Method of global design closure at top level and driving of downstream implementation flow
a global design and implementation flow technology, applied in the field of top-down design methods and systems, can solve the problems of large and complex socs of the day, ips typically end up having complexities similar, and limited access and knowledge of the internal structure of the ip
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
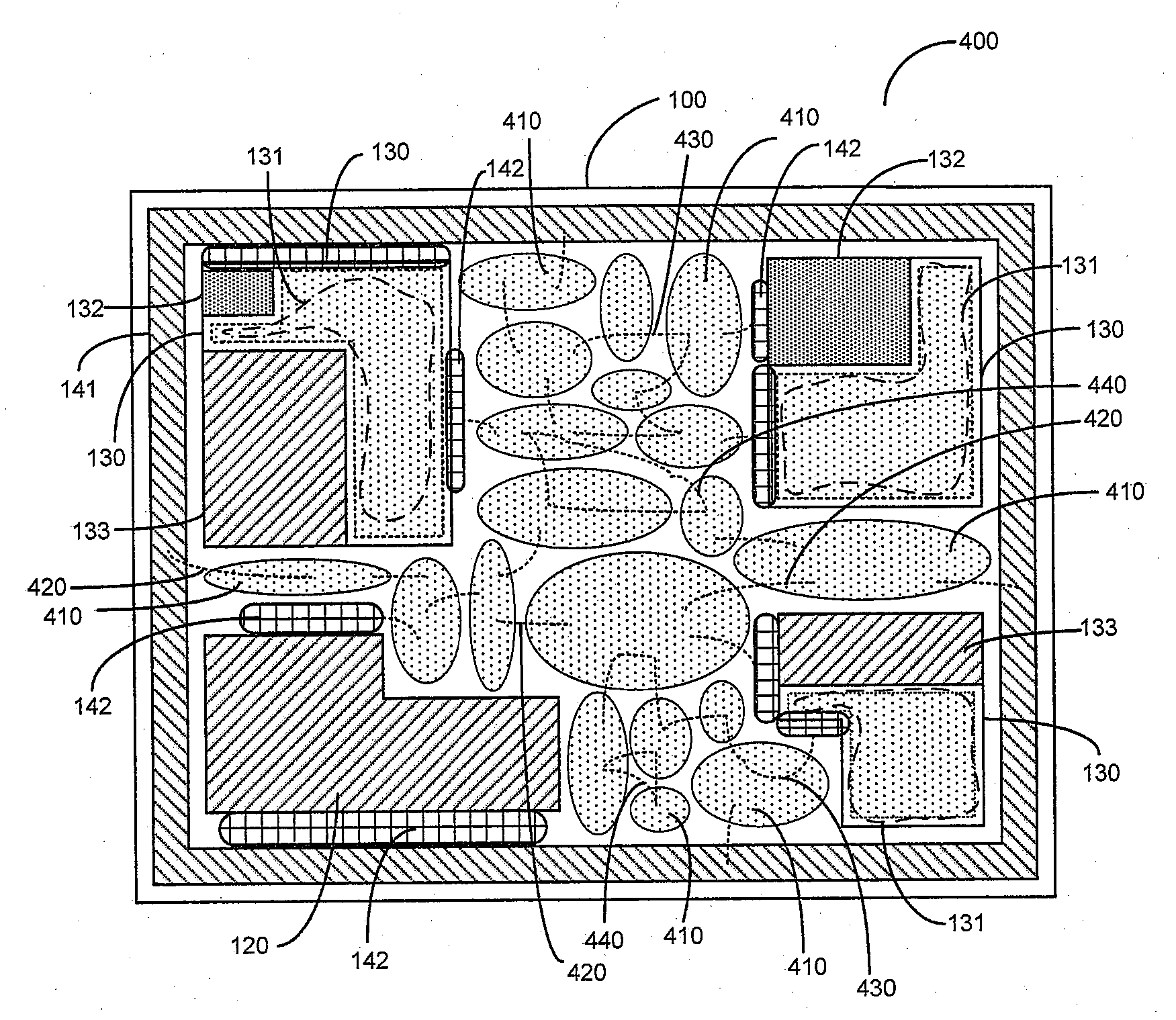
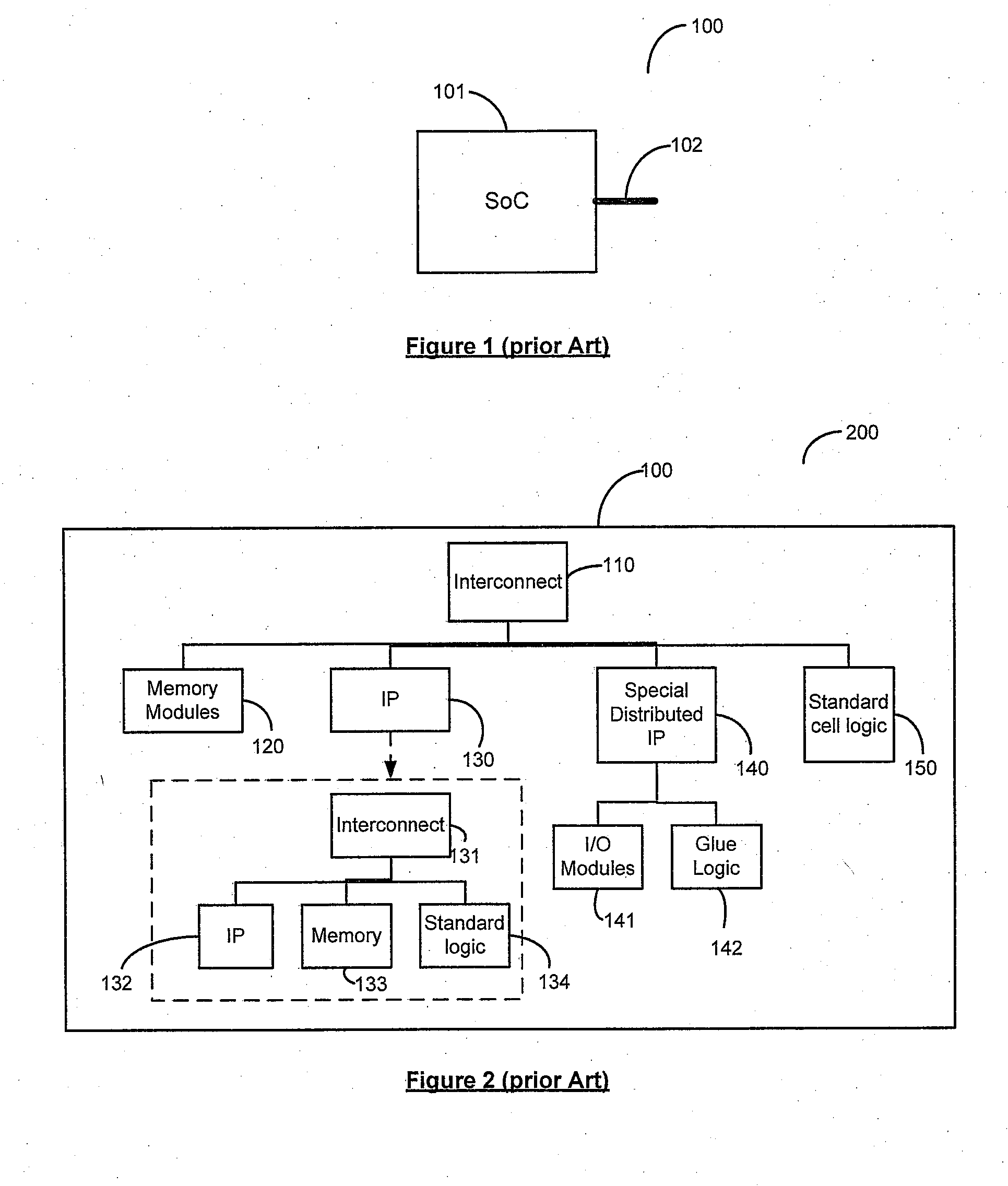
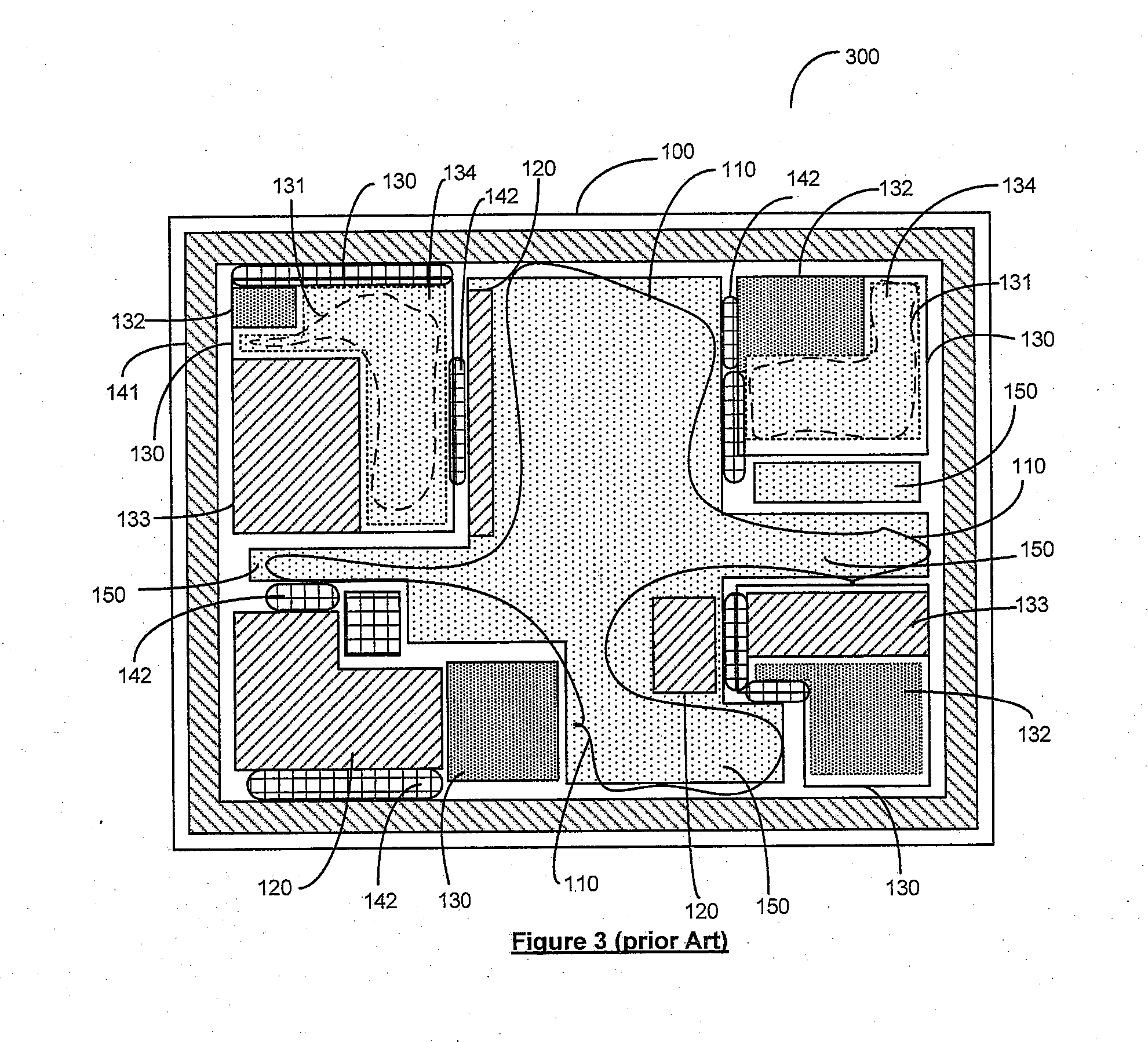
[0020]System-on-chip (SoC) 100 designs include large amount of interconnected intellectual property (IP) blocks 130, memory 120 and standard-cell logic 150, using complex bus fabrics 110. The IP blocks 130 are customized or hardened to the target constraints of SoC design 101 by fixing the core dimensions and shapes. Today SOC design-closure that validates design targets of area, timing, congestion and power constraints are accomplished post routing as a majority of validation problems are due to global-interconnect. This iterative and time consuming validation process towards the tail end of design cycle extends the design time and cost of design of the SOC.
[0021]A system and method are disclosed that allow the designers to achieve global design-closure and physical topology constraints, early in the design cycle, at much higher levels of abstraction. Using the results of this top-down global design-closure method the designers can guide the downstream, tools to achieve predictable...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com