Mutant factor viii compositions and methods
a technology of mutant factor viii and composition, which is applied in the field of recombinant human factor viii mutants, can solve the problems of insufficient expression level of fviii, excessive bleeding when hemophiliac is injured, and inefficient secretion of human fviii
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Construction, Expression and Purification of B-Domainless Factor VIII Mutants
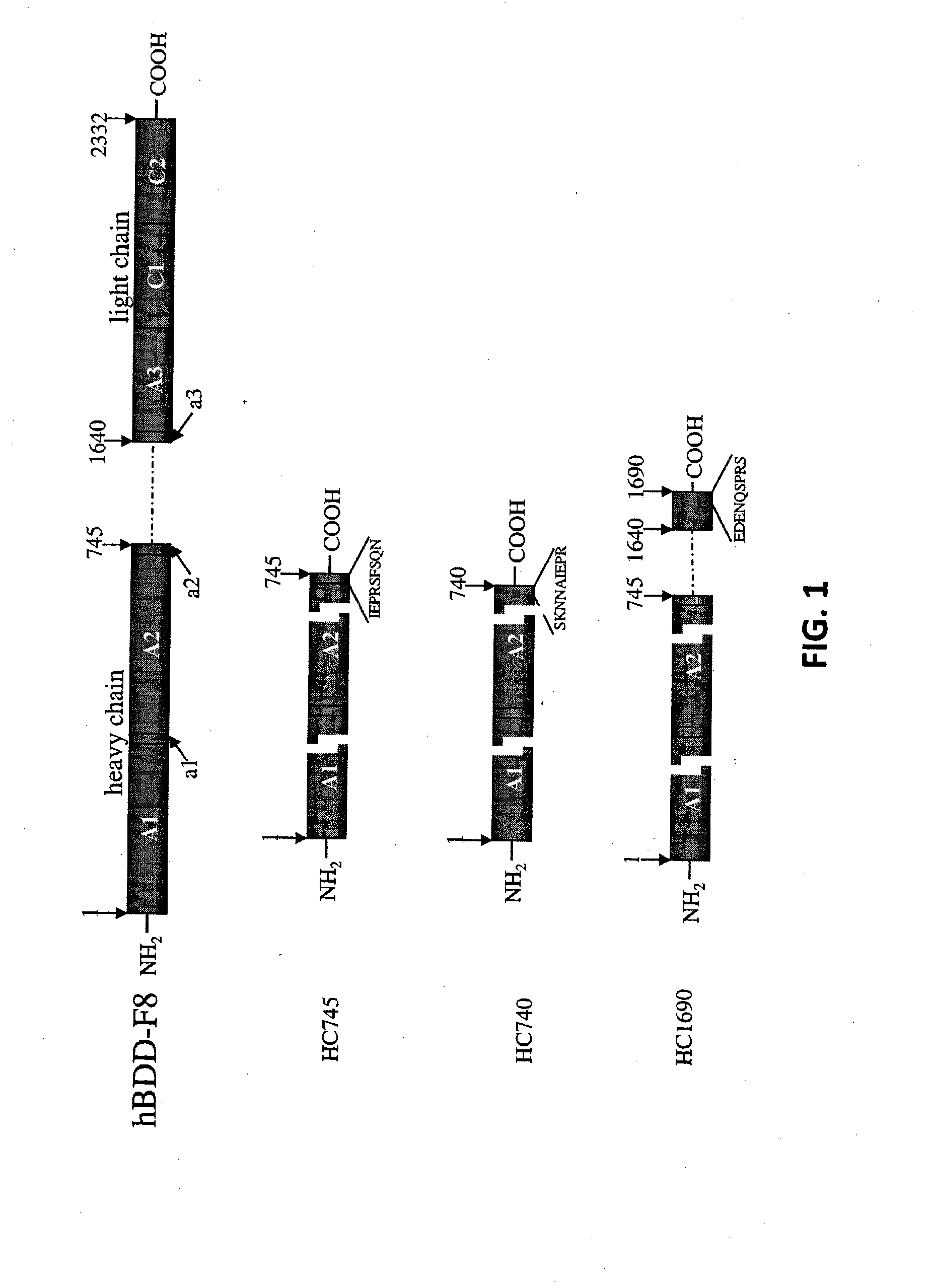
[0164]Plasmid pAAV-CB-F8 carries a B-domainless human factor VIII (hF8) cDNA under the control of a CB promoter (beta-actin promoter with a CMV enhancer). This plasmid, consistent with the construction shown in FIG. 10, was used as template for making various hF8 mutants. A hF8 cDNA fragment encoding the substitution mutations I86V, Y105F, A108S, D115E, Q117H, F129L, G132K, H134Q, M147T and L152P was synthesized chemically and used to replace the corresponding region of pAAV-CB-F8. The resulting plasmid (pAAV-CB-F8-X10) expresses a mutant factor VIII protein with the above 10 mutations (F8-X10; SEQ ID NO: 3).
[0165]A factor VIII cDNA fragment encoding the substitution mutations I86V, A108S, G132K, M147T, L152P was synthesized chemically and used to replace the corresponding region of pAAV-CB-F8. The resulting plasmid (pAAV-CB-F8-X5) expresses a mutant factor VIII protein with the above 5 mutations (F8-X5; SE...
example 2
Comparison of Different Factor VIII Mutants for Secretion in Tissue Culture Cells
[0171]Plasmids pAAV-CB-hBDD-F8 (wt), pAAV-CB-hBDD-F8-X10, pAAV-CB-hBDD-F8-X5 and pAAV-CB-hBDD-F8-G312K were separately transfected in BHK cells (panel A) or 293 cells (panel B). Secreted F8 in the media was harvested and assayed by aPTT assay at 48 hours post transfection. The expression / secretion by wild type human BDD-F8(hBDD) was set as 100%. As shown in FIG. 7, the hF8 mutants were secreted at about 2-8.5 fold higher expression levels than the wild type hF8.
example 3
Comparison of Human Factor VIII Mutant Secretion In Vivo
[0172]Plasmids pAAV-CB-hBDDF8 (B-domain deleted (BDD) wt hF8), pAAV-CB-hBDDF8-X10 (hF8-BDD with 10 substitutions; SEQ ID NO:3), pAAV-CB-hBDD-F8-X5(hF8 with 5 substitutions; SEQ ID NO:4) and pAAV-CB-hBDD-F8-G312K (hF8 with G132K substitution) were separately injected to Blab / c and F8 double knock-out mice. Secreted F8 in the blood was collected and assayed by aPTT assay at 48 hours post injection. The expression / secretion by wild type human F8 (hBDD-F8) was set as 100%. All mutants described here outperform the wild type factor VIII. As shown in FIG. 8, the hF8 mutants were secreted at about 1.2-5.2 fold higher expression levels than the wild type hF8.
EXAMPLE 4
Comparison of Different Factor VIII Mutants in Secretion
[0173]Plasmids encoding amino acids in hBDD-F8-X10 were modified to revert back the mutant substitutions to their corresponding wild type amino acids as indicated in the table. For example, hBDD-F8-X10-V86I means that...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com