Induction of peony embryoid
An embryoid and peony technology, which is applied in horticultural methods, botanical equipment and methods, plant cells, etc., can solve the problem that the embryoid seedlings are not strong enough for domestication, obtain embryoid and embryoid seedlings, and have no problems. Complete problems such as organ differentiation, and achieve the effects of improving breeding methods, shortening breeding cycles, and increasing proliferation coefficients
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] The acquisition of embodiment 1 explant
[0033] Peony carpels collected from robust plants were taken back to the laboratory, rinsed with running water for 24 hours, thoroughly scrubbed and cleaned, stripped of ovules, and disinfected on an ultra-clean bench. The ovules were first treated with 70% ethanol for 3 minutes, washed with sterilized distilled water for 3 times, then treated with 0.2% NaClO for 15 minutes, washed with sterilized distilled water for 3 times, peeled off the seed coat, broke open the endosperm, and picked out the seed embryo with a dissecting needle for inoculation .
Embodiment 2
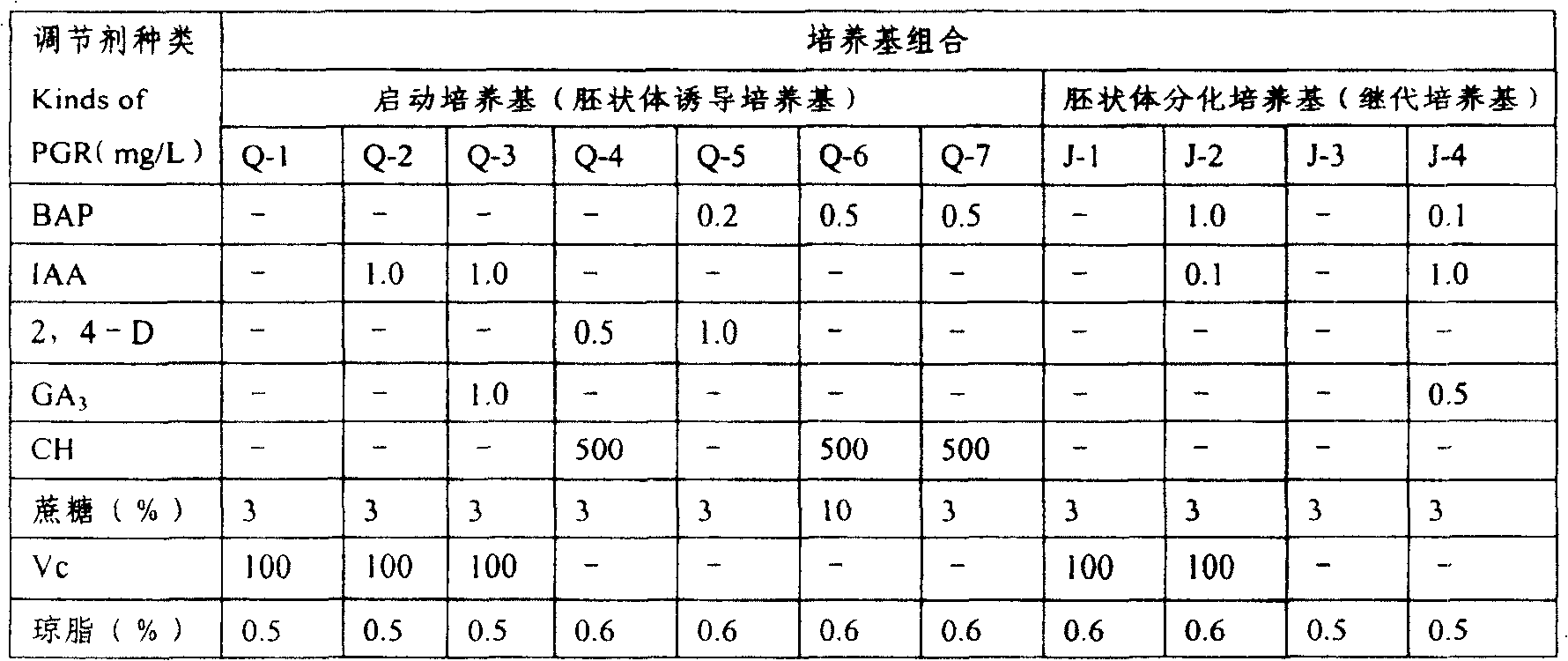
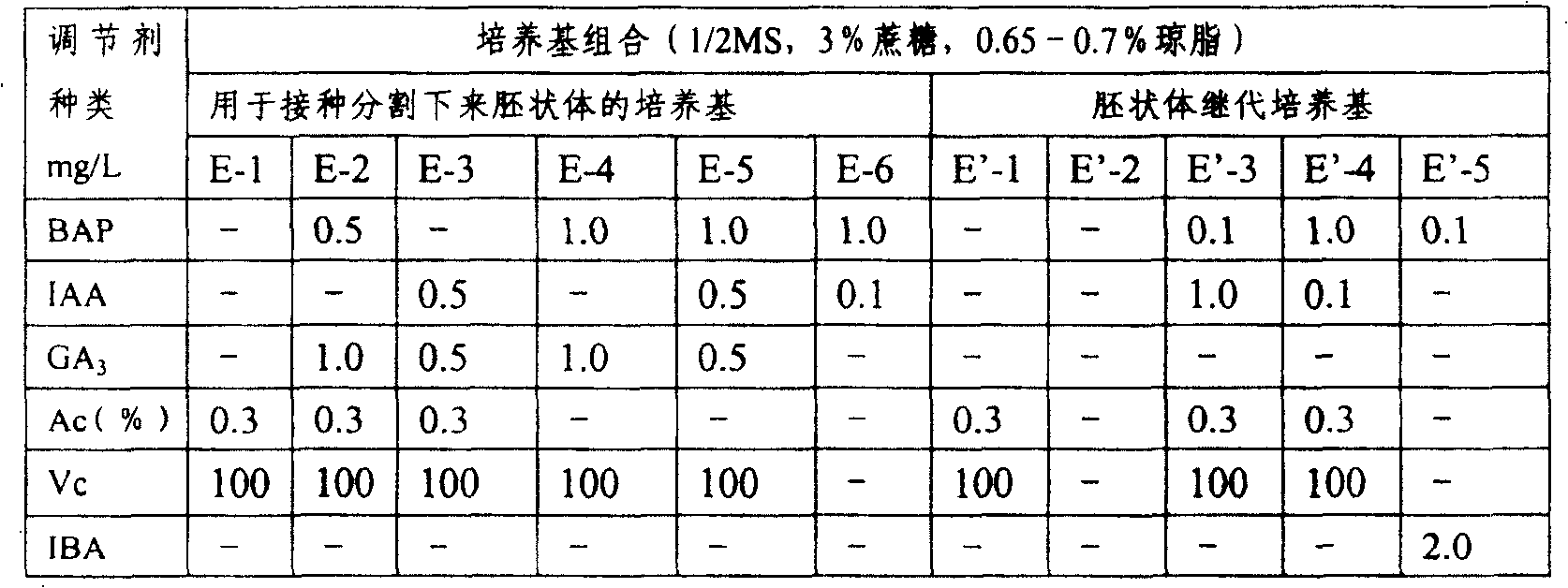
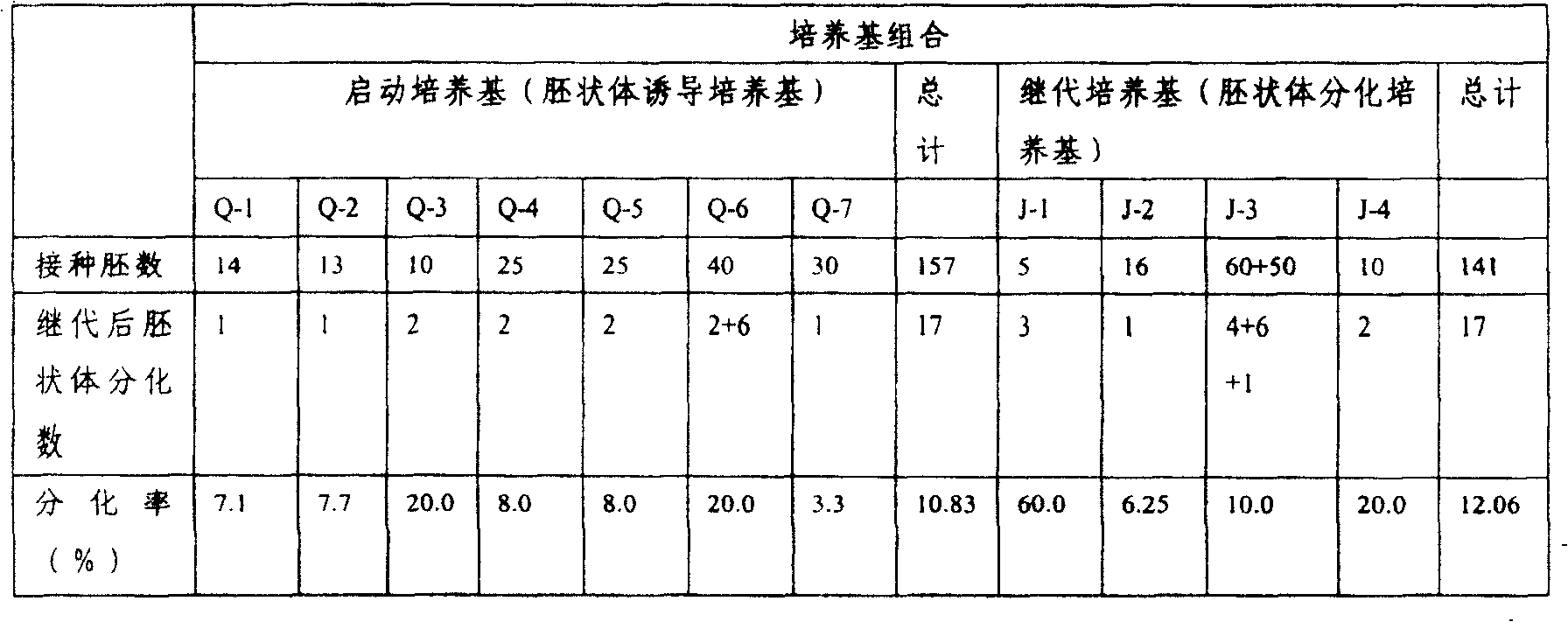
[0035] (1) After the isolated embryos were cultured on the starting medium Q-1 for 30 days, the rooted seedlings were subcultured (I) to J-2, and cultured for 35 days. After the embryoid body completed organ differentiation, it had two obvious cotyledons time division;
[0036] (2) Inoculate the divided embryoid bodies onto E-2, and after culturing for 30 days, subculture again (1) onto E-2;
[0037] (3) After 35 days, the embryoid body seedlings were subcultured (II) onto E'-1;
[0038] (4) Put the E'-1 seedlings in the refrigerator for 60 days at 4°C;
[0039] (5) Take it back to the cultivation room for cultivation;
[0040] (6) One month later, a few embryoid seedlings germinated, took root and became seedlings.
[0041] (7) Pick out the embryoid body seedlings with good roots and leaves and start seedling hardening.
[0042] Culture conditions: culture temperature 25±1°C, light 16h / d, light intensity 1600Lx.
Embodiment 3
[0044] (1) After the isolated embryos were cultured on the starting medium Q-2 for 40 days, the rooted seedlings were subcultured (I) to J-1, and cultured for 35 days. After the embryoid body completed organ differentiation, it had two obvious cotyledons time division;
[0045] (2) Inoculate the divided embryoid body onto E-2, and after culturing for 35 days, subculture again (1) onto E-2;
[0046] (3) After 35 days, the embryoid body seedlings were subcultured (II) onto E'-1;
[0047] (4) Put the E'-1 seedlings in the refrigerator for 90 days at 4°C;
[0048] (5) Take it back to the cultivation room for cultivation;
[0049] (6) One month later, a few embryoid seedlings germinated, took root and became seedlings.
[0050] (7) Pick out the embryoid body seedlings with good roots and leaves and start seedling hardening.
[0051] Culture conditions: culture temperature 25±1℃, light 20h / d, light intensity 2000Lx.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| induction rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com