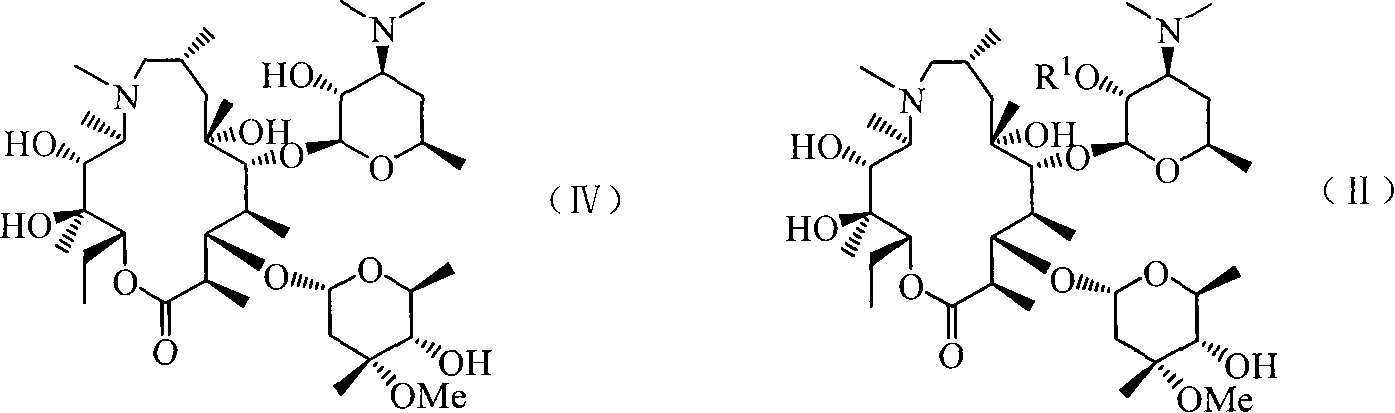
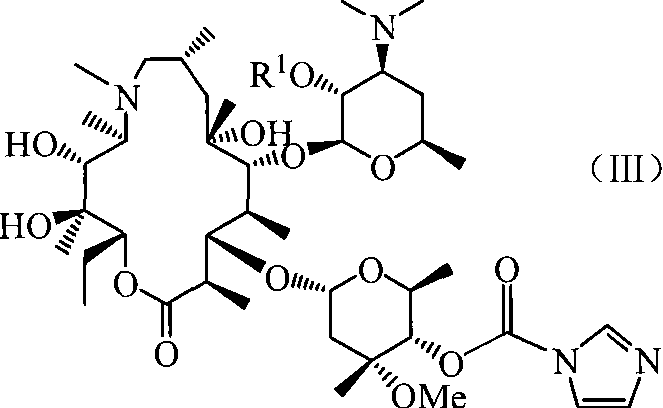
Azithromycin 4-phenproester derivative, its production and medicinal composition
A technology of drugs and compounds, applied in the field of azithromycin derivatives and its preparation, can solve the problems of not describing azithromycin 4″-carbamate derivatives
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] Embodiment 1: the preparation of the first intermediate
[0052] a) Preparation of 2′-O-acetyl-azithromycin
[0053] Dissolve azithromycin (2.0 g, 2.67 mmol) in anhydrous dichloromethane (20 mL), add acetic anhydride (0.75 mL, 7.96 mmol) and triethylamine (3.00 mL, 21.6 mmol), and stir at room temperature for 24 h. After the reaction was completed, an equal volume of 5% sodium bicarbonate solution was added, the layers were separated, extracted with dichloromethane (10 mL×2), the organic layers were combined, and dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate. It was filtered and evaporated to dryness under reduced pressure to obtain a white foamy solid, which was recrystallized from acetone-water (2:1) to obtain the white target product (1.84 g), with a yield of 92%. Melting point 167~170℃, R f It was 0.522 (the developing solvent was dichloromethane:methanol=10:1). Molecular formula is C 40 h 74 N 2 o 13 , molecular weight is 791.0, MS is 792.0 (M+H + ).
[0054] b) Pre...
Embodiment 2
[0056] Example 2: Preparation of the second intermediate 4″-O-(1-H-imidazole-1-carbonyl)-2′-O-acetyl-azithromycin
[0057] Dissolve 2′-O-acetyl-azithromycin (1.5 g, 1.90 mmol) in anhydrous toluene (20 mL), add triethylamine (0.60 mL, 4.33 mmol) and N, N′-dicarbonylimidazole (CDI) ( 0.672g, 3.80mmol), stirred at room temperature for 48h. After the reaction was completed, a saturated sodium bicarbonate solution (20 mL) was added, the layers were separated, extracted with toluene (6 mL×2), the organic layers were combined and dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate. Filter and evaporate to dryness under reduced pressure to obtain 1.6 g of white foamy solid with a yield of 95.4%. Melting point 147~150℃, R f It was 0.592 (the developing solvent was dichloromethane:methanol=10:1). Molecular formula is C 44 h 76 N 4 o 14 , molecular weight is 884.5, MS is 885.5 (M+H + ).
Embodiment 3
[0058] Embodiment 3: Preparation of target product azithromycin 4 "-carbamate derivative
[0059] a) Preparation of 4″-O-propylcarbamoyl-2′-O-acetyl-azithromycin (target product)
[0060] 4″-O-(1-H-imidazole-1-carbonyl)-2′-O-acetyl-azithromycin (1.33 g, 1.50 mmol) was dissolved in N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) (15 mL ), add DBU (0.33mL, 2.25mmol) and n-propylamine (0.25mL, 2.25mmol), and stir at room temperature for 12h. After the reaction is complete, add water (30mL), extract with ethyl acetate (15mL×3), combine the organic layers, Wash with saturated brine (15mL×3), dry over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and evaporate to dryness under reduced pressure to obtain 1.15g of white foamy solid, yield 87.3%. Melting point 143~145°C, R f It was 0.611 (the developing solvent was dichloromethane:methanol=10:1). Molecular formula is C 44 h 81 N 3 o 14 , molecular weight is 876.1, MS is 877.1 (M+H + ).
[0061] b) Preparation of 4″-O-benzylcarbamoyl-2′-O-acetyl-azithromycin (target p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com