Charging method and charging device
a charging device and charging method technology, applied in parallel/serial switching, indicating/monitoring circuits, transportation and packaging, etc., can solve the problems of not equalizing the voltage of plural cells in parallel connection, and difficulty in accurately reducing the power source voltage to a target value during constant voltage charging, so as to improve the accuracy of voltage value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
[0048]A description will hereinafter be made on an embodiment of the invention with reference to the drawings.
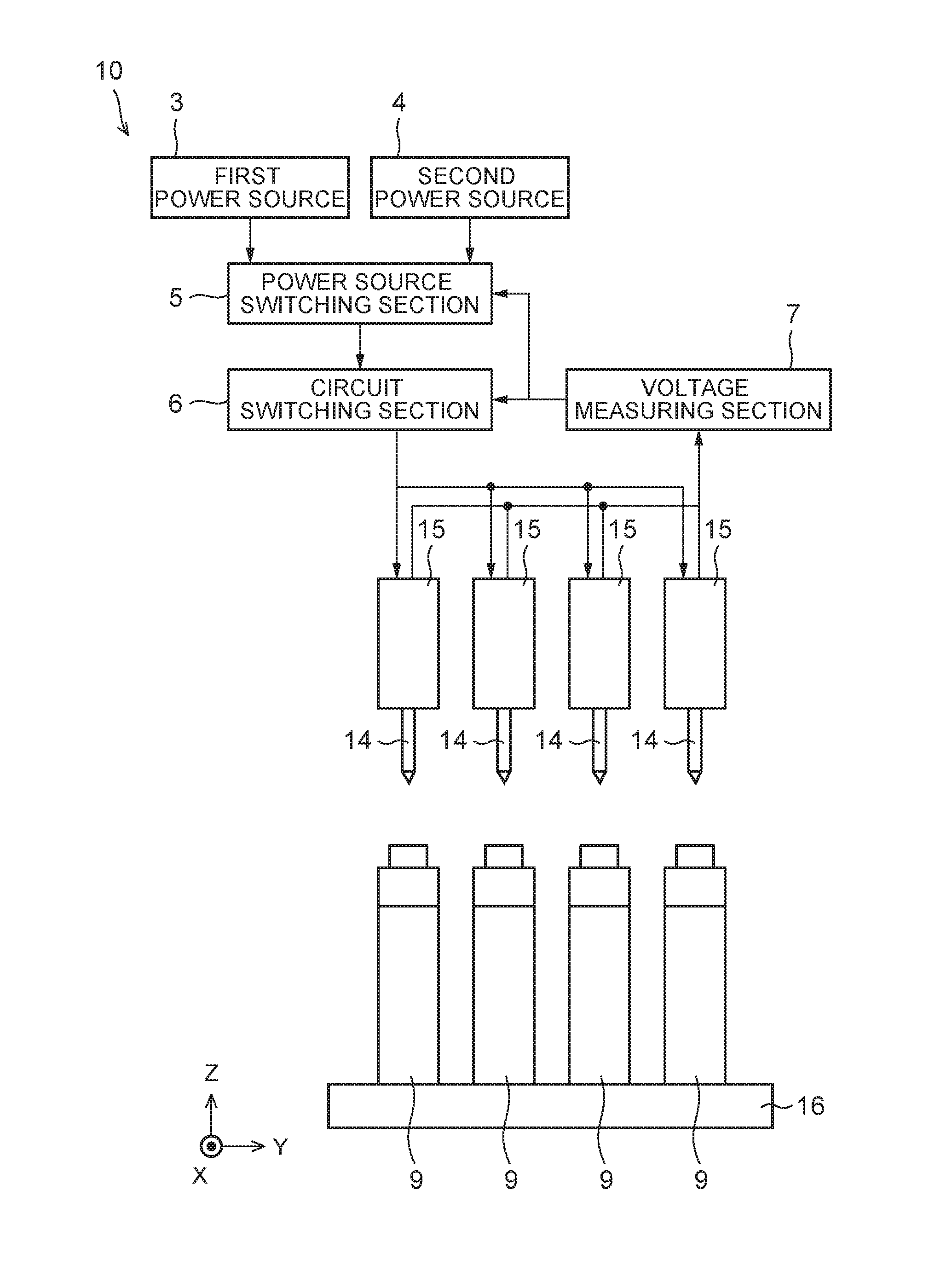
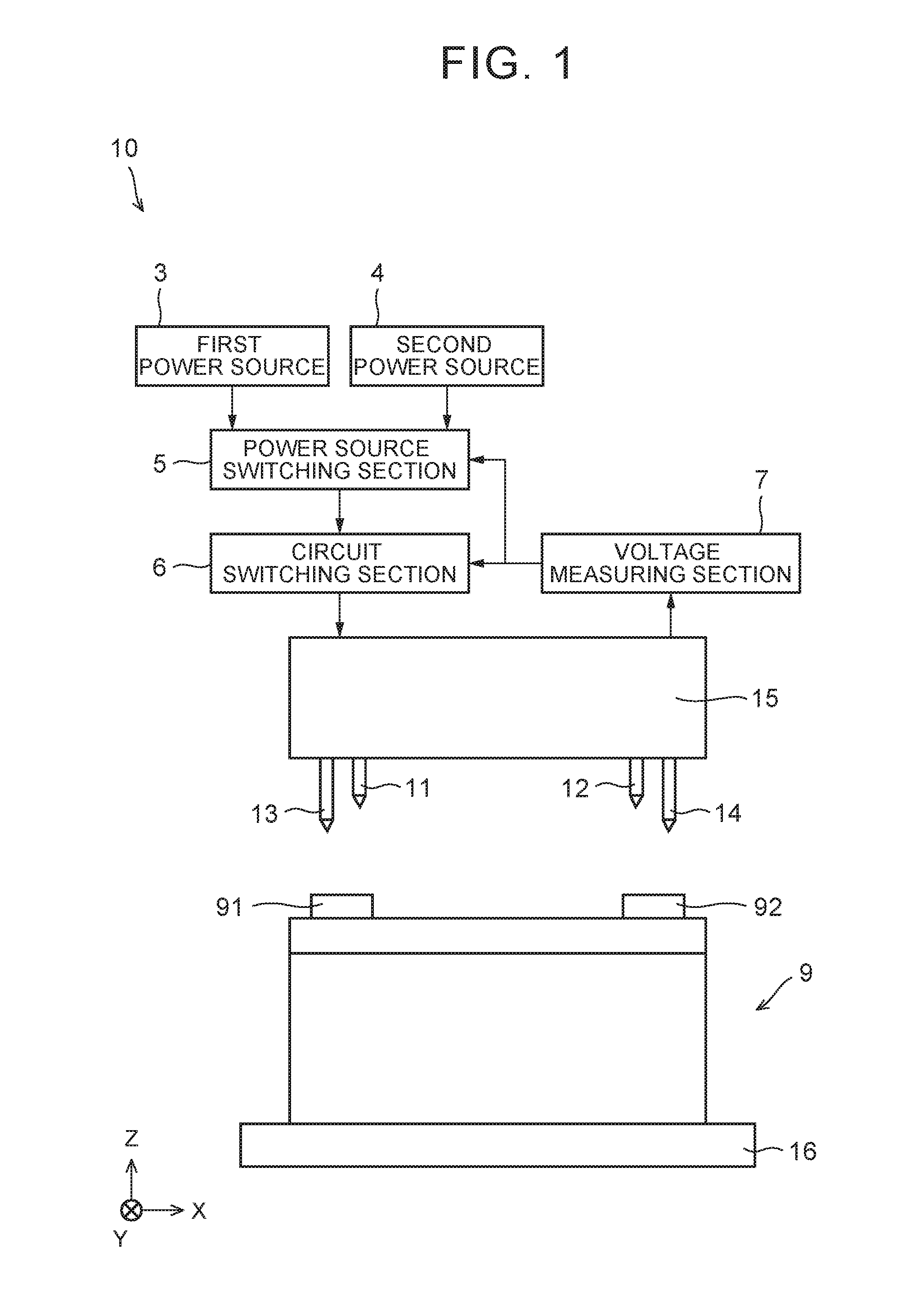
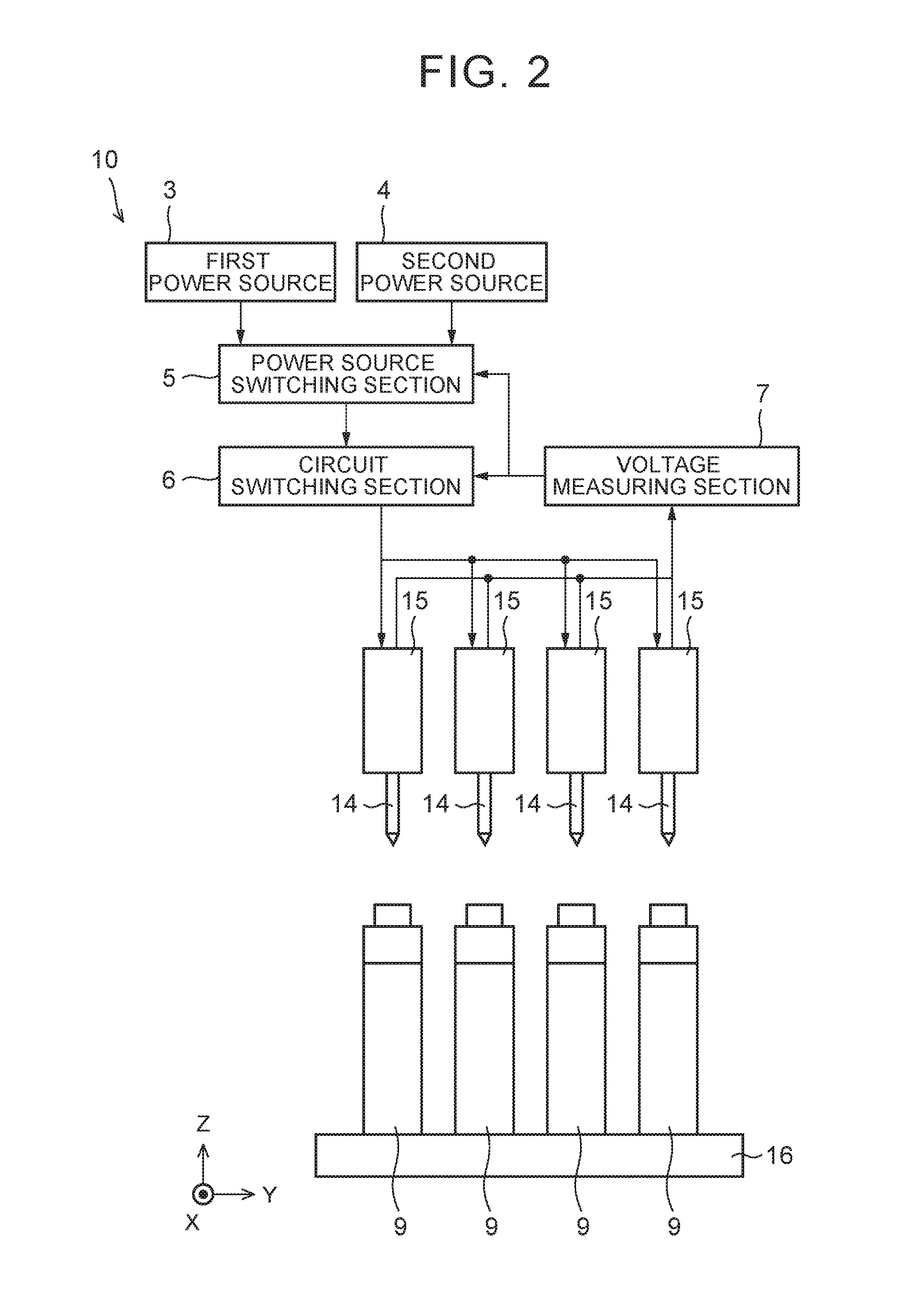
[0049]As shown in FIG. 1 and FIG. 2, a charging device 10 has a positive electrode terminal conductive pin 11, a negative electrode terminal conductive pin 12, a positive electrode terminal voltage measuring pin 13, a negative electrode terminal voltage measuring pin 14, a pin holding section 15, a first power source 3, a second power source 4, a power source switching section 5, a circuit switching section 6, and a voltage measuring section 7. A secondary battery cell 9 has a positive electrode terminal 91 and a negative electrode terminal 92. The positive electrode terminal 91 and the negative electrode terminal 92 are arranged on a terminal surface of the cell 9.
[0050]The charging device 10 charges the cell 9 by connecting the positive electrode terminal 91 and the negative electrode terminal 92 of the cell 9 to the first power source 3 or the second power source 4 and ap...
example
[0083]An example in which the four cells 9 (No. 1 to No. 4) were charged by using the charging device 10 according to this embodiment will be described. As shown in FIG. 9, the four cells 9 were connected in series and were subjected to the constant current charging by the first power source 3. FIG. 11 is a chart of a relationship between time and the voltage when the serial constant current charging was conducted. In FIG. 11, when one of the plural cells 9 reached the specified reference voltage, the constant current charging was stopped. Thereafter, the voltage difference among the plural cells 9 was measured, and it was determined that the voltage difference among the four cells 9 is smaller than the specified value.
[0084]After one of the cells 9 reached the reference voltage, as shown in FIG. 10, the cells 9 were connected in parallel and were subjected to the constant voltage charging by the second power source 4. FIG. 12 is a chart of a relationship between the time and the vo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com