mAb-DRIVEN CHIMERIC ANTIGEN RECEPTOR SYSTEMS FOR SORTING/DEPLETING ENGINEERED IMMUNE CELLS
a technology of engineered immune cells and chimeric antigen receptors, which is applied in the field of improved chimeric antigen receptors, can solve the problems of inability to provide prolonged expansion and anti-tumor activity in vivo, car t cells can promote acute adverse events after being transferred into patients, and discrimination, so as to enhance the cytotoxicity of engineered immune cells and promote cdc cytotoxicity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
n of Rituximab-Driven Depletion Systems Embedded in an Anti-CD123 CAR
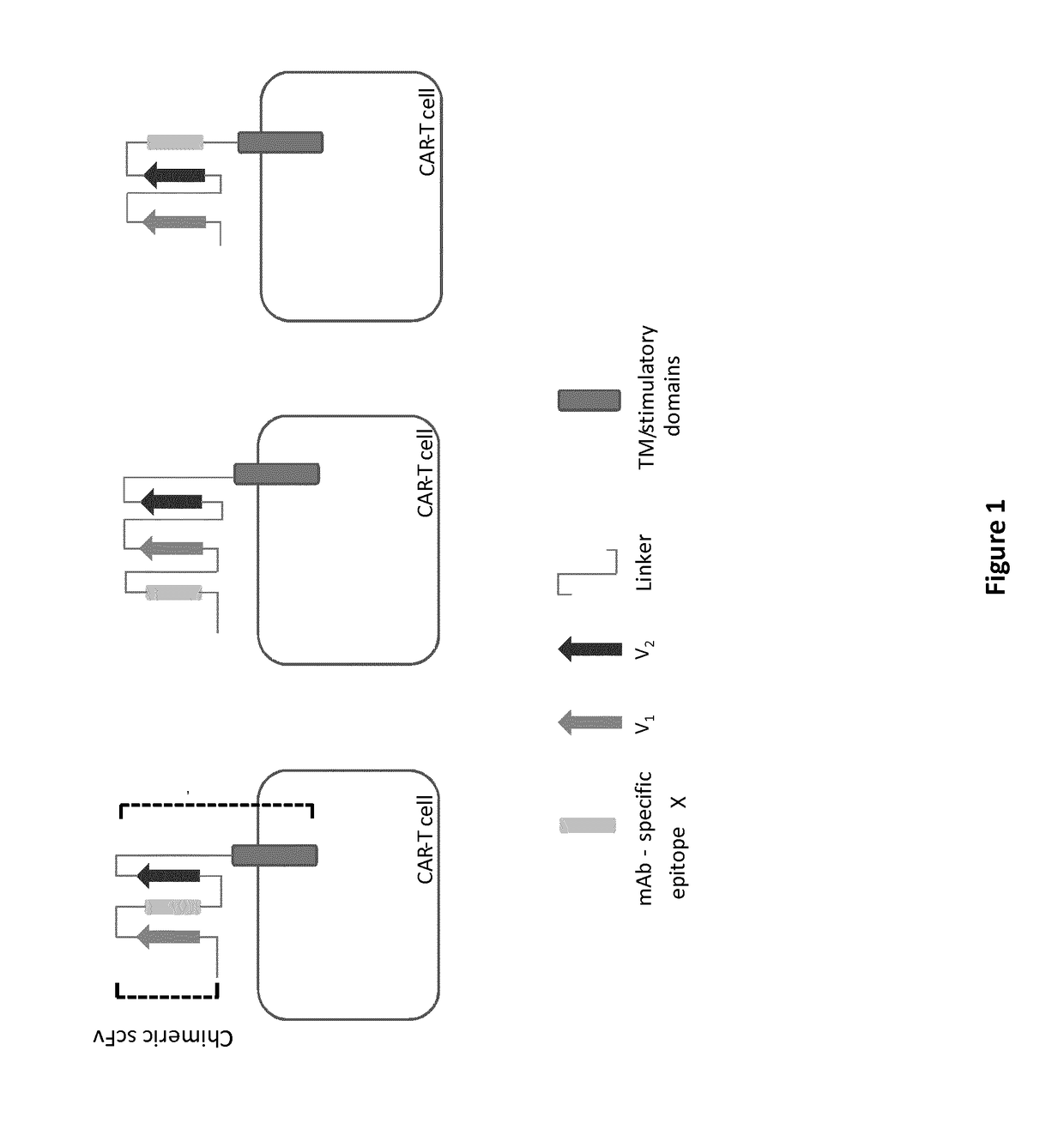
[0254]All 10 CARs having different conformations in terms of chimeric scFv (anti-CD123 scFv with CD20 mimotope(s)) are depicted in FIG. 4: their resulting polypeptide sequences are shown in SEQ ID NO 1 to 10.
[0255]The DNA construct of the 10 CARs are transcribed into their corresponding mRNA via in vitro transcription and used to transfect by electroporation primary T cells freshly isolated from buffy coat via a standard ficoll procedure. One day post transfection, T cells were recovered and used to performed a flow based cytotoxicity assay as described as follows.
Generation of Anti CD123 CAR T Cells.
[0256]To generate primary T cells expressing anti-CD123 CAR, primary T cells are first purified from buffy-coat samples and activated using Dynabeads human T activator CD3 / CD28. 3 days post activation, 1 million of activated T cells are transduced with lentiviral vectors harboring an anti-CD123 CAR expression cassette ...
example 2
ty of the mAb-Driven Depletion Systems in the Anti-CD123 Chimeric Antigen Receptor
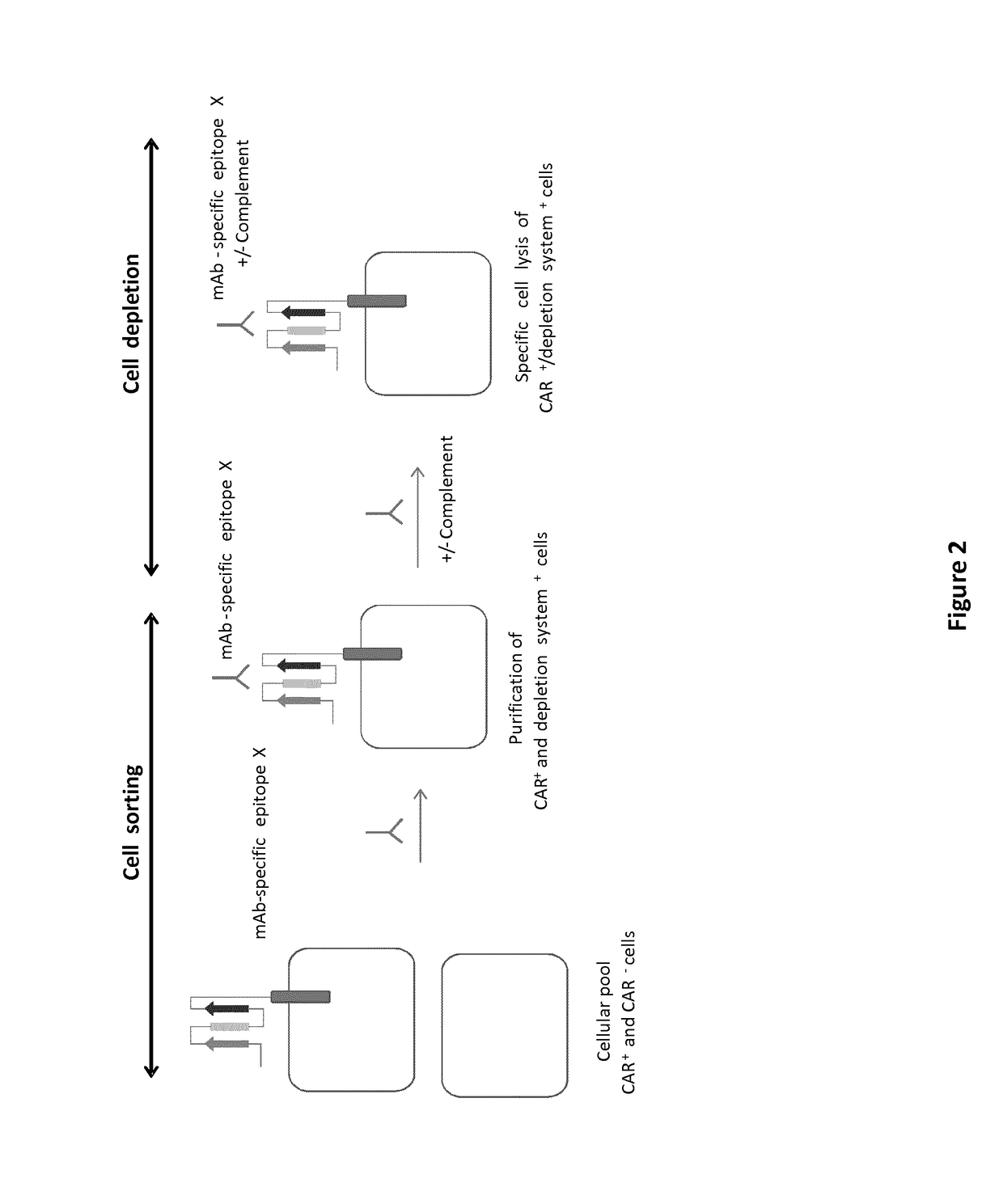
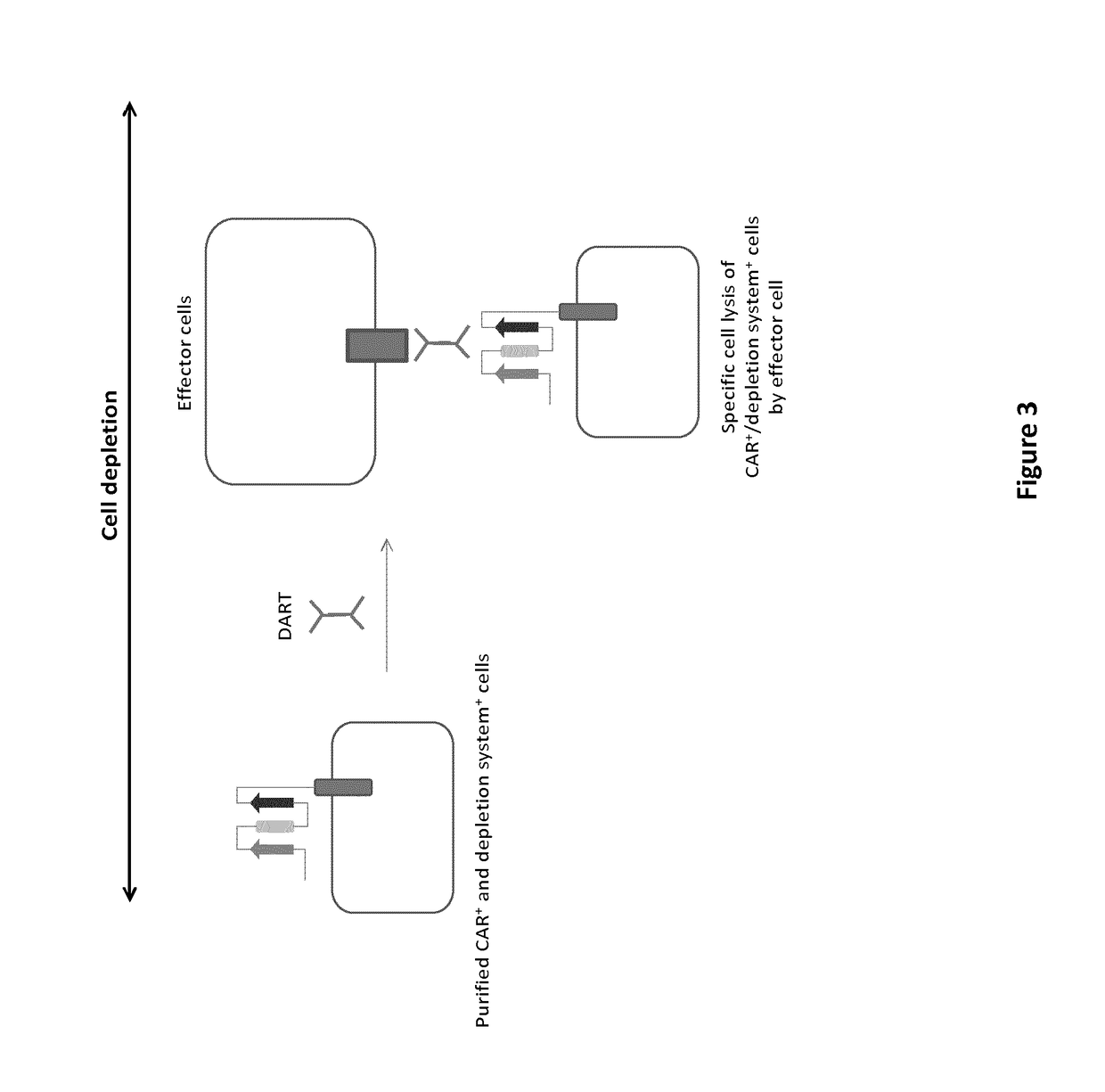
[0261]To further demonstrate the flexibility of the mAb-driven depletion system, different epitopes or mimotopes (SEQ ID NO 35-42) specific for cetuximab, palivizumab and nivolumab mAbs are inserted within the anti-CD123 CAR constructions using the same procedure and architecture as the one used for the CD20 mimotope described in Example 1. The results aim to show that transfected T cells retain their cytolytic activity and degranulation capacity toward CD123 positive tumor cells. In addition, the experiments are designed also to indicate that transfected T cells are depleted by some of the aforementioned mAbs
example 3
-Dependent Depletion of Anti-CD123 CAR Containing an mAb-Driven Depletion System
[0262]To explore the ability of the mAb-driven depletion system to allow depletion of anti-CD123 CAR T cells, transduced T cell expressing a CAR of SEQ ID NO 1, 2, 3 or 4 or an unmodified anti-CD123 CAR (SEQ ID NO 142), were subjected to a complement dependant cytotoxicity assay (CDC).
[0263]CDC Assay
[0264]The CDC assay consisted in incubating 0.2 106 transduced T cells either alone, or in the presence of Rituximab (RTX, ROCHE, 400 ng) and Babby Rabbit Complement (BRC, AbD Serotec, ref# C12CA, 100 μL of the solution diluted according to the manufacturer protocol) for 3 hours at 37° C. in a final volume of 400 μL of Xvivo 10% FBS. At the end of incubation, anti CD123-CAR T cells were recovered and labeled with recombinant CD123 protein fused to an FC fragment (SEQ ID 143) and a PE labeled anti-FC secondary monoclonal antibody (Jackson ImmunoResearch, ref#115-115-164, diluted 1 / 200). Cells were then recover...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com