Lithographic hotspot detection using multiple machine learning kernels
a machine learning and hotspot detection technology, applied in the field of hotspot identification, can solve the problems of long runtime, many regions of layouts may still be susceptible to lithography process, unwanted shape distortion of printed layout patterns,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
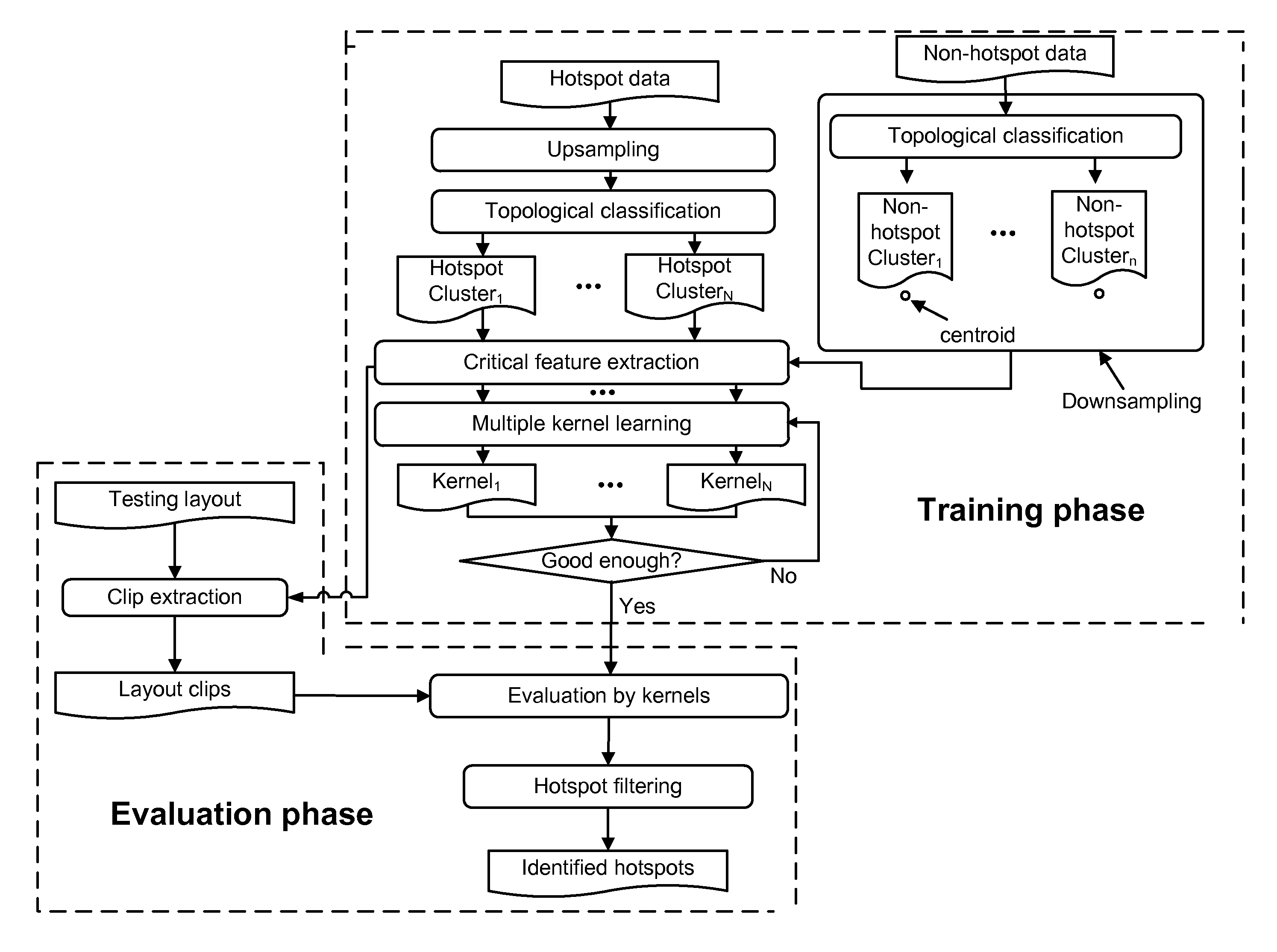
[0027]The Figures (FIGS.) and the following description describe certain embodiments by way of illustration only. One skilled in the art will readily recognize from the following description that alternative embodiments of the structures and methods illustrated herein may be employed without departing from the principles described herein. Reference will now be made in detail to several embodiments, examples of which are illustrated in the accompanying figures. It is noted that wherever practicable similar or like reference numbers may be used in the figures and may indicate similar or like functionality.
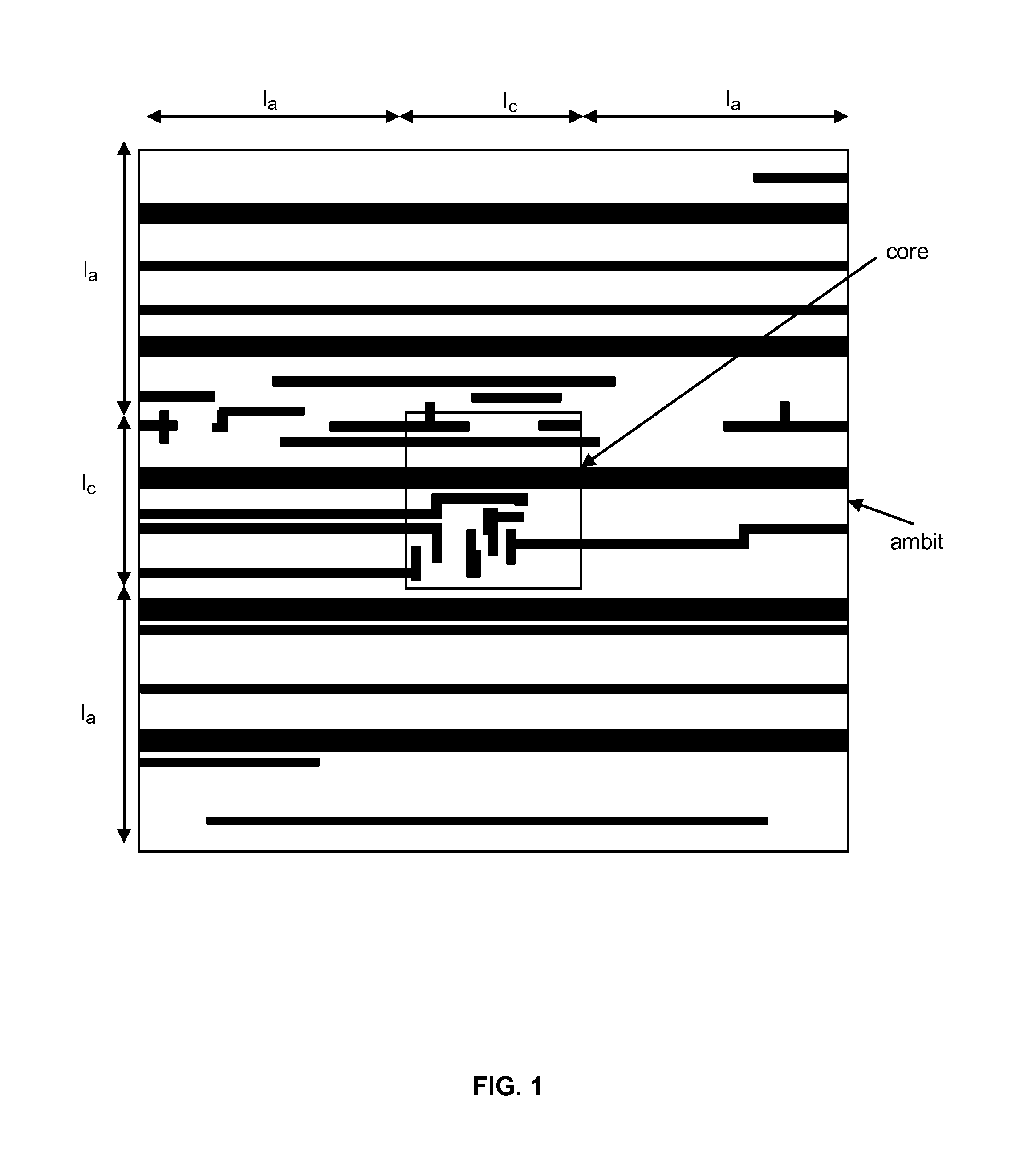
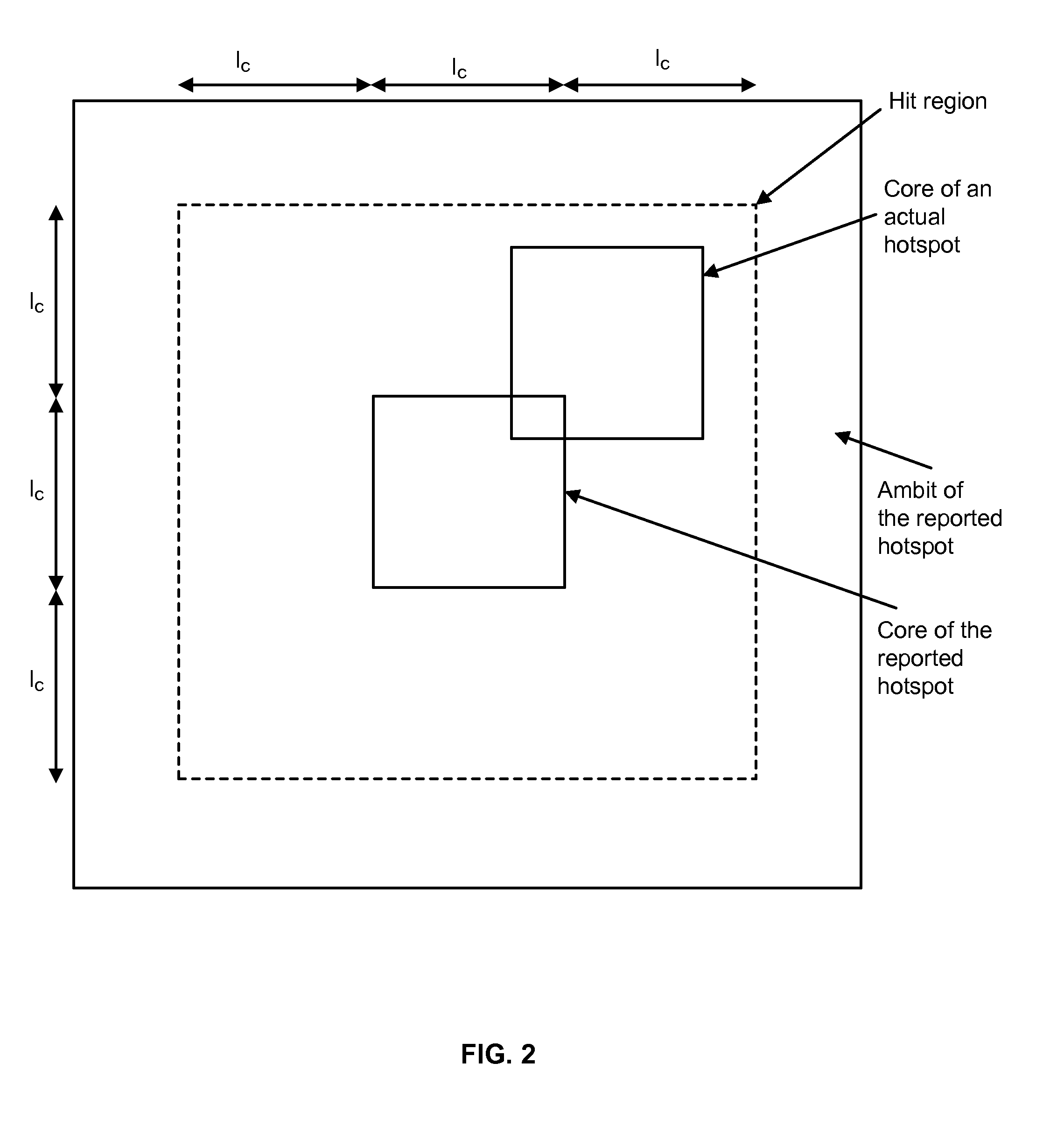
[0028]As used herein, a “hotspot” is a layout pattern that is at risk of inducing a printability issue at the fabrication stage. As used herein, a “hit” is an actual hotspot that has been correctly identified as a hotspot. Accuracy is the ratio of the number of total hits over the number of all actual hotspots. Additionally, as used herein, an “extra” is a non-hotspot that is mistake...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com