Optoelectric composite substrate and electronic apparatus
A photoelectric composite and substrate technology, applied in circuits, lasers, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of VCSEL chip size increase, collapse, and inability to convert laser into parallel light or concentrating light.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
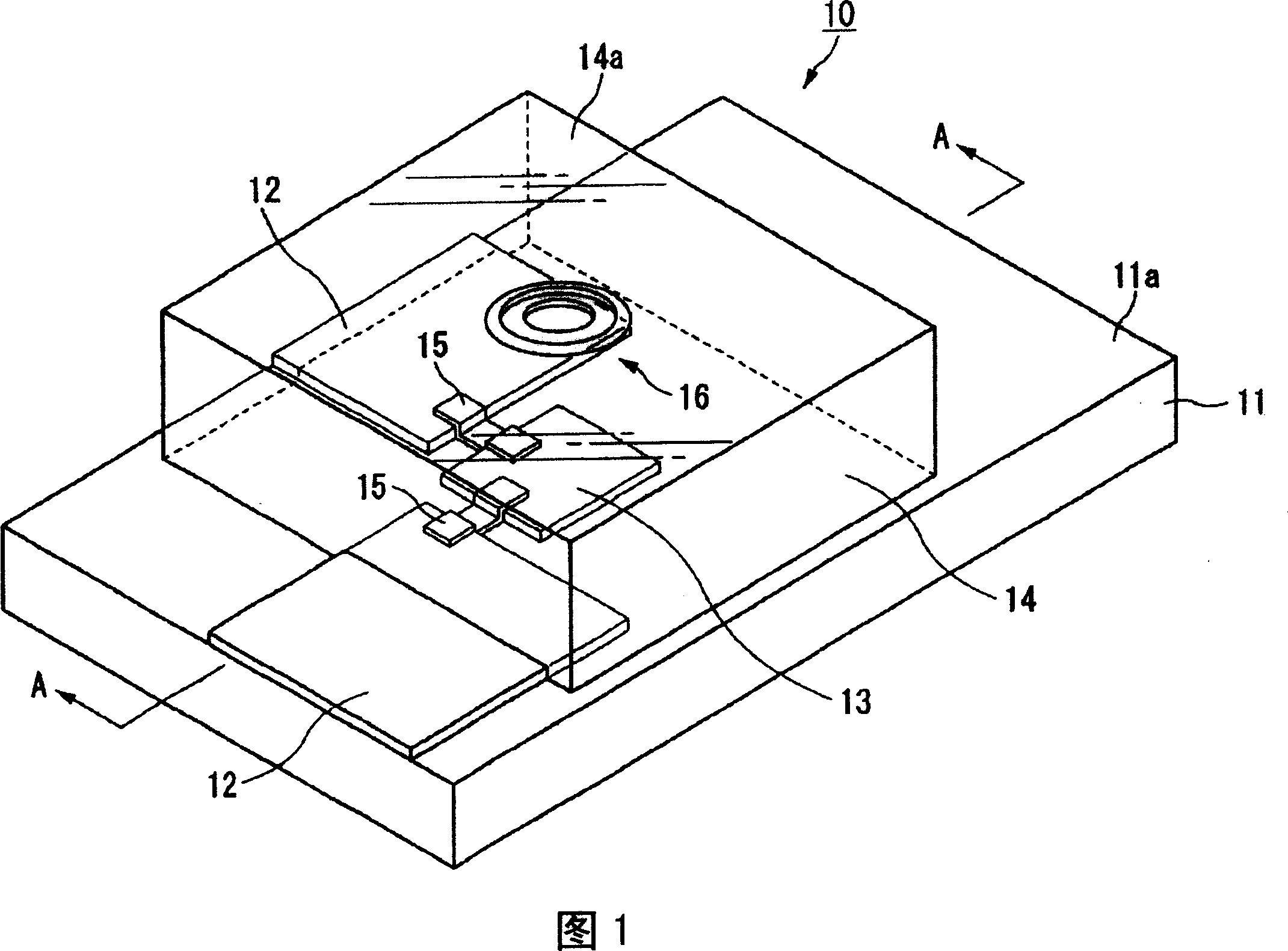
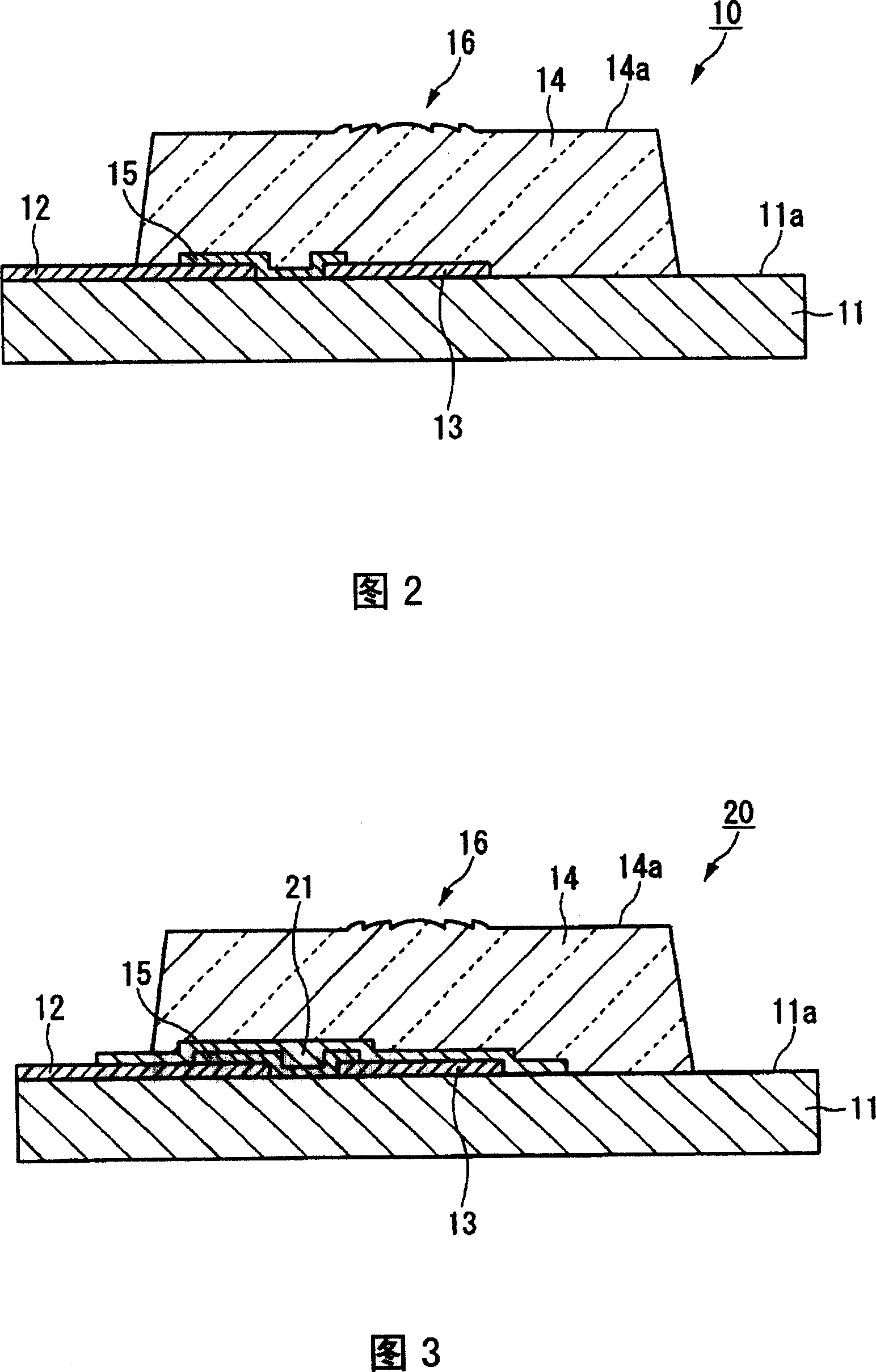
[0060] FIG. 1 is a perspective view showing main parts of an optoelectronic composite substrate 10 according to a first embodiment of the present invention, and FIG. 2 is a cross-sectional view taken along line A-A in FIG. 1 . As shown in FIGS. 1 and 2 , the photoelectric composite substrate 10 of this embodiment includes: a substrate 11 , a printed wiring 12 formed on the surface 11 a side of the substrate 11 , a thin optical element 13 mounted on the surface 11 a side of the substrate 11 , and The lens mold 14 is formed on the surface 11 a side of the substrate 11 so as to cover the thin optical element 13 . In addition, in this embodiment, a case where the photoelectric composite substrate 10 is a printed wiring board with little flexibility is described as an example, but a flexible FPC (flexible printed wiring board) may also be used.
[0061] For the substrate 11 , for example, a substrate made of at least phenolic resin or glass epoxy resin, a semiconductor substrate su...
no. 2 approach
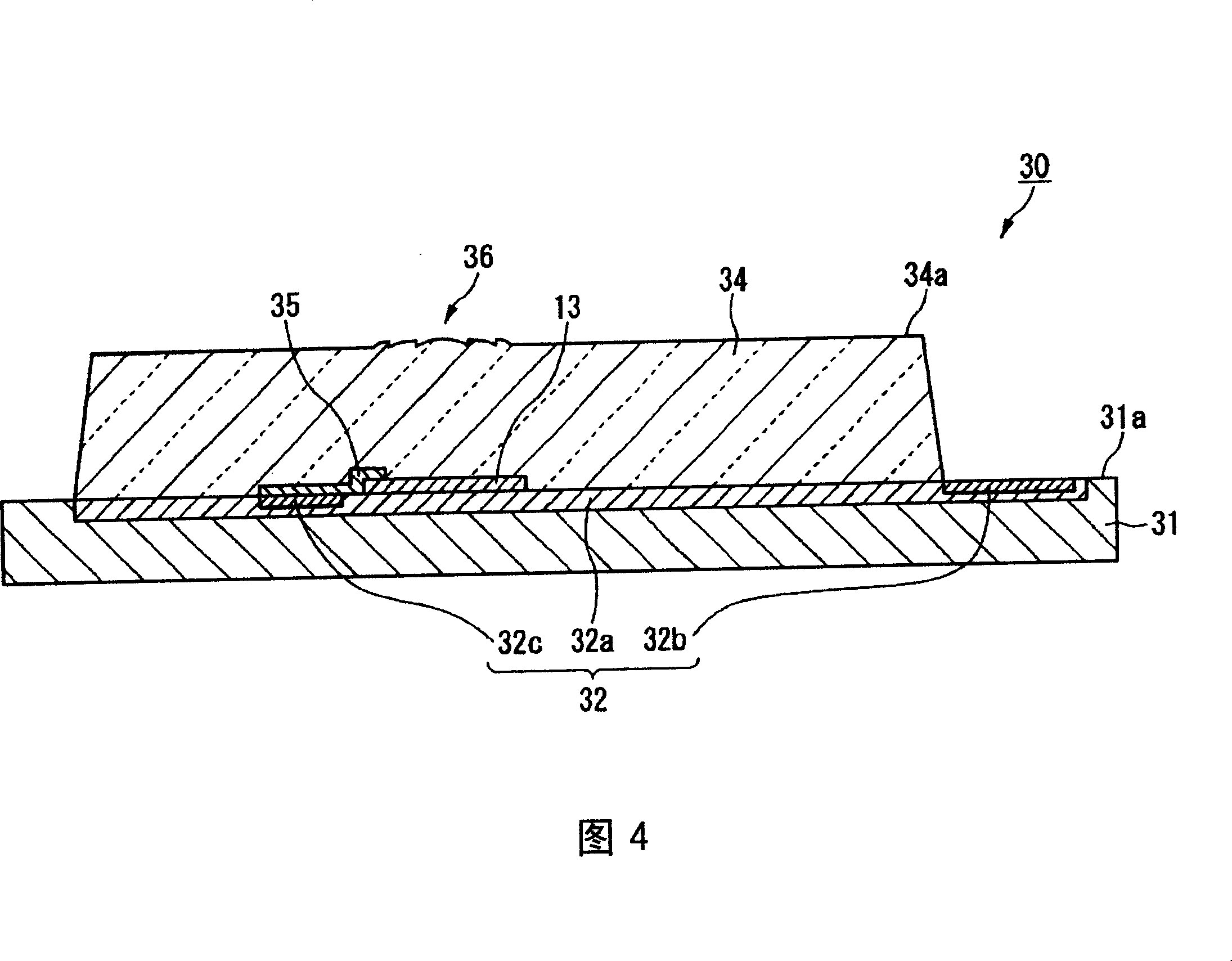
[0083] 4 is a cross-sectional view showing the main part of the photoelectric composite substrate 10 according to the second embodiment of the present invention, and the components corresponding to the configuration of the photoelectric composite substrate 10 according to the first embodiment described with reference to FIGS. 1 and 2 are indicated. same mark. As shown in FIG. 4 , the optoelectronic composite substrate 30 of this embodiment includes: a substrate 31 , a thin optical element 13 mounted on the surface 31 a side of the substrate 31 , and an The lens mold 34. In addition, in the example shown in FIG. 4, wiring equivalent to the printed wiring 12 included in the photoelectric composite substrate 10 shown in FIGS. side.
[0084] The substrate 31 is, for example, a semiconductor substrate such as a silicon substrate, and the circuit 32 related to the thin optical element 13 is formed on the side of the surface 31 a. The circuit 32 is constituted by at least a circui...
no. 3 approach
[0091] 5 is a cross-sectional view showing main parts of an optoelectronic composite substrate 30 according to a third embodiment of the present invention, and the same symbols are attached to components corresponding to those included in the optoelectronic composite substrate 30 according to the second embodiment described with reference to FIG. 4 . The photoelectric composite substrate 40 of the third embodiment shown in FIG. 5 is different from the photoelectric composite substrate 30 of the second embodiment shown in FIG. , corresponding to each of the thin optical elements 13, 43, lens elements 36a, 36b are formed on the surface 34a of the lens mold 34, respectively. In addition, in this embodiment, it is assumed that the thin optical element 13 is a light emitting element such as a VCSEL, and the thin optical element 43 is a light receiving element such as a PD.
[0092] In the circuit 32 formed on the surface 31a side of the substrate 31, in addition to the circuit part...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com