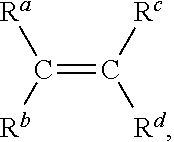
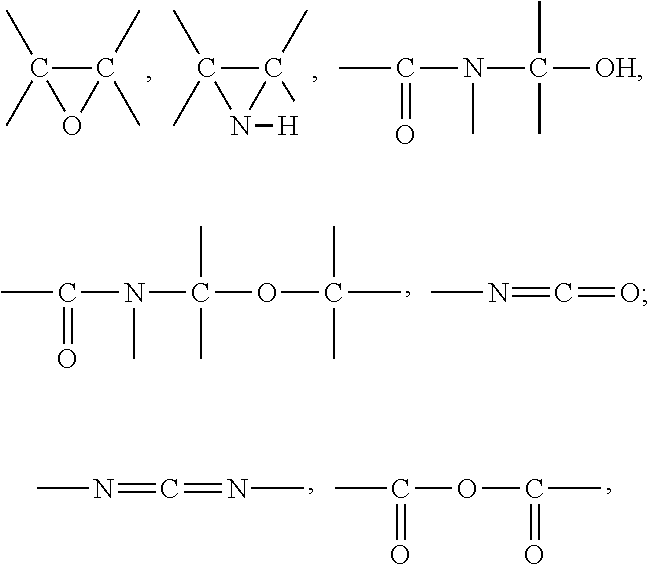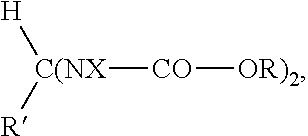Rubber compositions
a technology of compositions and rubber, applied in the field of rubber compositions, can solve the problems of not increasing the strength and stiffness of rubber compounds obtained with their aid, and achieve the effects of increasing the strength and stiffness of rubber compounds, reducing the processing viscosity of rubber compounds, and high molar mass
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0033]A resin based on n-hexylcarbamate and formaldehyde was made according to the following procedure:
example 1.1
n-Hexyl Carbamate
[0034]14.45 kg of n-hexanol were charged into a reaction vessel equipped with a stirrer, a thermometer, a nitrogen inlet, and a dropping funnel. 1.2 g of a commercial dibutyltin oxide (Fascat 4100, Elf-Atochem) and 6.0 kg of urea were added, and the resulting mixture was heated to reflux (160° C.). The reaction was continued for five hours, and reflux was maintained by reducing the pressure. The mass fraction of residual urea in the reaction mixture had fallen to 1.0%. After separation of the excess hexanol by distillation under reduced pressure, a clear melt of n-hexyl carbamate (CAS-No. 2114-20-7) was obtained which solidified at 55° C.
example 1.2
Adduct Resin of n-Hexyl Carbamate and Formaldehyde
[0035]The carbamate of n-hexanol made in Example 1.1 was melted to 95° C. in a reaction vessel, and 11 kg of an aqueous solution of formaldehyde having a mass fraction of formaldehyde of 37% was added over thirty minutes under stirring, and cooling to 60° C. When this temperature was reached, 90 g of an acid ion exchange resin (®Amberlyst 15 dry, sulphonic acid-functional reticulated resin based on styrene-divinylbenzene copolymers, The DOW Chemical Co.) were added, and the vessel was deaerated by evacuation-nitrogen purge cycles. The contents of the vessel were then heated up to 95° C., taking advantage of the exothermic reaction, held at that temperature for one hour, whereupon the temperature was slowly increased up to 135° C. to distil off the remaining water. The viscosity of the remaining pale yellow resin was 8.9 Pa·s, measured at 70° C. at a shear rate if 25 s−1. A mass fraction of 0.08% of remaining formaldehyde was determin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com