Method for extracting metals from concentrated sulphurated minerals containing metals by direct reduction with regeneration and recycling of the reducing agent, iron, and of the flux, sodium carbonate
a technology of concentrated sulphurated minerals and metals, applied in the field of mining and metallurgy, can solve problems such as pollution of the environmen
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
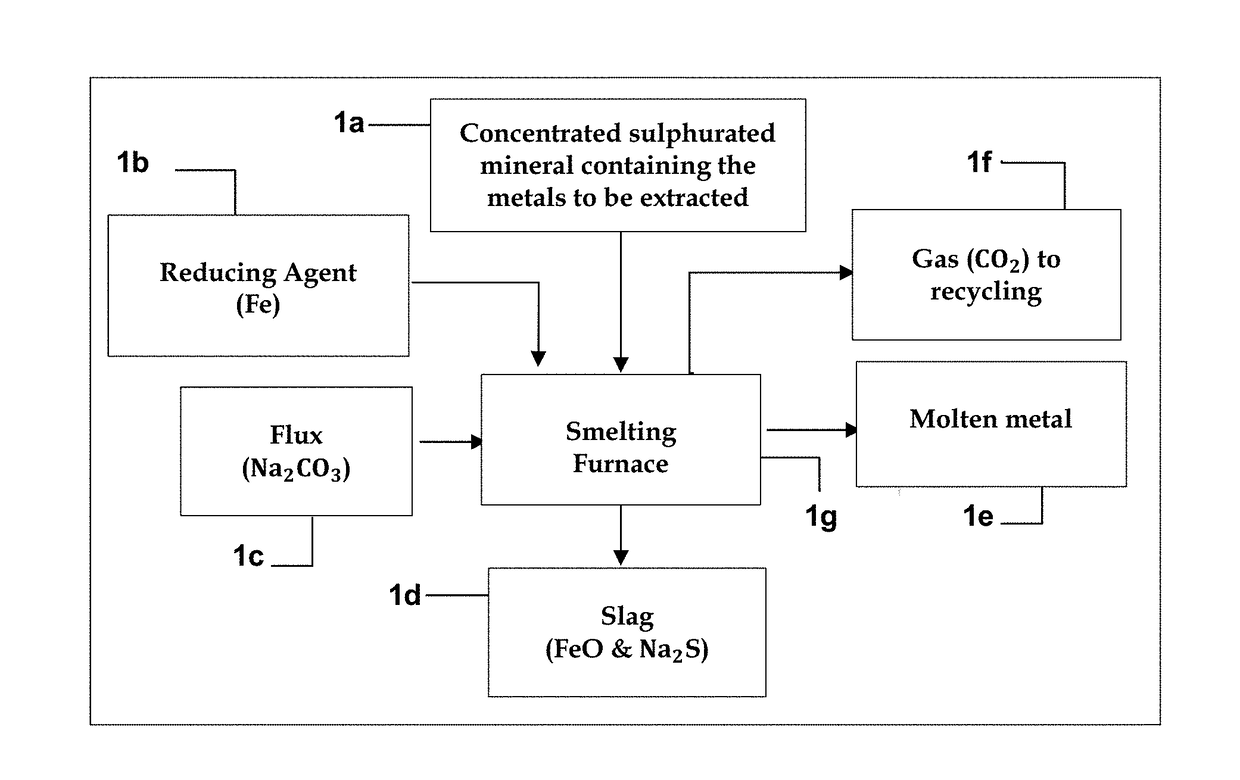
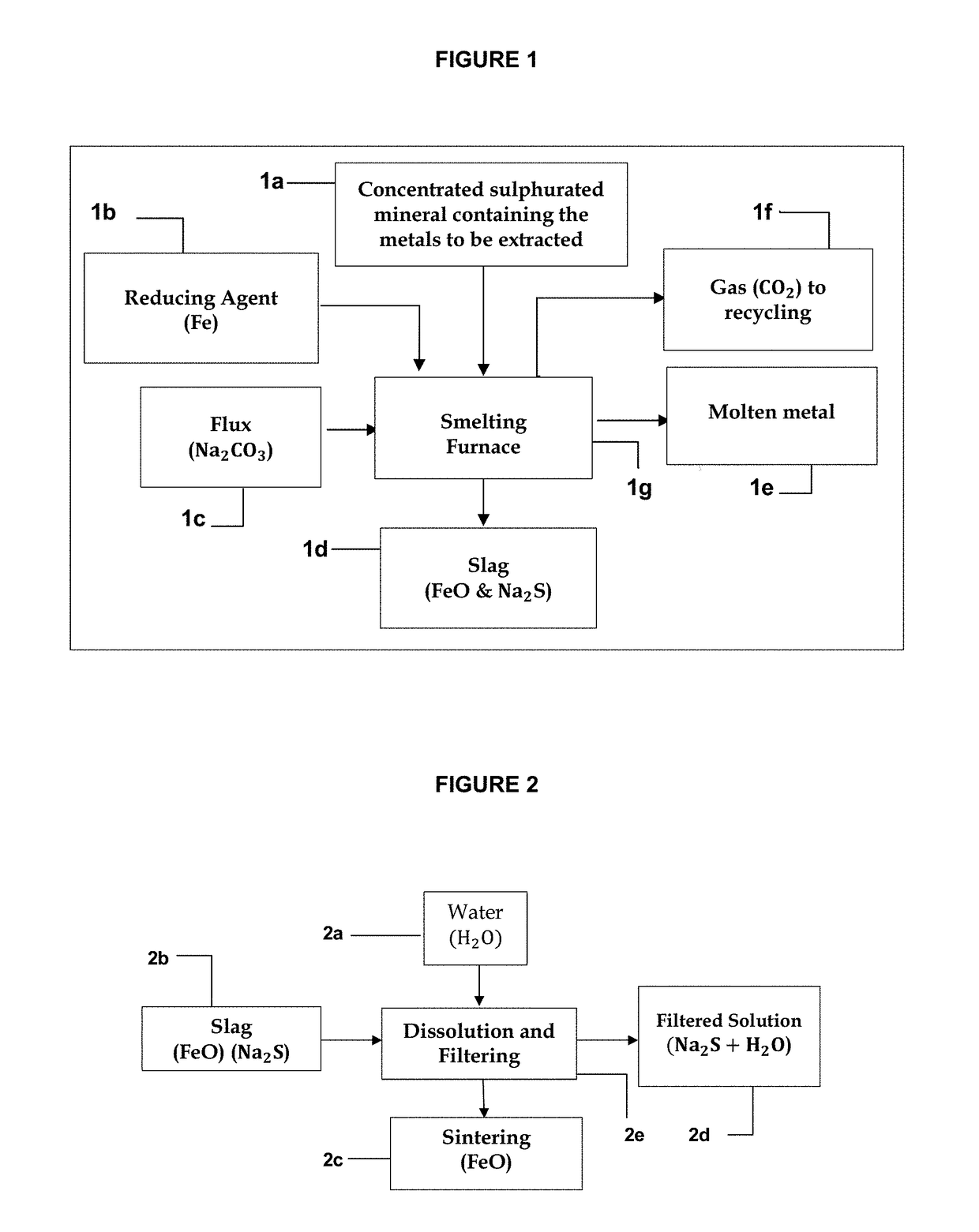
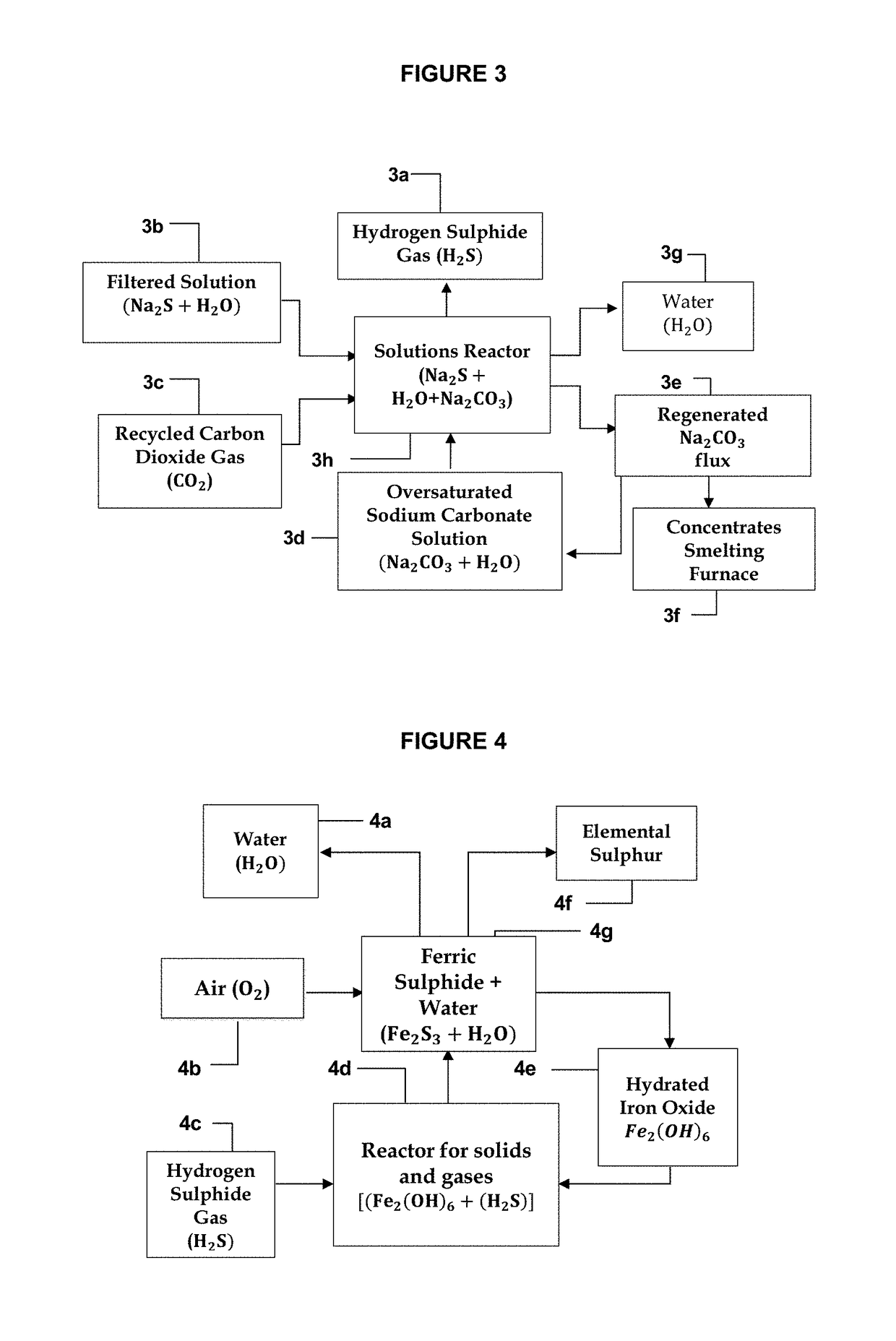
[0014]The technological innovation developed allows extracting, in addition to iron, metals such as, but not limited to, lead, silver, zinc, copper, molybdenum, antimony, arsenic, with or without associated iron, and with gold that could be hosted as inclusion in certain cases, from sulphurated minerals containing them. For this purpose, an improved direct reduction process is applied to the metals to be extracted, which is achieved without sulphur dioxide emissions nor producing slags commonly generated by conventional pyrometallurgical plants, thus minimizing environmental pollution. In addition, through the proposed regeneration and recycling of iron as reducing agent and sodium carbonate as flux, the operating costs of the process are substantially reduced.
[0015]This technology can be also applied to the remediation of tailings deposits containing various ferrous and non-ferrous metal sulphides. Currently, the metallurgical mining matrix worldwide states that concentration plant...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| compression strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| metallic | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| chemical formula | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com