Disruptors of early/recycling endosomes
a technology of endosomes and disruptors, which is applied in the direction of peptides/protein ingredients, drug compositions, peptides, etc., can solve the problems of difficult compound delivery, many exogenous molecules and many exogenous molecules that are introduced into cells using rme cannot escape degradation in the late endosome or the lysosom
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
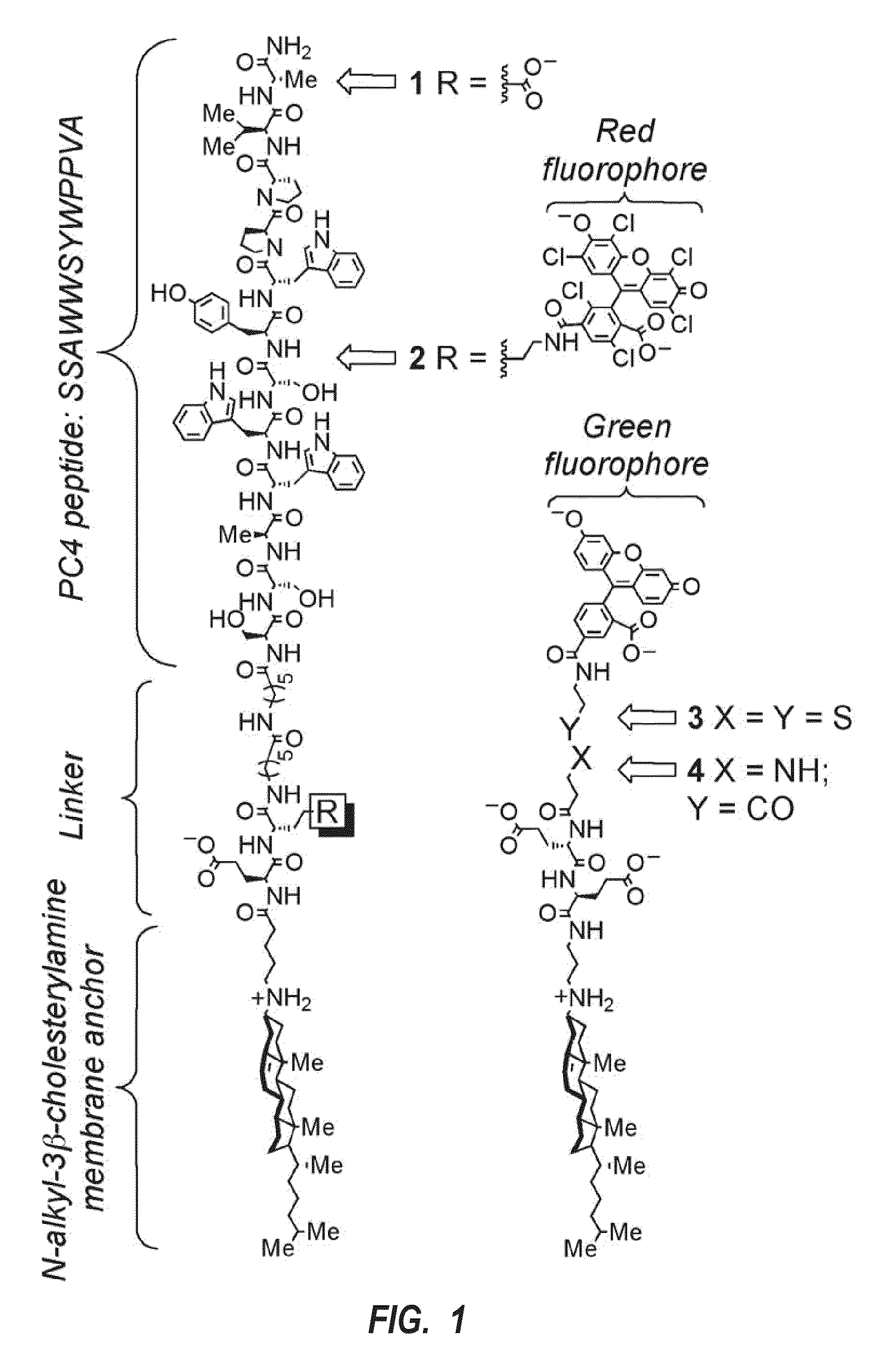
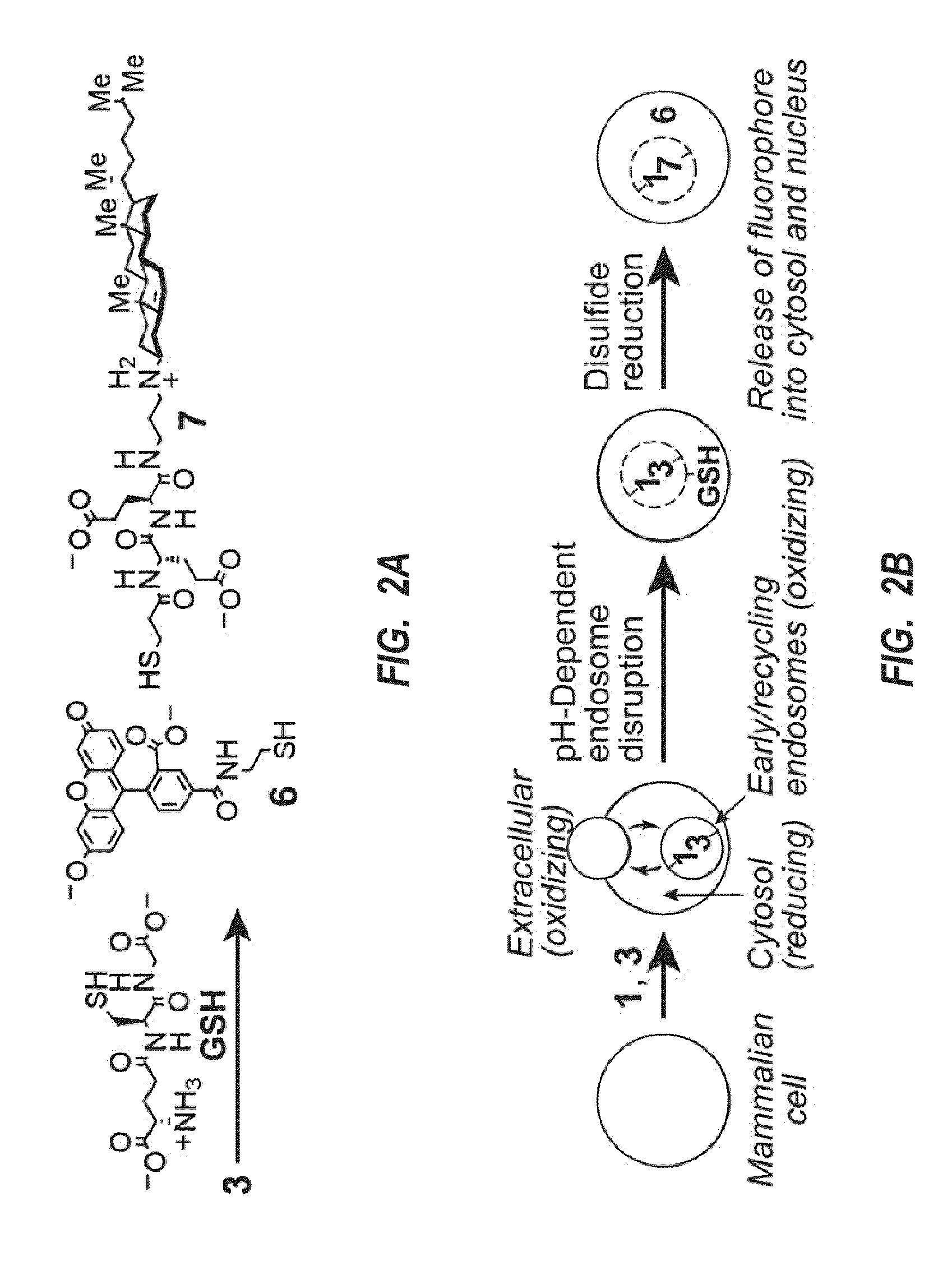
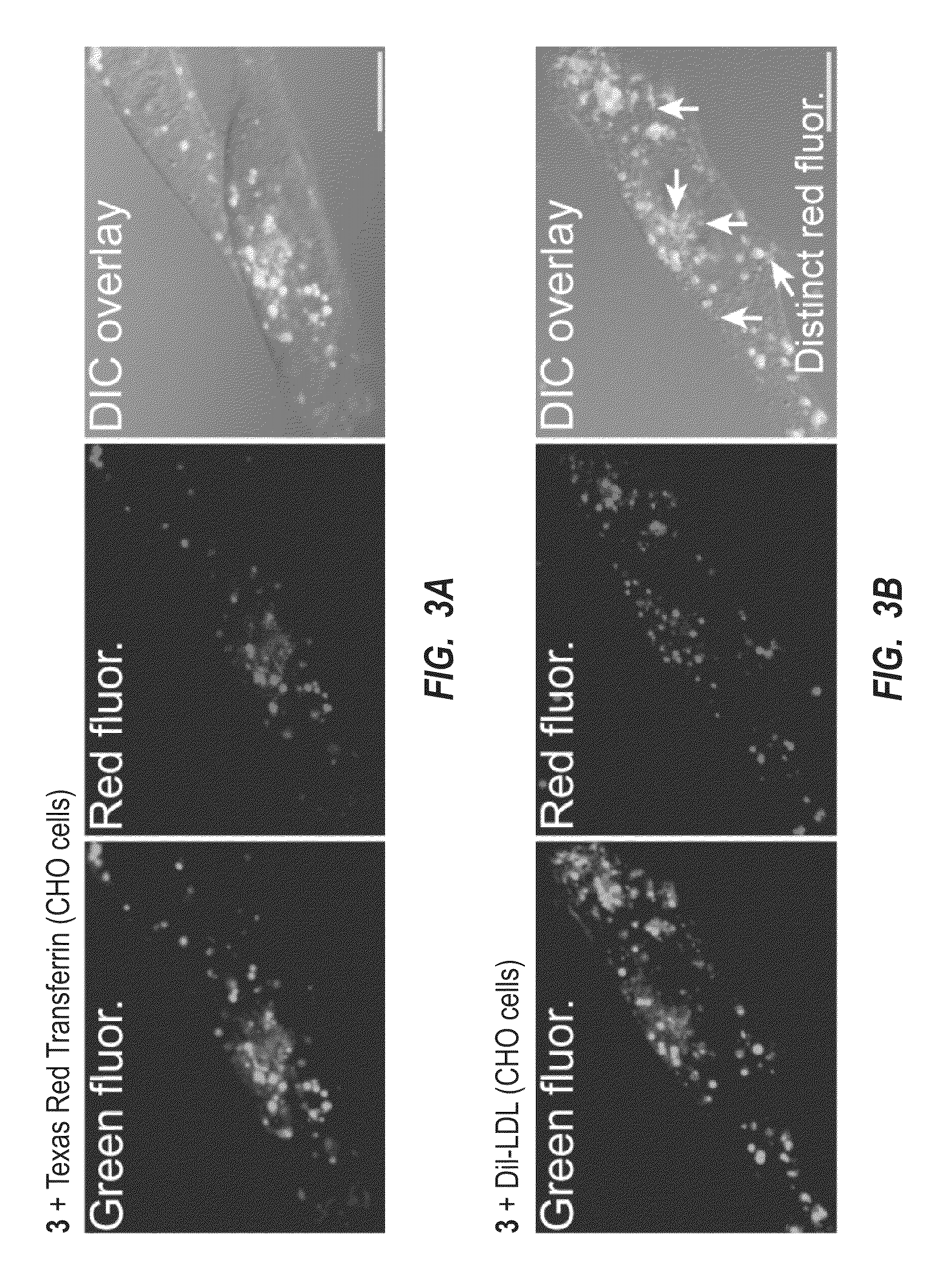
[0029]The present invention is related to delivery platforms and systems, and methods for using the platforms and systems for delivering an exogenous cargo molecule (i.e., agent) to a target cell via a synthetic ligand that may be capable of employing receptor-mediated endocytosis. The delivery platforms and systems can include: a receptor-targeting or membrane-binding ligand; a selectively cleavable anionic linker, an agent to be delivered into a cell, and an endosomal disruption member. These components can be combined and linked in various embodiments as described herein ranging from a dual component system or a single substance that has all of these components.
[0030]The delivery platforms and systems can be used to deliver various agents selected from a protein, peptide, polypeptide, nucleic acid (RNA, DNA, RNA / DNA hybrid, or a mimic thereof such as PNA, morpholinos, and related oligomers), siRNA, carbohydrates, lipids, marker, luminophore, tracer substance, molecular probe, oli...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com