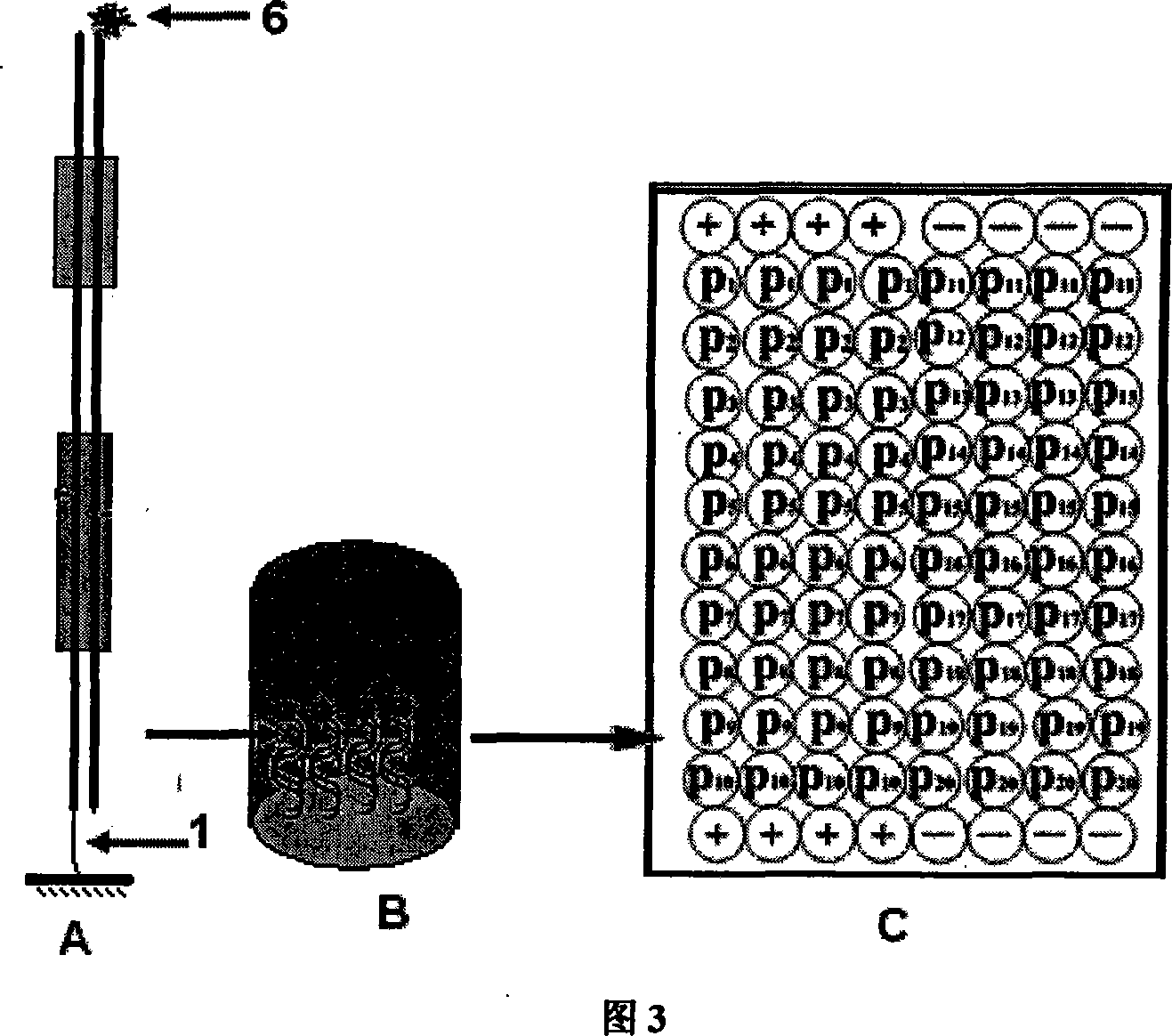
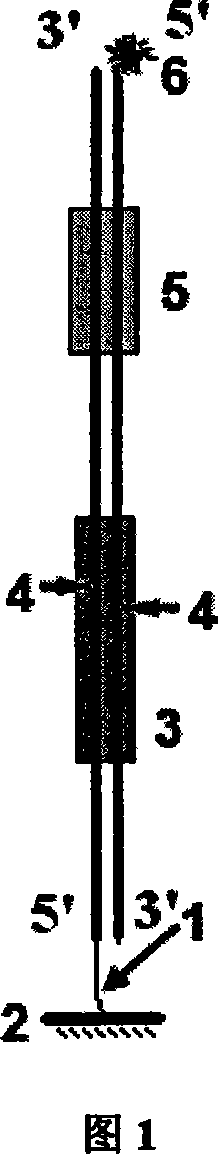DNA binding protein detection method based on moving endonuclease
A technology that combines proteins and detection methods, applied in the field of non-labeled detection in biomedicine, can solve the problems of low-abundance protein loss, improve detection efficiency and sensitivity, time-consuming and labor-intensive problems, achieve comprehensive biological significance, avoid radioactive pollution, and operate Safe and fast effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Example 1. Non-labeled detection of DNA-binding proteins based on streptavidin-coated 96-well plates (this method is applicable to all commercial microplate reader detection systems, and the detection instrument recommended in this embodiment is Tecan, Switzerland Infinite TM F200 automatic microplate reader. )
[0031] 1. Probe synthesis and immobilization
[0032] 1.1 According to the above description of the probe design method and accompanying drawing 3, double-stranded oligonucleotide detection probe P n The linking group 1 on the biotin molecule, CP n The signal molecule 6 above is digoxin molecule. As shown in Table 1, the 20 detection probes have the same sequence except the binding site sequence of the DNA-binding protein according to different proteins to be detected. In addition, two pairs of complementary sequences were separately synthesized as negative (-) and Positive control (+).
[0033] serial number
P n
Embodiment 2
[0042] Example 2. Non-labeled detection of DNA-binding proteins based on DNA microarray chips (this method is applicable to the general operation of all DNA microarray chips)
[0043] 1. Synthesis of detection probes
[0044] The design and synthesis of all probes were the same as in Example 1. The difference is that the P n Linking group 1 in is labeled with an amino group, and the CP n The signal molecule 6 in is labeled with Cy3 fluorescent molecule.
[0045] 2. Microarray preparation
[0046] According to the probe prepared in step 1, as shown in Figure 4, the probe P n and its corresponding complementary probe CP n All were mixed and dissolved in double-distilled water at a concentration of 100 μM, incubated at 95°C for 5 minutes, and then naturally cooled to room temperature overnight to make P n and CP n Fully annealed to a double-stranded structure. Take the above refolding solution and dissolve it into an equal volume of 2×carbonate buffer (0.2M Na 2 CO 3 / 0...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com