Additive compositions and polymer compositions containing the same
a technology of additive compositions and polymer compositions, applied in the field of additive compositions, can solve the problems of ineffective nucleating agents in increasing the stiffness inconsistent shrinkage of the molded part produced,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0071]The following examples demonstrates the production of polymer compositions according to the invention. The example further describes certain physical properties exhibited by the polymer compositions.
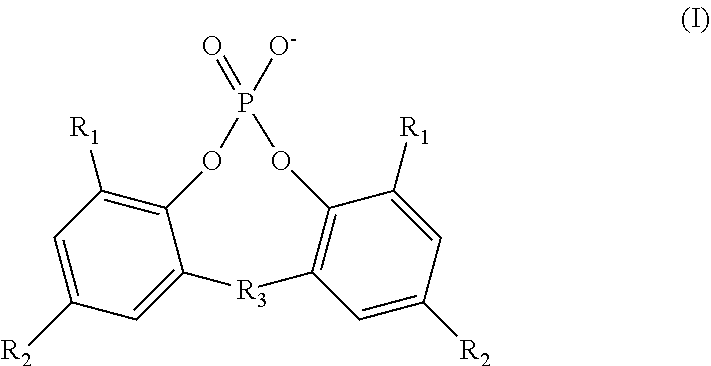
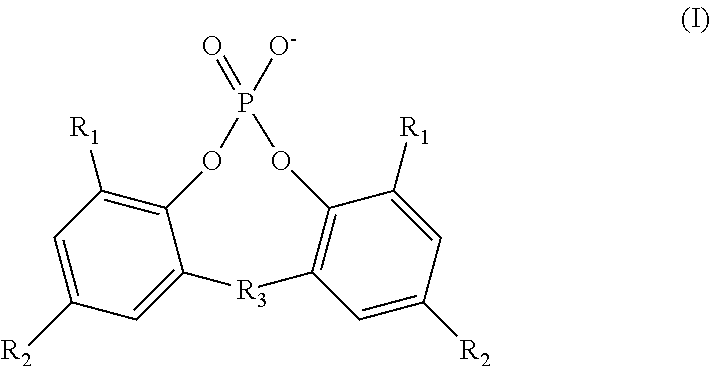
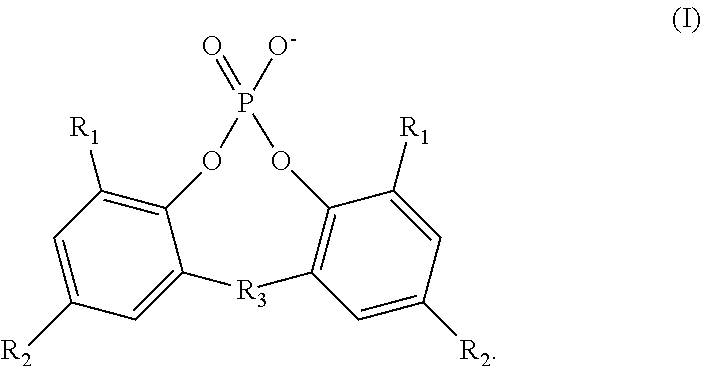
[0072]Fourteen polymer compositions (Samples 1A-1N) were produced with additive compositions as described in Table 1 below. The polymer compositions were produced by individually adding the necessary salts to the polymer. In the table, “PE” denotes the 2,2′-methylene-bis-(4,6-di-tert-butylphenyl) phosphate anion, and “AC” denotes the benzoate anion, except for Sample 1J in which the anion is the 4-tert-butylbenzoate anion. The mole percentage (mol. %) of anions reported in the table is the mole percentage of the total amount of phosphate ester anions and aromatic carboxylate anions present in the additive composition. The mole percentage (mol. %) of cations reported in the table is the mole percentage of the total amount of sodium cations, aluminum (III) cations, lithium cations, a...
example 2
[0075]The following examples demonstrates the production of polymer compositions according to the invention. The example further describes certain physical properties exhibited by the polymer compositions.
[0076]Ten polymer compositions (Samples 2A-2J) were produced with additive compositions as described in Table 3 below. The polymer compositions were produced by individually adding the necessary salts to the polymer. In the table, “PE” denotes the 2,2′-methylene-bis-(4,6-di-tert-butylphenyl) phosphate anion, and “AC” denotes the benzoate anion, except for Sample 2J in which the anion is the 4-tert-butylbenzoate anion. The mole percentage (mol. %) of anions reported in the table is the mole percentage of the total amount of phosphate ester anions and aromatic carboxylate anions present in the additive composition. The mole percentage (mol. %) of cations reported in the table is the mole percentage of the total amount of sodium cations, aluminum (III) cations, lithium cations, and zi...
example 3
[0078]The following examples demonstrates the production of polymer compositions according to the invention. The example further describes certain physical properties exhibited by the polymer compositions.
[0079]Twelve polymer compositions (Samples 3A-3L) were produced with additive compositions as described in Table 5 below. The polymer compositions were produced by individually adding the necessary salts to the polymer. In the table, “PE” denotes the 2,2′-methylene-bis-(4,6-di-tert-butylphenyl) phosphate anion, “CD” denotes the cis-endo-bicyclo[2.2.1]heptane-2,3-dicarboxylate anion for Samples 3A and 3B and the cis-hexahydrophthalate anion for Sample 3C, and “AC” denotes the benzoate anion, except for Sample 3I in which the anion is the 4-tert-butylbenzoate anion. The mole percentage (mol. %) of anions reported in the table is the mole percentage of the total amount of phosphate ester anions, cycloaliphatic dicarboxylate anions, and aromatic carboxylate anions present in the additi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| crystallization temperatures | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| barrel temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com