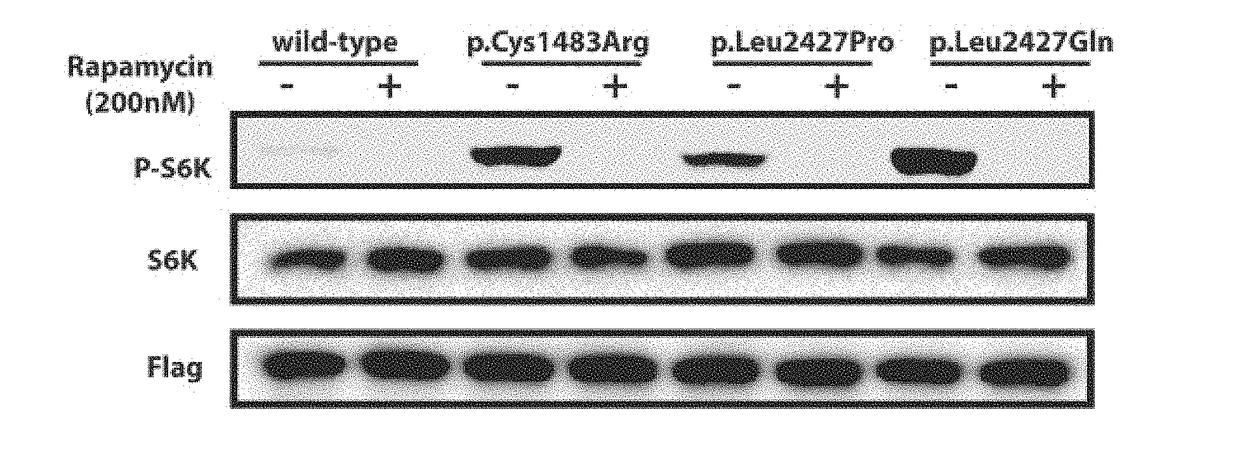
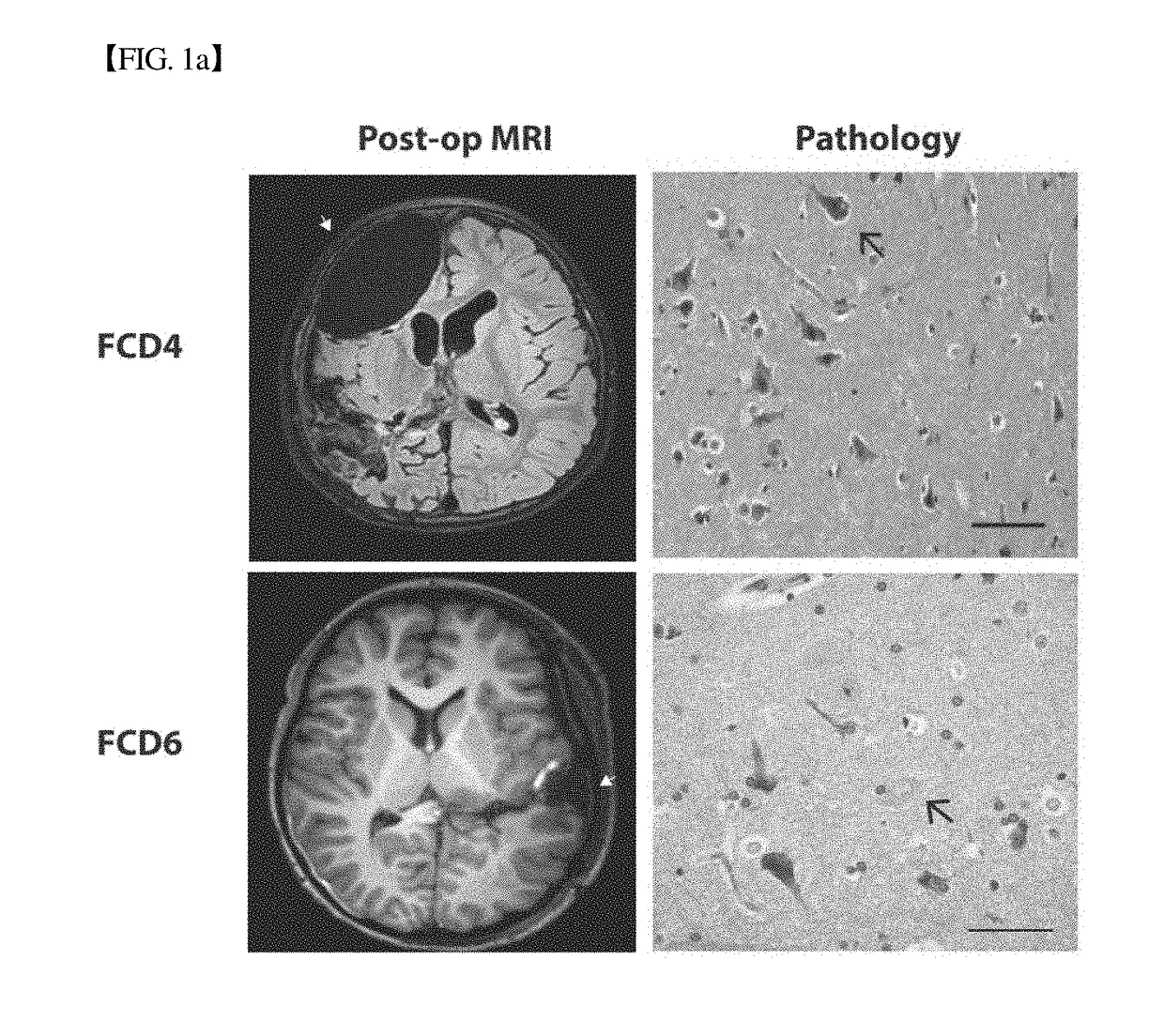
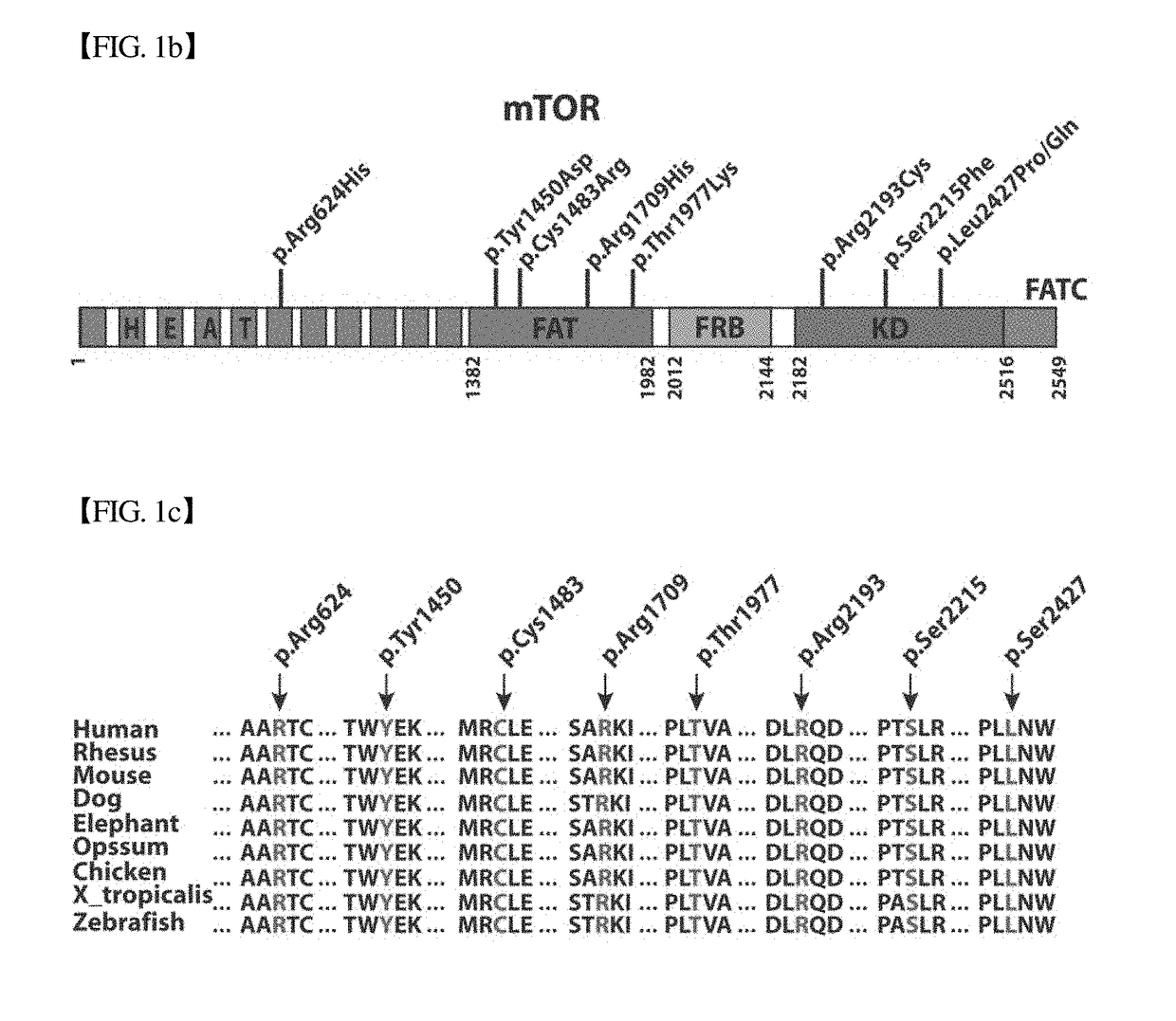
COMPOSITION FOR PREVENTION OR TREATMENT OF INTRACTABLE EPILEPSY COMPRISING mTOR INHIBITOR
a technology of intractable epilepsy and inhibitors, which is applied in the field of prevention or treatment of intractable epilepsy, can solve the problems of inability to develop novel and more effective fcd therapies, inability to identify such mutations, and poor understanding of the molecular genetic etiology of fcdii, and achieve the effect of reducing the frequency of ons
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1-1
ion of 3 Candidate mTOR Mutations from 4 Patients Through Whole Exome Sequencing
[0183]Deep whole exome sequencing (read depth 412-668×) was performed on brain tissue samples from four FCDII patients (designated FCD3, FCD4, FCD6, and FCD23, respectively). Selection was made of three candidate genetic mutations that were found simultaneously using the two algorithms Virmid and Mutect.
[0184]To obtain data of the whole exome sequencing, libraries of sequences were prepared using the Agilent library preparation protocols (Agilent Human All Exon 50 Mb kit) according to the manufacturer's instructions. The libraries were subjected to sequencing on Hiseq2000 (Ilumina). For more accurate analysis, sequencing was carried out with a read depth of about 500×, five-times higher than the general sequencing depth. The sequencing data was prepared into a file that can be analyzed using the Best Practices Pipeline suggested by Broad Institute (https: / / www.broadinstitute.org / gatk / ).
example 1-2
n of 3 Gene Mutant Candidates by Site-Specific Amplicon Sequencing and Identification of One Genetic Mutation (L2427P)
[0185]Site-specific amplicon was performed for the candidate mutations—(read depth, 100-347, 499×). The samples were obtained from the same brain tissue block through biological replication, thereby minimizing any unexpected sequencing artifacts or erroneous calls that can mimic low-frequency somatic mutations. For the site-specific amplicon sequencing, the samples were determined to have a mutation when the percentage of mutated reads exceeded 1%.
[0186]Site-Specific Amplicon Sequencing
[0187]Two pairs of primers carrying two target regions of mTOR target gene codon sites (amino acids Cys1483 and Leu2427) were designed (Table 2).
TABLE 2SEQIDTarget regionprimerNOChr1:11174301~Forward5′-TAGGTTACAGGCCTGGATGG-11Chr1:111745133′Reverse5′-CTTGGCCTCCCAAAATGTTA-123′Chr1:11217133~Forward5′-TCCAGGCTACCTGGTATGAGA-13Chr1:112173443′reverse5′-GCCTTCCTTTCAAATCCAAA-143′
[0188]Each prim...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com