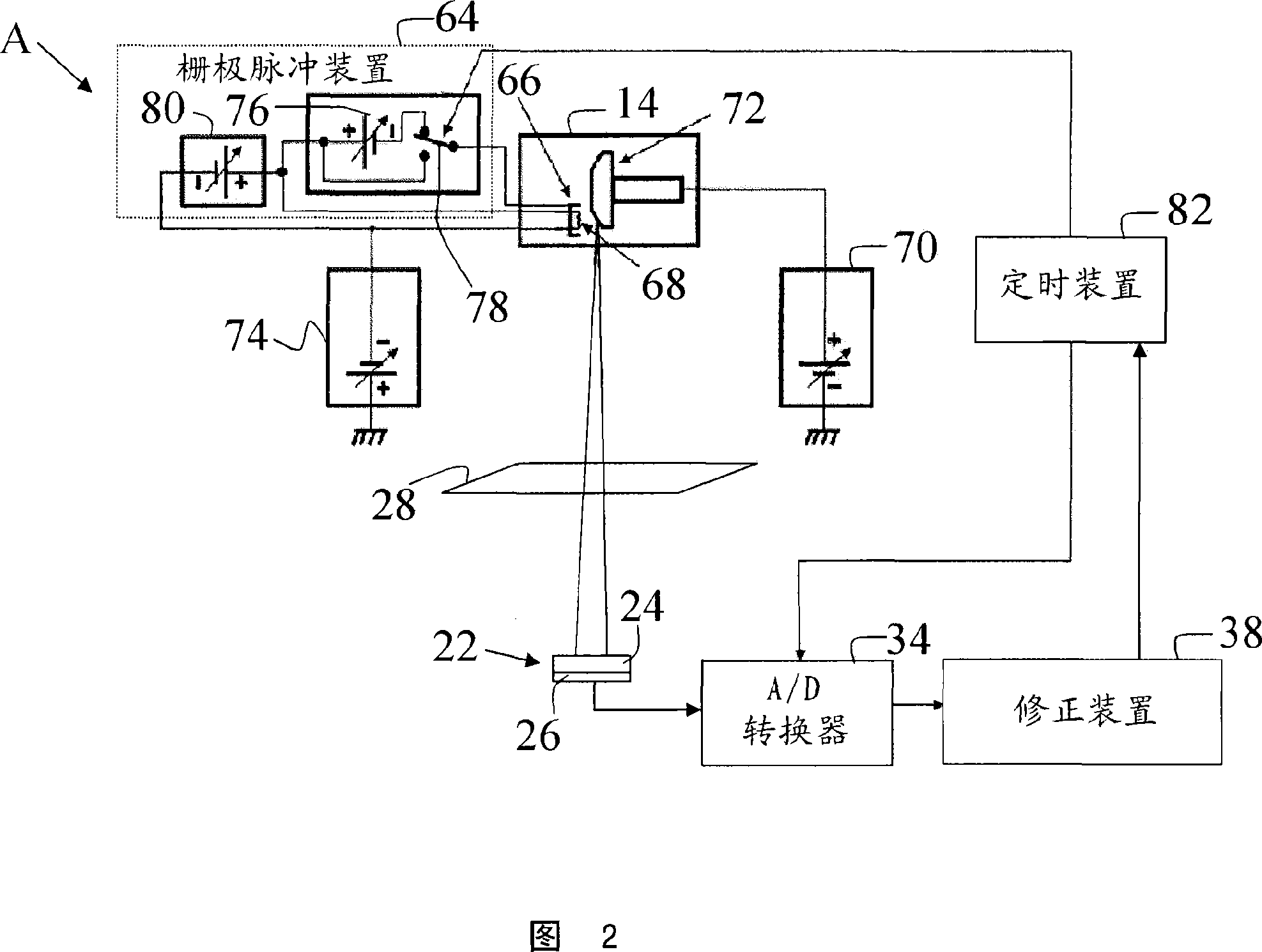
[0035] Referring to FIG. 1 , an imaging system 10 includes a computed tomography scanner 12 that houses or supports a first radiation source 14 that, in one embodiment, projects a beam of radiation onto a region defined by the scanner 12. An x-ray source or x-ray tube in area 16 is inspected. The radiation beam after passing through the examination region 16 is detected by a two-dimensional radiation detector 18 comprising a plurality of detection modules or detection elements 20 arranged to detect the radiation beam after passing through the examination region 16 . Detector 18 includes an X-ray-to-analog signal conversion layer 22 that is characterized by a gain A(t) and / or offset B(t) that generally vary with time. In one embodiment, conversion layer 22 includes an array of scintillation crystals or scintillators or scintillation layer 24 coupled to photodiode array 26 . In another embodiment, the conversion layer 22 comprises a plurality of direct conversion semiconductors...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com