Pig fat deposition related protein and encoding genes and use thereof
A technology of fat deposition and pig fat, applied in the fields of application, genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement, etc., can solve the problems of delaying the progress of breeding, cloning without reaching the position, and limited number of detected genes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
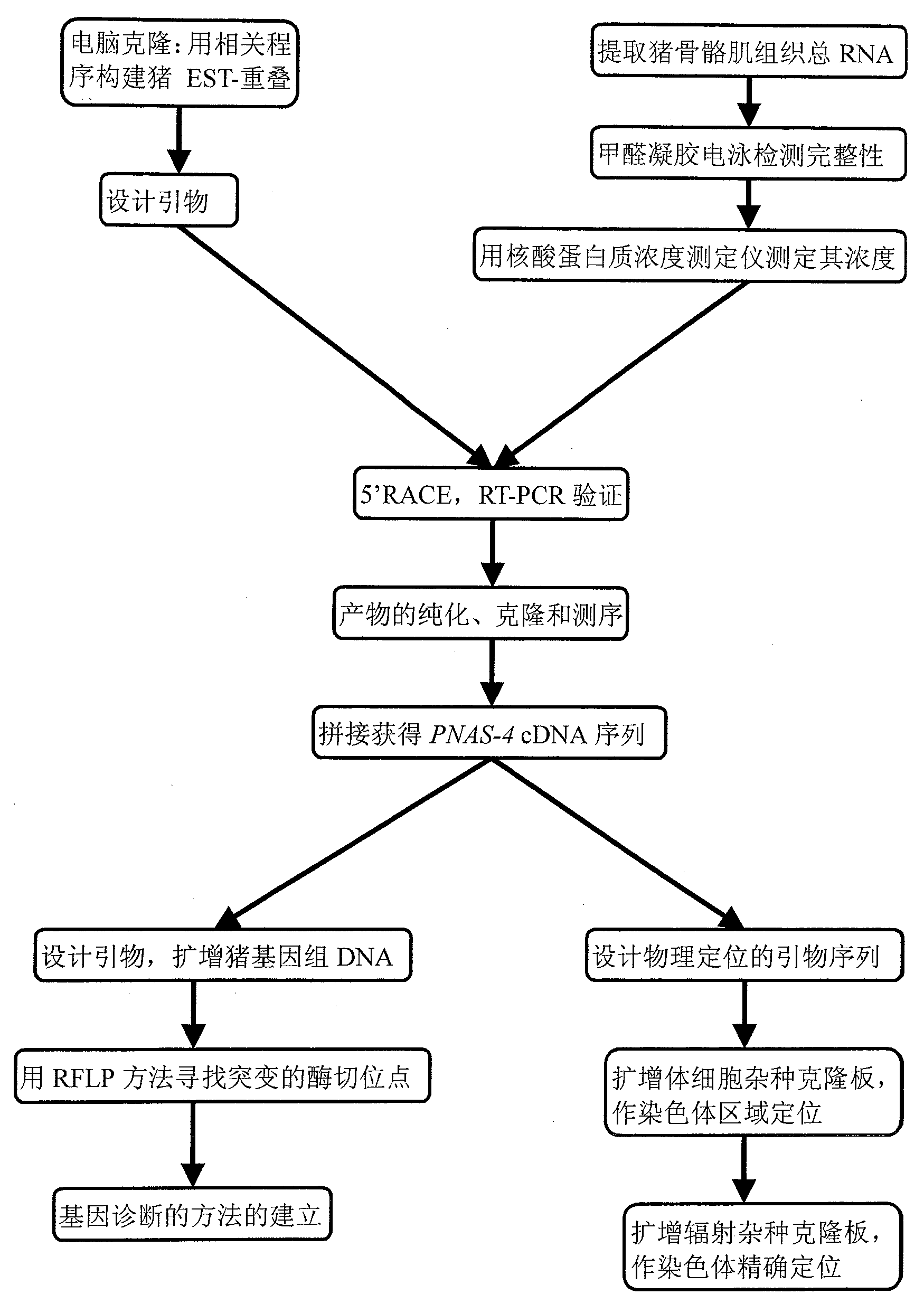
[0052] Embodiment 1, the acquisition of pig fat deposition-related protein (CGI-146) and its full-length cDNA gene and genomic gene (pig PNAS-4 gene)
[0053] 1. Acquisition of full-length cDNA gene of porcine fat deposition-related protein
[0054] Total RNA was extracted from the skeletal muscle of the 55-day-old large white pig embryo. After mRNA purification, cDNA synthesis, proteinase K and SfiI digestion, and cDNA fractionation, the obtained cDNA was combined with pBluescript II SK + Vector ligation, thereby constructing pig fetal skeletal muscle cDNA library (Zhu Zhengmao, doctoral dissertation, Huazhong Agricultural University, 2003). Clones were randomly selected for commercial sequencing, and the results obtained by the sequencing were non-redundant by the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI, National Center for Biotechnology Information, http: / / www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov / BLAST / ) Retrieval database (nr) and obtain the corresponding sequence biological info...
Embodiment 2
[0068] Embodiment 2, pig PNAS-4 gene physical localization:
[0069] 1. Acquisition of experimental materials for physical positioning
[0070] The pig×rodent somatic cell hybrid panel (SCHP) was used for chromosome region mapping, and the pig radiation hybrid panel (INRA-Minnesota porcine radiation hybrid panel, IMpRH) co-constructed by the University of Minnesota, USA was used for chromosome accuracy. For positioning, see references for the preparation methods of two sets of somatic cell hybrid panels (Yerle et al., A somatic cell hybrid panel for pig regional gene mapping characterized by molecular cytogenetics. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1996, 73: 194-202; Yerle et al., Construction of a whole -genome radiation hybrid panel for high-resolution gene mapping in pigs. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1998, 82: 182-188).
[0071] Among them, SCHP includes 27 somatic hybrid cell lines, Nos. 1-19 are pig×hamster somatic hybrid cell lines, No. 20-27 are pig×mouse somatic hybrid cell lines, and ...
Embodiment 3
[0077] The single nucleotide polymorphism and RFLP polymorphism detection of the partial DNA sequence of embodiment 3, pig PNAS-4
[0078] 1. Detection of single nucleotide polymorphisms in the partial DNA sequence of pig PNAS-4
[0079] 1) Distribution of single nucleotide polymorphisms of pig PNAS-4 gene
[0080] In order to reflect the single nucleotide polymorphism of the porcine PNAS-4 gene more preparedly, two mutation sites with a distance of 20kb were selected for detection in this experiment.
[0081] The DNA samples used for polymorphism detection came from 7 pig herds, see Table 2. Genomic DNA was extracted by conventional methods and stored at -20°C for future use.
[0082] Table 2. Number of populations and samples detected by SNPs
[0083] Variety combination
[0084] Note: LD=Landrace, LW=Larege White, T=Tongcheng
[0085] Using the genome of the material described in Table 2 as a template, the following primers were used to ampl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com