Systems and methods using weighted-ensemble supervised-learning for automatic detection of ophthalmic disease from images
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
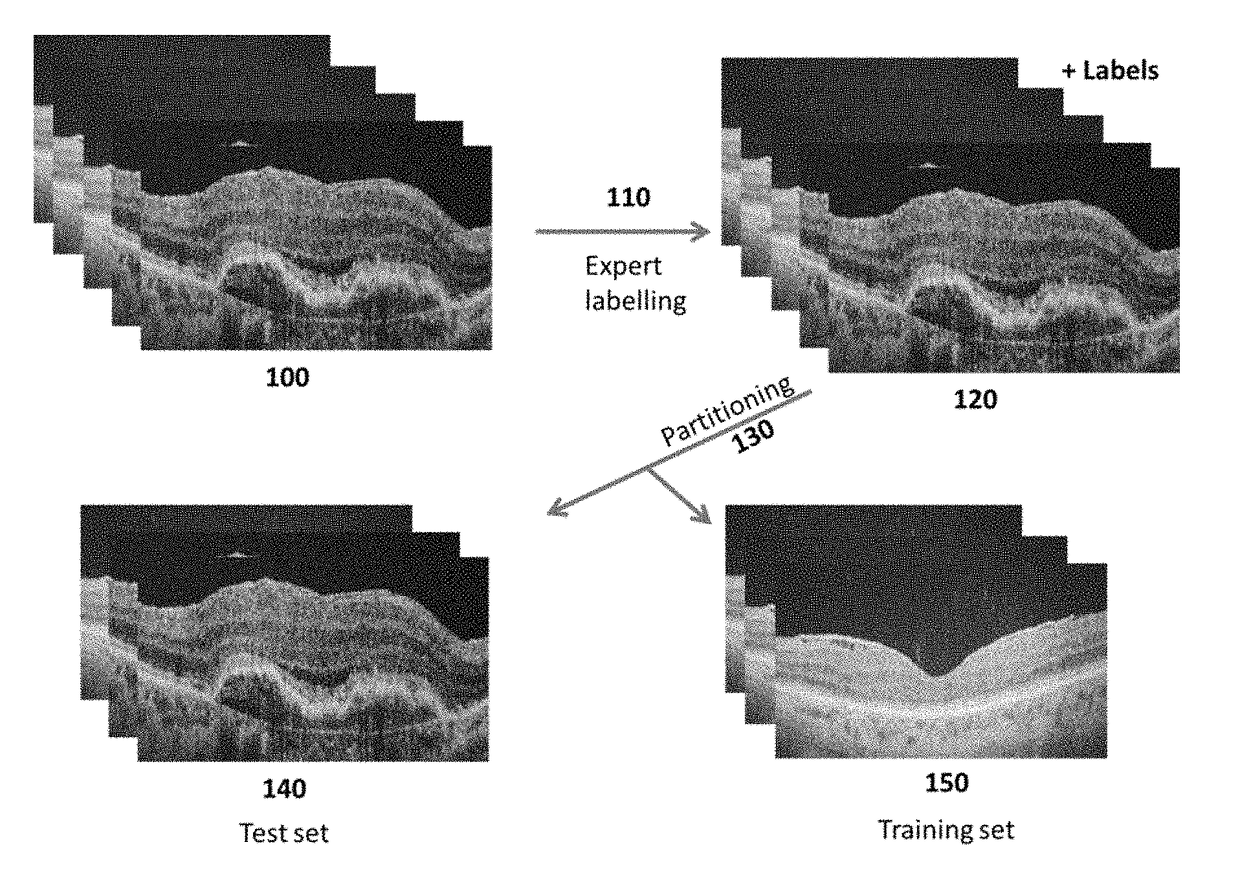
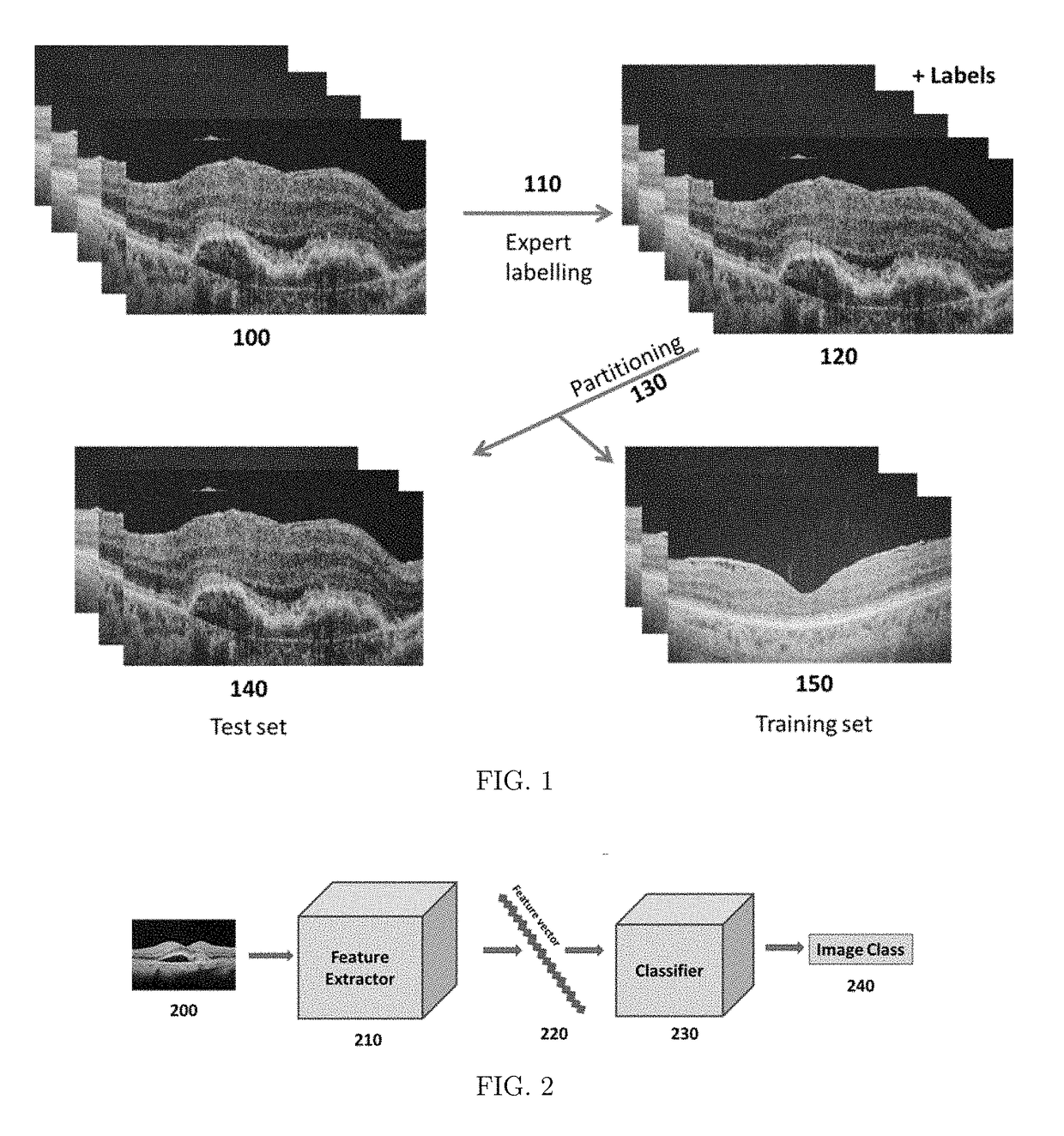
[0038]The illustration in FIG. 1 is a preferred embodiment of the pre-training processing steps carried out on the data. The schematic includes an unlabeled set of images 100. In step 110, the unlabeled data in 100 is labeled by an expert or some other entity with sufficient knowledge to do so competently. This labeling yields a labeled data set depicted in 120. In the step 130 the labeled data set 120 is partitioned into a training set, 150, and test data set, 140. The choice of partitioning fraction is itself a learnable hyper-parameter—in the sense that various fractions can be tried empirically to determine the fraction with best most generalizable results. Various forms of pre-processing such as data augmentation and random shuffling can be done to the data set of labeled images 120 to yield a data set of processed tomograms. The processed and labeled images are then partitioned into a training set, 150, and a test set, 140. In turn, the training and test sets are entered as in...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com