Electrophotographic photosensitive member
a photosensitive member and electrophotography technology, applied in the field of electrophotography photosensitive members, can solve the problems of difficult absorption of surface layers, difficult to achieve image deletion phenomena, and difficult to achieve phenomenon such as the above-described image deletion phenomenon, and achieve good electrophotographic properties. , the effect of minimizing light absorption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
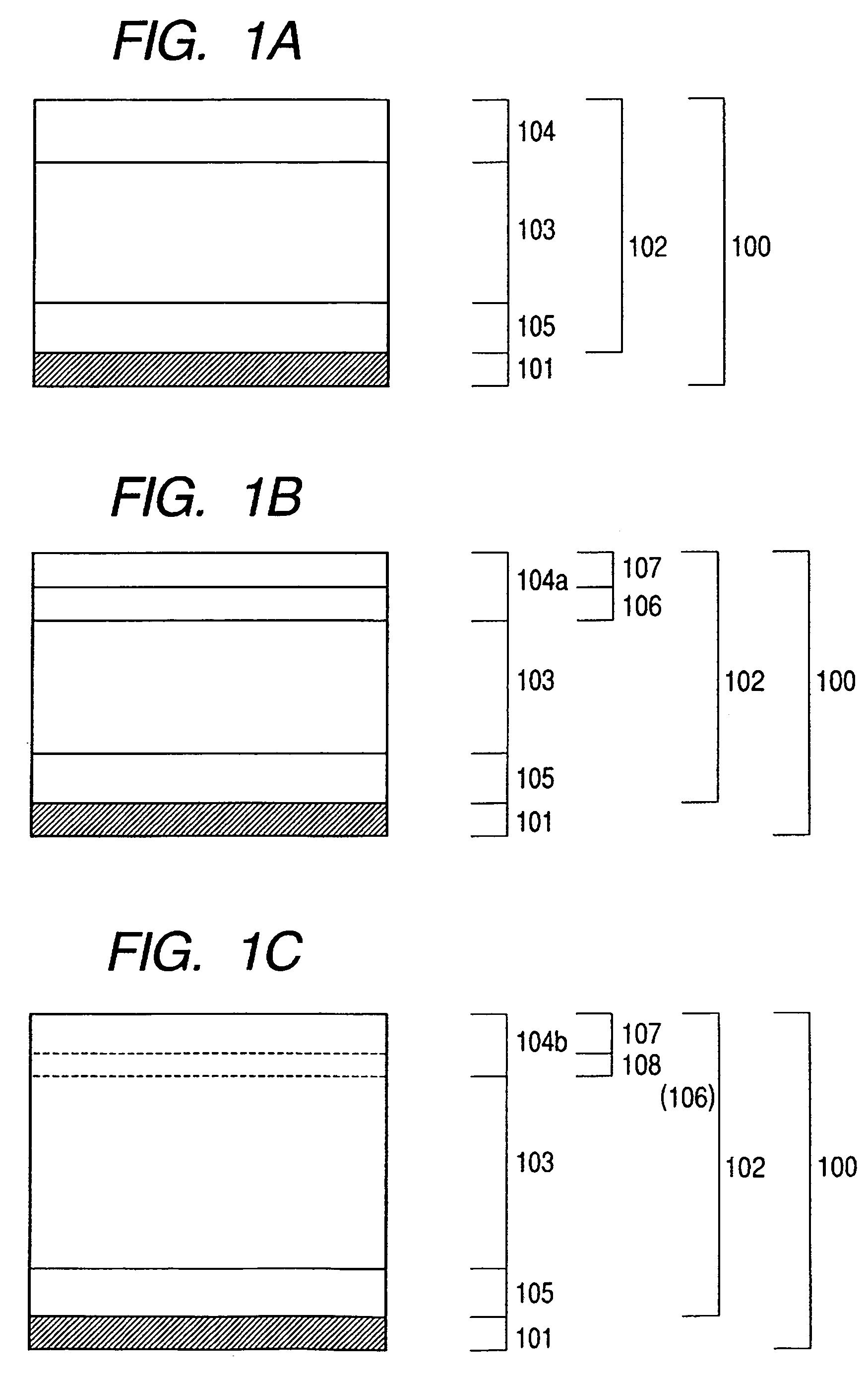
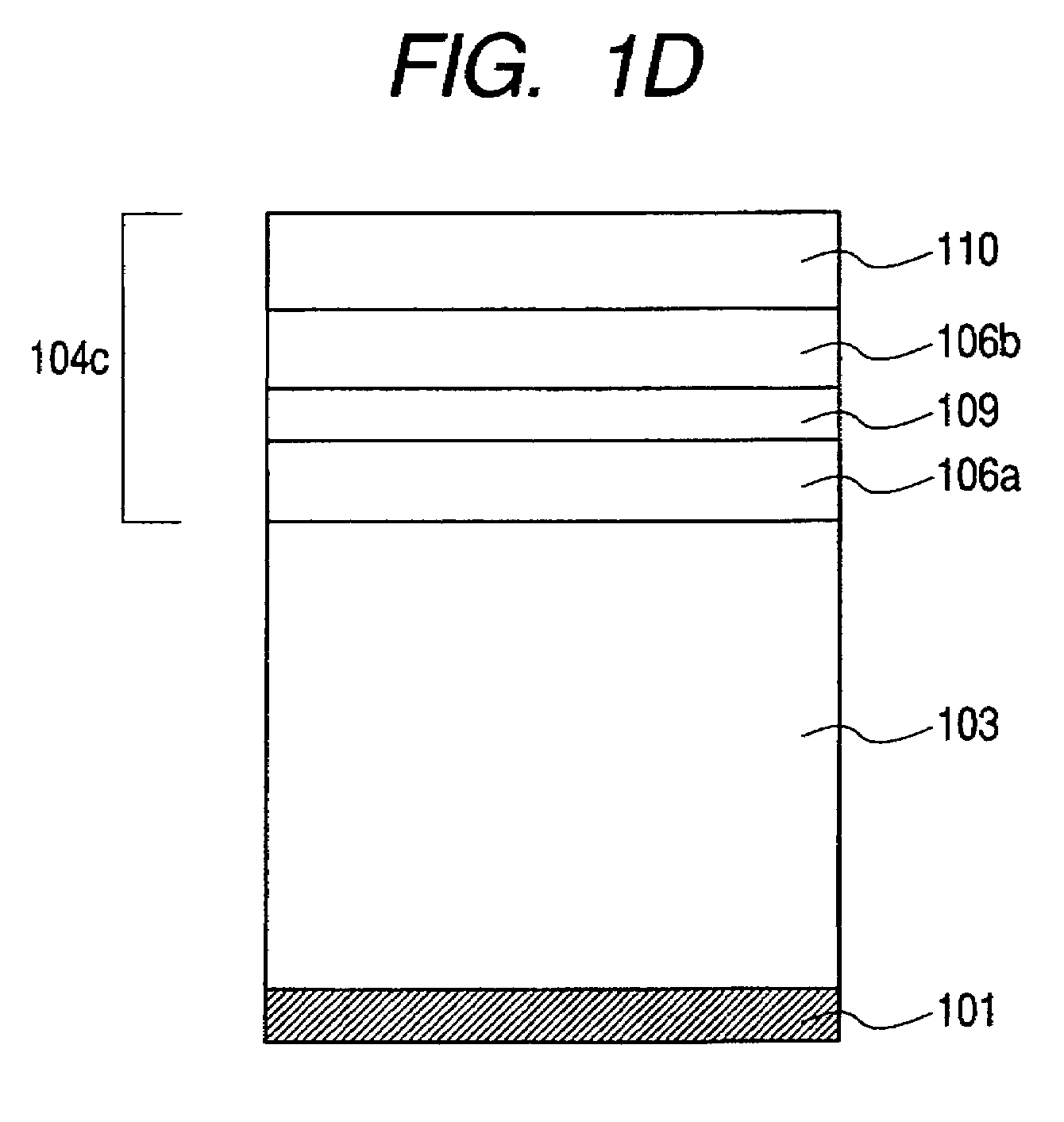
[0282]A plasma CVD apparatus shown in FIG. 2 was used to sequentially superimpose deposition films under the conditions shown in Table 1 on an aluminum cylinder (support), which had a diameter of 84 mm and a length of 381 mm and was subjected to mirror finish, to thereby produce a photosensitive member composed of a top injection-blocking layer and a surface layer. All lower injection-blocking layers and photoconductive layers were produced under the conditions shown in Table 1 as common conditions. Surface layers were produced under the conditions shown in Table 2 for the flow rate of an SiH4 gas, the mixing ratio between SiH4 and N2 and electric energy per amount of an SiH4 gas, and under the conditions shown in Table 1 for the others. Thus, photosensitive members A to H different from each other in nitrogen atom concentration in a surface layer were produced.
[0283]The photosensitive members A to H thus produced were evaluated as follows.
[0284]Each photosensitive member was set in...
example 2
[0296]A plasma CVD apparatus shown in FIG. 2 was used to sequentially superimpose deposition films composed of a lower injection-blocking layer, a photoconductive layer, a top injection-blocking layer, and a surface layer under the conditions shown in Table 3 on an aluminum cylinder (support), which had a diameter of 84 mm and a length of 381 mm and was subjected to mirror finish, to thereby produce a photosensitive member. All lower injection-blocking layers and photoconductive layers were produced under the conditions shown in Table 1 as common conditions. Surface layers were produced with the flow rate of a CH4 gas changed variously as shown in Table 4. Thus, photosensitive members 2A to 2H different from each other in carbon atom concentration in a surface layer were produced.
[0297]Each of the photosensitive members 2A to 2H thus produced was evaluated for the following items in addition to (1) a nitrogen atom concentration and (3) the property of transmitting light having a wav...
example 3
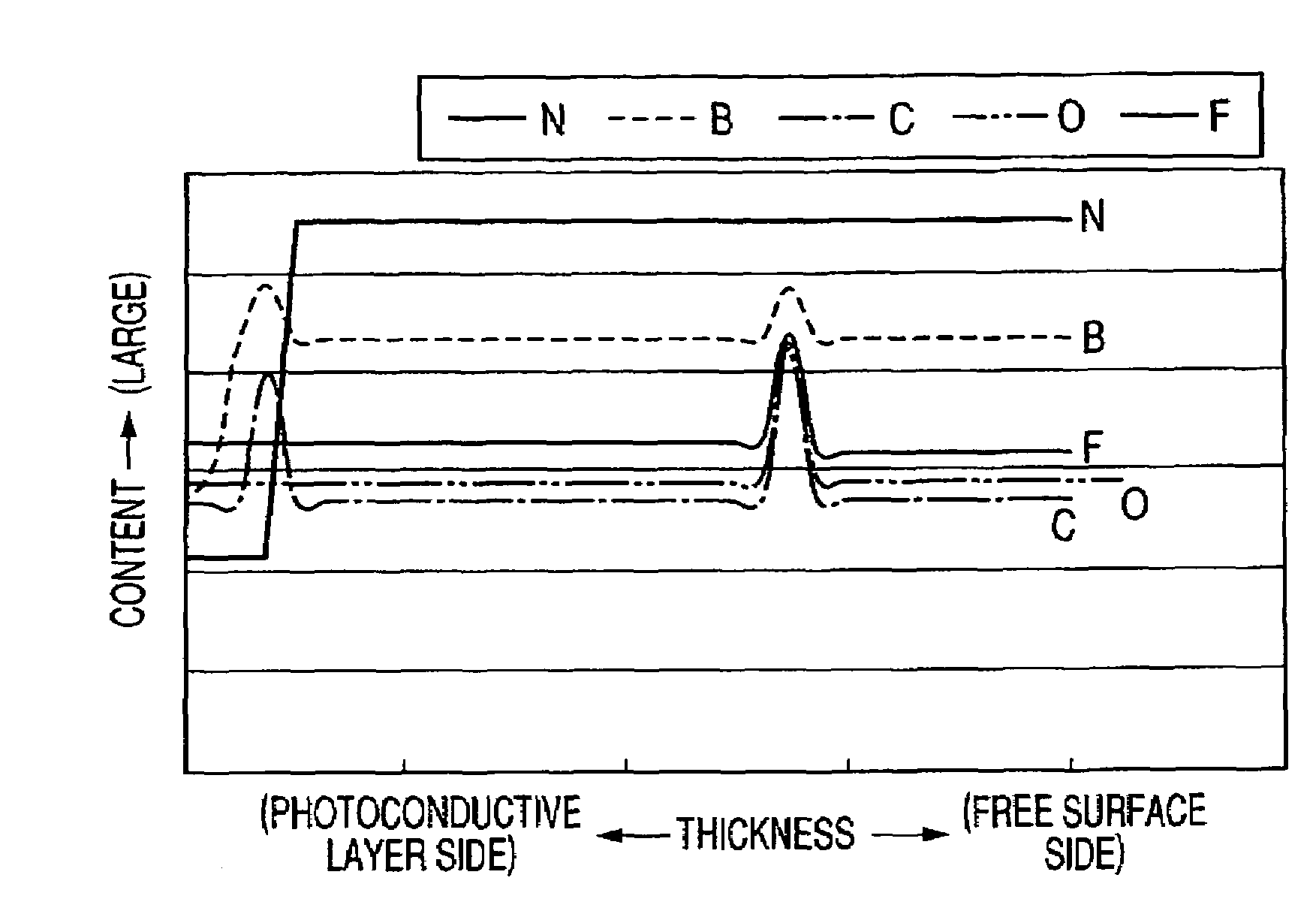
[0305]A plasma CVD apparatus shown in FIG. 2 was used to sequentially superimpose deposition films composed of a lower injection-blocking layer, a photoconductive layer, and a surface region layer under the conditions shown in Table 5 on an aluminum cylinder (support), which had a diameter of 84 mm and a length of 381 mm and was subjected to mirror finish, to thereby produce a photosensitive member.
[0306]In this case, each of a carbon atom concentration and a boron atom concentration (boron is a Group 13 element in the periodic table) was caused to have a local maximum value by changing the amount of each of a CH4 gas and a B2H6 gas to be introduced during the formation of a surface region layer. A method of introducing a gas for forming a local maximum value in a surface region layer shown in Table 3 involved: increasing the amount of each of the CH4 gas and the B2H6 gas from a certain value in a linear fashion over a predetermined time period as shown in Table 5 when forming the c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com