Method of production of steel sheet semi-finished products by press hardening with locally-modified structure in spots for welding
a technology of local modification and semi-finished products, which is applied in the direction of heat treatment furnaces, furnace types, furnace types, etc., can solve the problems of spot welding joints, relative poor ability to undergo plastic deformation, and structural failure risk under external loading, so as to improve the process and reduce the risk of structural failur
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
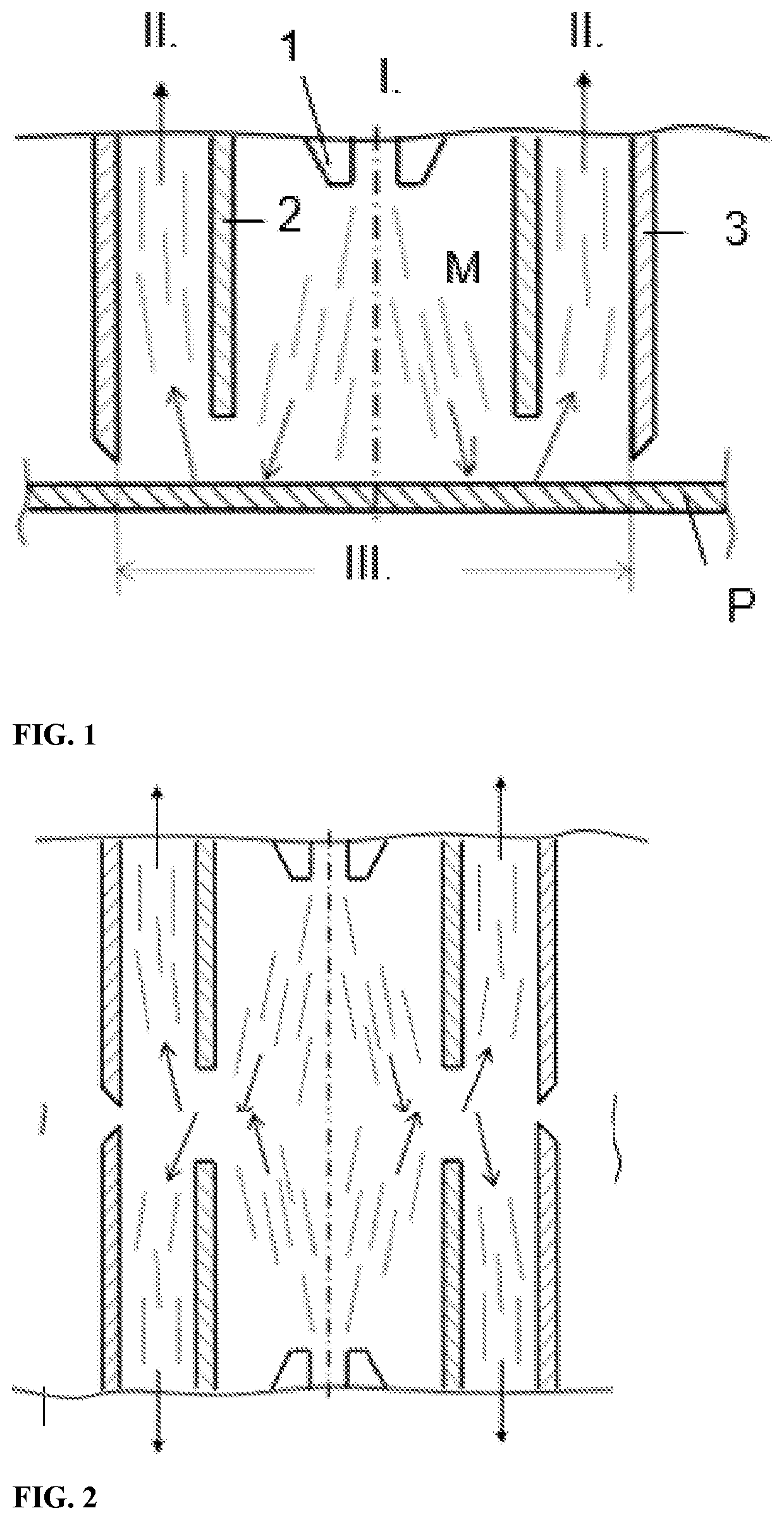
[0024]Steel blank P made of a sheet stock of 22MnB steel of 1.5 mm thickness is placed into a continuous heating furnace. It passes through the furnace for five minutes and heats up to 950° C., at which the initial ferritic-pearlitic structure transforms to austenite. Once this heating austenitizing process ends, the semi-finished product P is pushed out from the furnace and is set, with the aid of guides and stops and after two seconds, in an exactly-defined position in the cavity of a cooling fixture. At the same time, it is approached by a cooling head fitted with cooling nozzles 1. Over 2.5 seconds, the spots to be welded are cooled with water M pressurized at 6 bar. The cooling medium M is screened from the surroundings by a concentric shroud 2 whose diameter is 12 mm. The shroud 2 also guides the cooling medium M away from the spot being cooled. After the cooling ends, the semi-finished product P is transferred to a tool by means of a handling device. 5 to 7 seconds after the ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com