Methods and compositions for the identification, characterization and inhibition of farnesyltransferase
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example ii
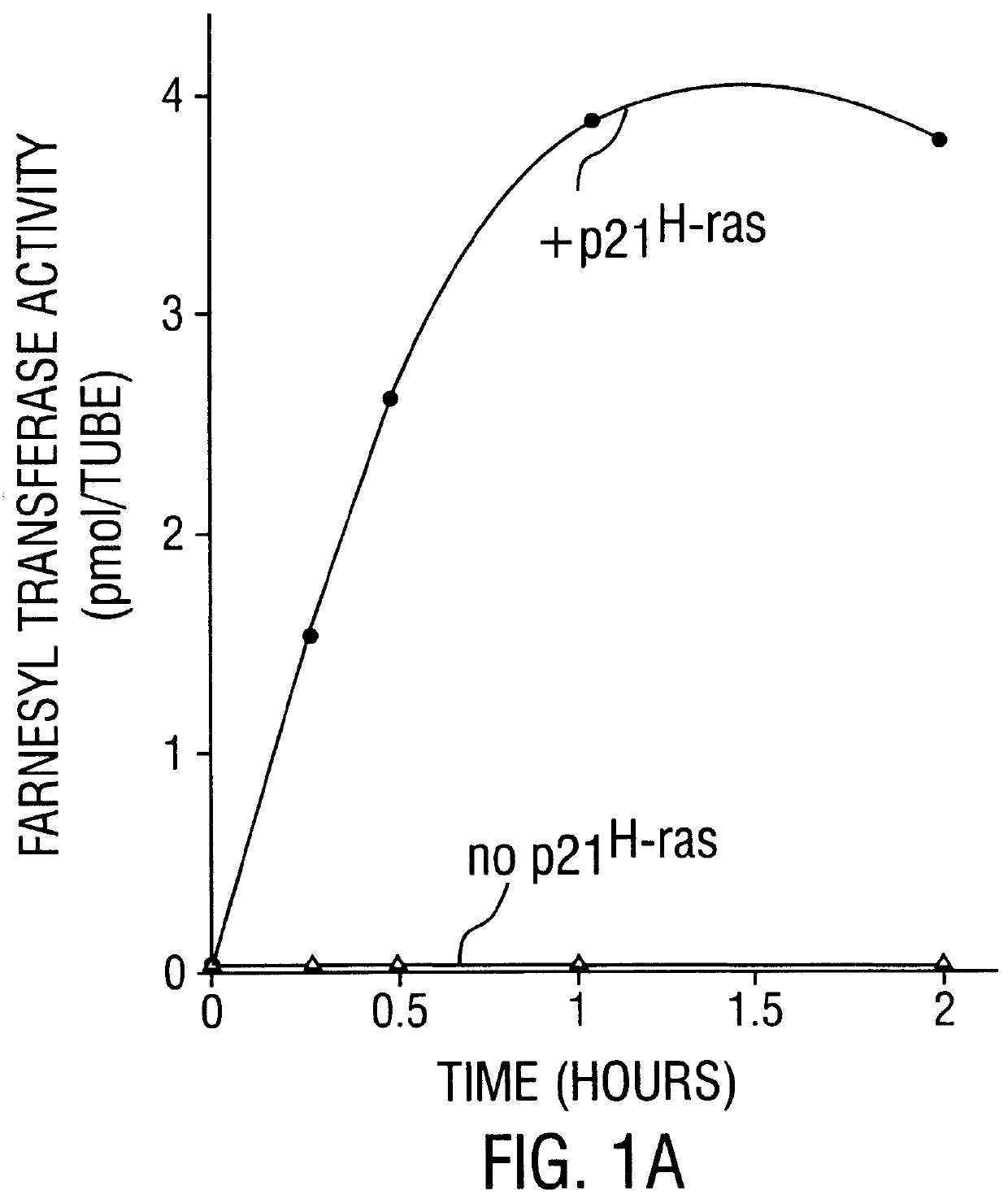
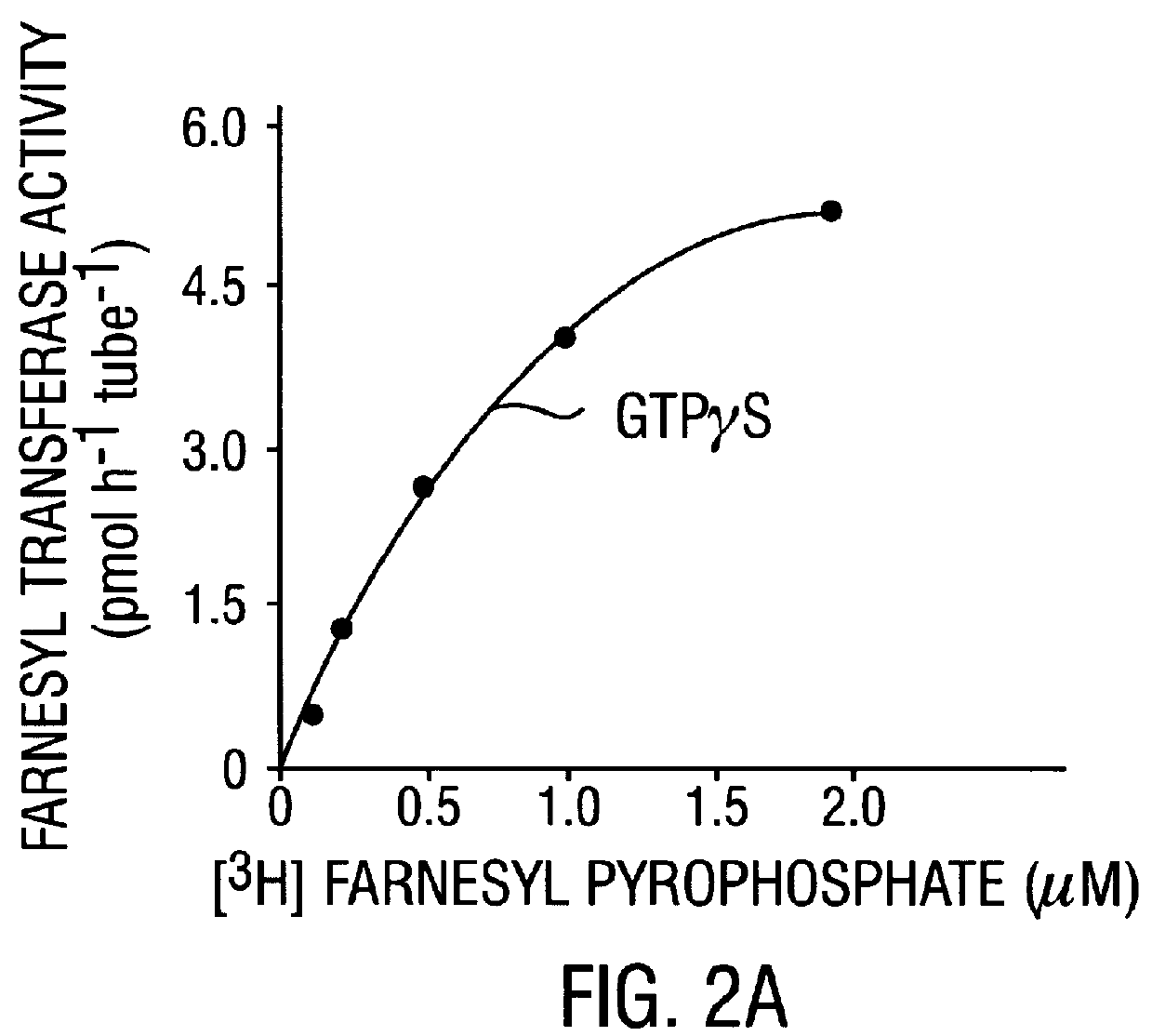
Further Characterization of Farnesyltransferase
In the present Example, a series of tetrapeptides were tested for their ability to bind to the rat brain p21.sup.H-ras farnesyltransferase as estimated by their ability to compete with p21.sup.H-ras in a farnesyl transfer assay. Peptides with the highest affinity had the structure Cys-A1-A2-X, where A1 and A2 are aliphatic amino acids and X is a C-terminal methionine, serine, or phenylalanine. Charged residues reduced affinity slightly at the A1 position and much more drastically at the A2 and X positions. Effective inhibitors included tetrapeptides corresponding to the COOH-termini of all animal cell proteins known to be farnesylated. In contrast, the tetrapeptide CAIL, which corresponds to the COOH-terminus of the only known examples of geranylgeranylated proteins (neural G protein .gamma. subunits) did not compete in the farnesyl transfer assay, suggesting that the two isoprenes are transferred by different enzymes. A biotinylated he...
example iii
Recombinant Cloning of the Farnesyltransferase .alpha. and .beta. Subunit cDNAs
This example demonstrates the recombinant cloning of cDNAs corresponding to both the .alpha. and .beta. subunit of rat farnesyltransferase. The method employed by the inventors involved the application of the peptide sequence information, as detailed above, to prepare specific primers for PCR-based sequencing, which sequences were then used for the construction of probes with which to screen cDNA libraries. The cloning of each of these cDNAs by the inventors' laboratory has recently been reported (36, 36a).
1. Methods
a. General Methods
General molecular biological techniques were employed in connection with the cloning reactions described below, as set forth in Sambrook et al., (ref 24). cDNA clones were subcloned into bacteriophage M13 or plasmid pUC vectors and sequenced by the dideoxy chain termination method (25) using the M13 universal sequencing primer or gene specific internal primers. Sequencing rea...
example iv
Recombinant Cloning of the Human Farnesyltransferase .alpha. and .beta. Subunit cDNAs
The inventors have now succeeded in cloning the cDNAs for the human counterpart of both the .alpha. and .beta. subunits of the farnesyltransferase gene. This was carried out using standard molecular cloning techniques with the aid of the information gained from the rat farnesyltransferase gene disclosed above.
To clone the human .alpha.-subunit cDNA, an M13 probe of 200 to 300 nucleotides corresponding to the 5' end of the cDNA for the rat farnesyltransferase was used to screen a human retinal .lambda.gt10 cDNA library. Approximately 1.0.times.10.sup.6 plaques were screened, and 27 positives were identified. Positive clones were analyzed by polymerase chain reaction (PCR), and the clone with the largest insert was purified and subcloned for DNA sequencing. The resulting nucleotide sequence, and corresponding deduced amino acid sequence, obtained for the human .alpha.-subunit is set forth as SEQ ID NO...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Structure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com