Semiconductor device having an improved connection arrangement between a semiconductor pellet and base substrate electrodes and a method of manufacture thereof
a technology of semiconductor pellet and base substrate electrode, which is applied in the direction of semiconductor devices, semiconductor/solid-state device details, coatings, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the size of the semiconductor device as a whole, reducing the operating speed reducing the efficiency of the semiconductor device, so as to achieve the effect of increasing the connection strength between the bonding wire and the second electrode pad, increasing the young's modulus, and effective transmission of bonding force and ultrasonic vibration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
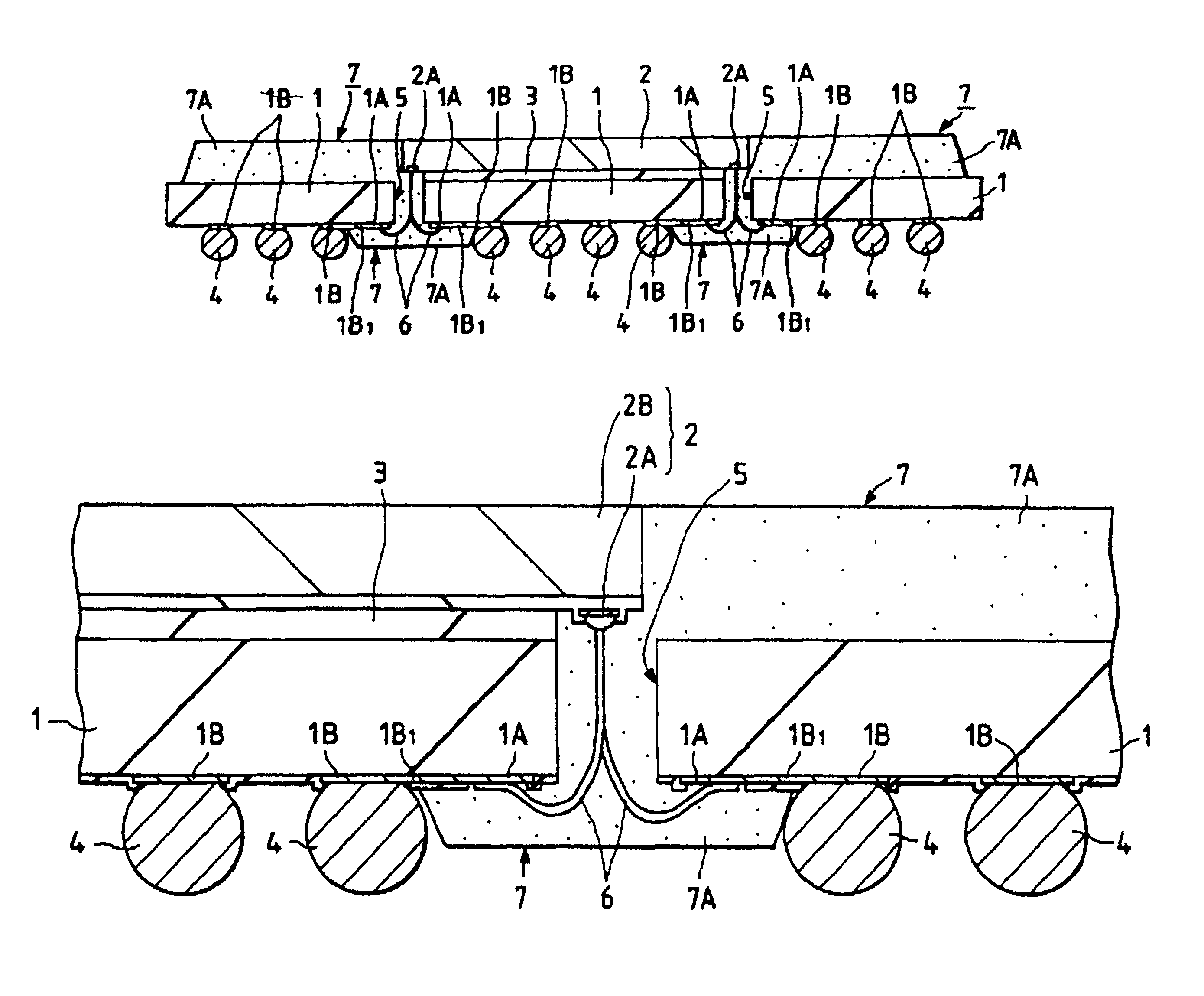
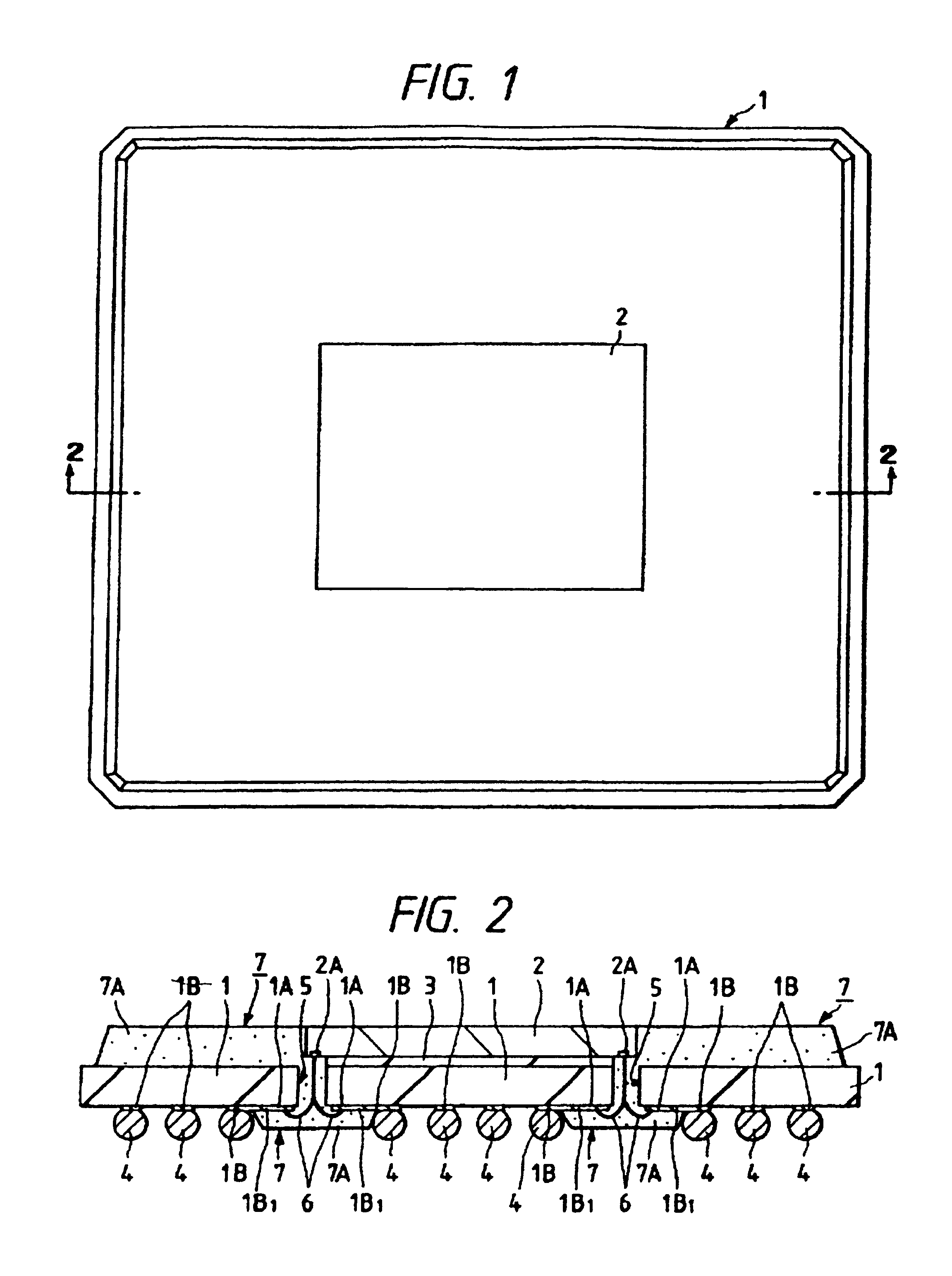
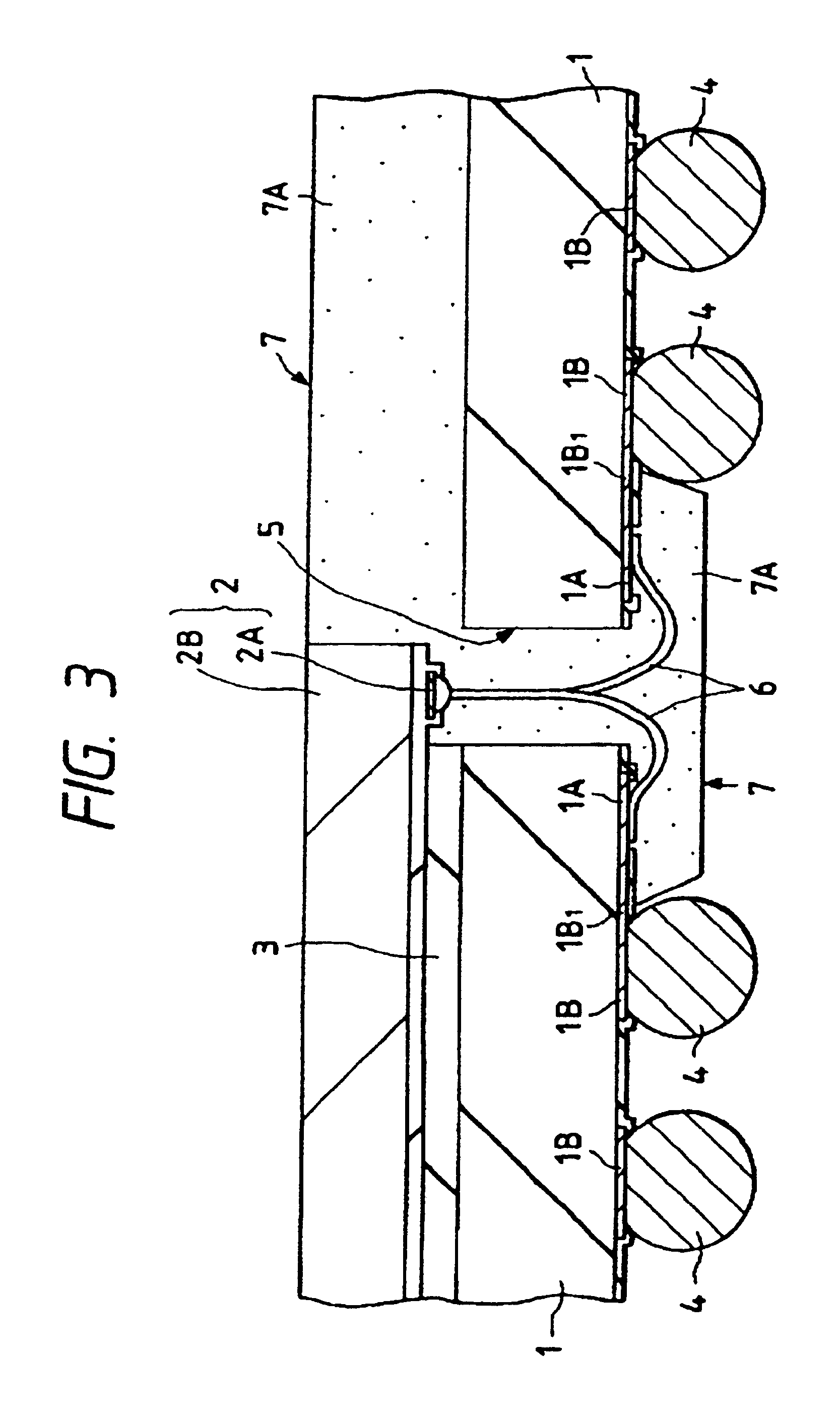
[0053]The outline construction of a semiconductor device, as a first embodiment of this invention, that uses the BGA structure is shown in FIG. 1 (plan view of the main surface side), FIG. 2 (cross section taken along the line A—A of FIG. 1), FIG. 3 (enlarged cross section of an essential part of FIG. 2) and FIG. 4 (enlarged plan view showing the back side of an essential part of the semiconductor device with the resin sealing body removed).
[0054]As shown in FIGS. 1, 2, 3 and 4, the semiconductor device has a semiconductor pellet 2 mounted on a pellet mounting area of the main surface of a base substrate 1, with a plurality of bump electrodes 4 arranged in grid on the back of the base substrate 1 opposite the main surface.
[0055]The base substrate 1 may be formed of a printed circuit board. The printed circuit board may, for example, have a structure in which wiring is formed over the surface of a rigid substrate of glass fiber impregnated with epoxy resin, polyimide resin or maleimi...
embodiment 2
[0105]The outline configuration of a semiconductor device as the second embodiment of this invention that employs a BGA structure is shown in FIG. 12 (cross section) and FIG. 13 (enlarged plan view of an essential part of the back side showing the state of the back side removed of the resin sealing body).
[0106]As shown in FIG. 12 and 13, the semiconductor device has the semiconductor pellet 2 mounted facedown on the pellet mounting area of the main surface of the base substrate 1 with an insulating layer 3 in between. A plurality of bump electrodes 4 are arranged in grid on the back of the base substrate 1.
[0107]Arranged in the central area of the main surface of the semiconductor pellet 2 along the longer sides thereof is a row of bonding pads 2A, which are electrically connected to the second electrode pads 1A arranged on the back of the base substrate 1 through the bonding wires 6 passing through the slits 5 formed in the base substrate 1. The second electrode pads 1A are electri...
embodiment 3
[0110]The outline configuration of a semiconductor device as the third embodiment of this invention that employs a BGA structure is shown in FIG. 14 (plan view of an essential part of the back side showing the state of the back side removed of the resin sealing body).
[0111]As shown in FIG. 14, the semiconductor device has a semiconductor pellet 2 mounted facedown on a pellet mounting area of the main surface of the base substrate 1, with an insulating layer 3 in between. Bump electrodes 4 are arranged in grid on the back of the base substrate 1.
[0112]At the outer periphery of the main surface of the semiconductor pellet 2, a plurality of bonding pads 2A are arranged along the sides of the pellet. At the central portion of the main surface of the semiconductor pellet 2, a plurality of bonding pads 2A are arranged along the longer or shorter side of the pellet. The bonding pads 2A are electrically connected to the second electrode pads 1A arranged on the back of the base substrate 1 b...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com