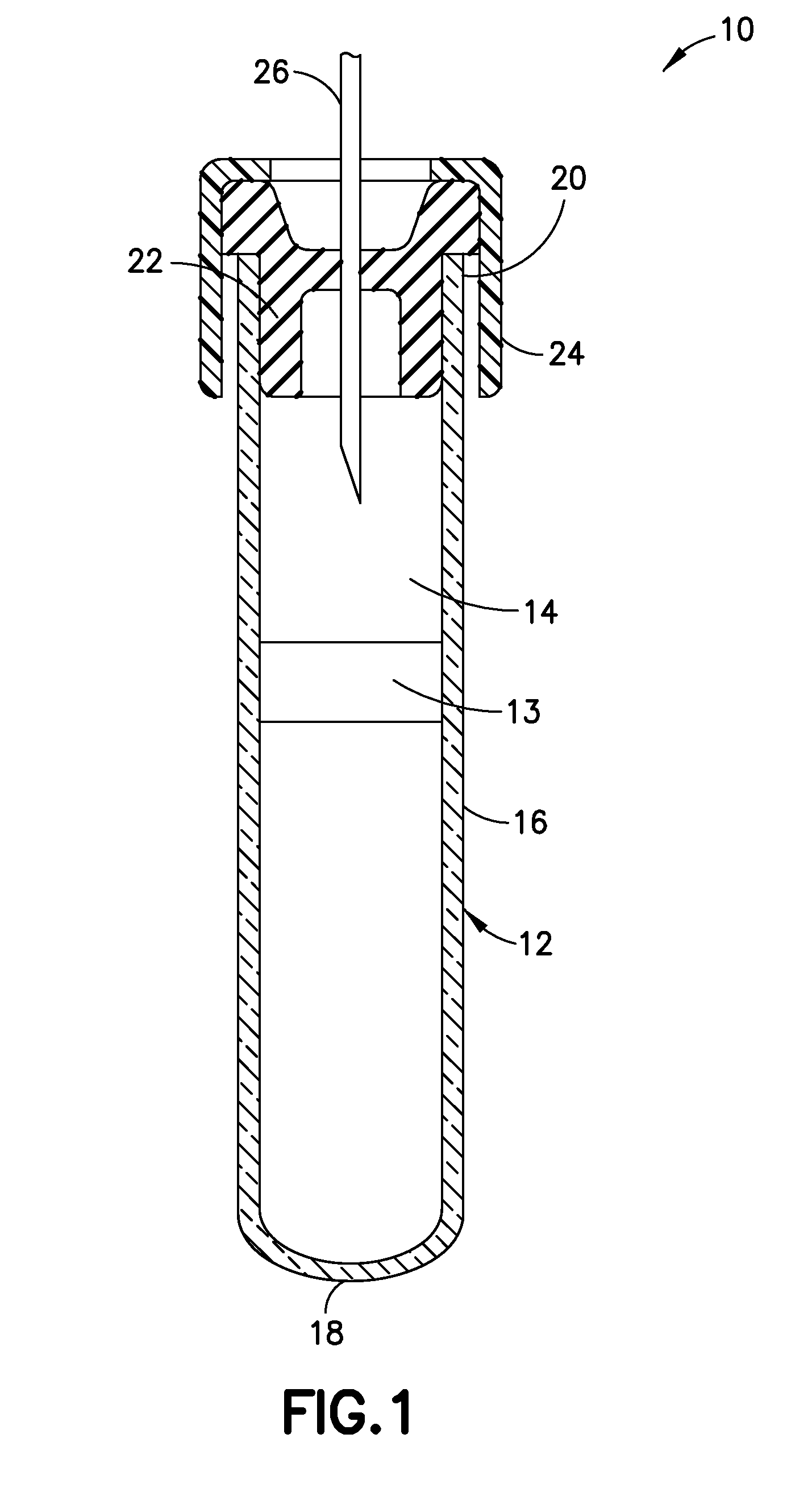
Blood collection devices containing contact pathway inhibition additives
a technology of contact pathway and additives, which is applied in the field of blood collection devices containing contact pathway inhibition additives, can solve the problems of cti-inclusion blood collection tubes that cannot be sterilized, amplification of accumulated factor xiia via involvement of kallikrein-kinin, and fibrin clot formation active thrombin generation and fibrin clot formation, etc., to achieve robust effect, prolong clotting time, and stabilize thrombin generation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
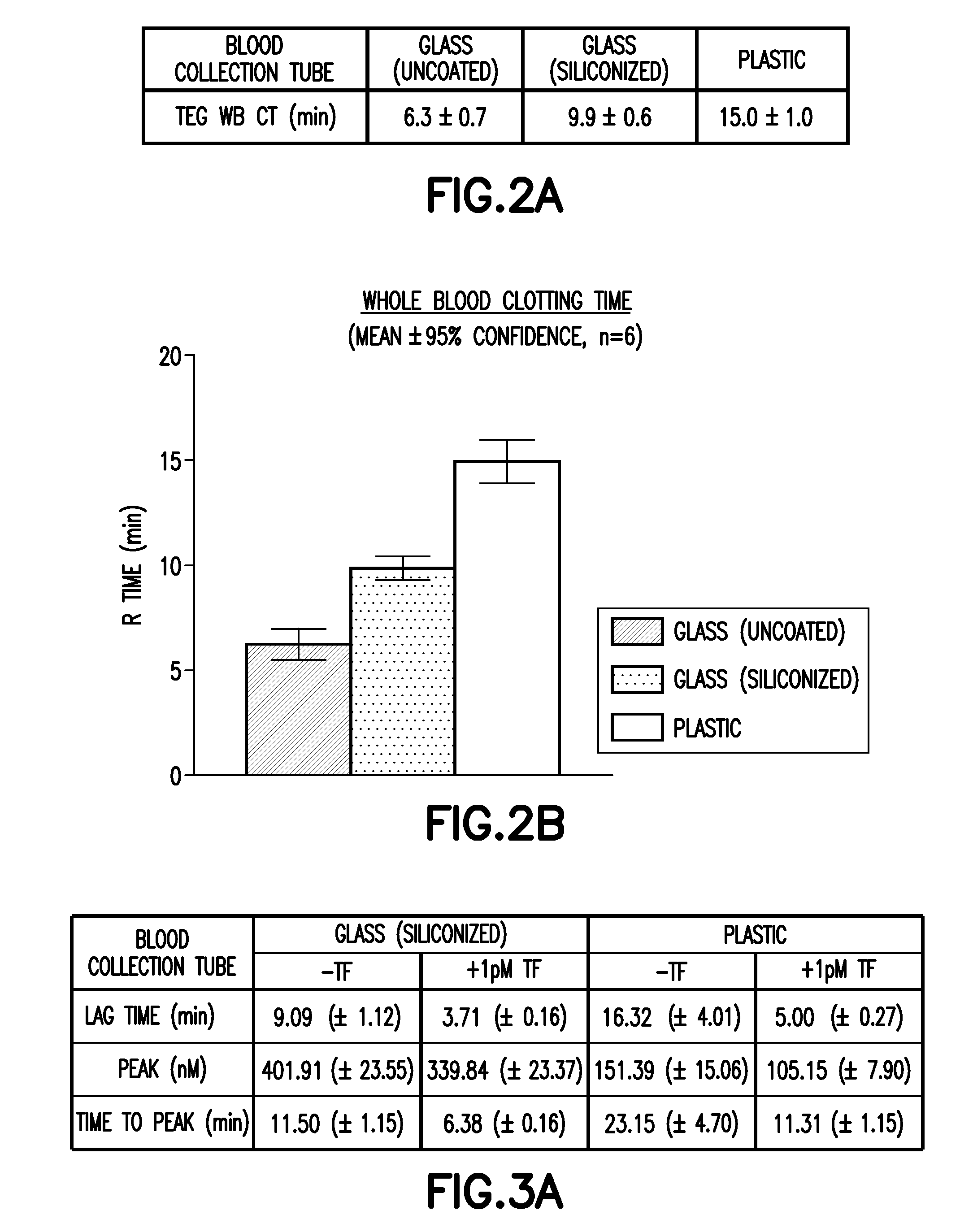
[0059]Thrombelastography (TEG) is useful in testing coagulation efficiency of whole blood (WB) and has found important applications during surgery and anesthesiology. The CAT assay performed in plasma is used to investigate patients with hypo- or hypercoagulopathies. These assays are highly sensitive relative to traditional coagulation tests and vulnerable to contact activation where accumulated factor XIIa in citrated specimens can markedly augment down-stream thrombin generation (TG). Accordingly, the effect of blood collection tubes comprised of different polymeric containment materials and the select use of targeted intrinsic pathway inhibitors on select outputs of the TEG and CAT assays are examined.
[0060]Citrated human WB is transferred from a blood collection bag into coated (siliconized) glass or plastic blood collection tubes, or uncoated glass, polypropylene (PP), polystyrene (PS), or polyethylene terephthalate (PET) conical bottom tubes, either alone or in the presence of...
example 2
[0063]As shown in FIG. 4(A) various concentrations of aprotinin were used in tests to determine the impact on whole blood clotting time using TEG. Citrated blood samples incubated in uncoated glass tubes were subjected to different concentrations of aprotinin measured in KIU (kallikrein inhibiting units) / mL and compared to blood samples without aprotinin but contained in siliconized glass tubes or plastic tubes. Results from this assay show that concentrations of aprotinin of 1000 KIU / mL and higher mitigate the contact coagulation pathway in uncoated glass tubes to a level equivalent to mitigation of the contact coagulation pathway in blood samples stored in siliconized glass tubes or plastic tubes.
[0064]CAT assay of samples with different amounts of aprotinin show that as aprotinin amounts is increased per sample, thrombin generation is decreased and delayed, even in the presence of CaCl2 and TF. This result is shown in FIG. 4(B) for siliconized glass (top panel) and plastic tubes ...
example 3
[0065]The aPTT assay was used to show that aprotinin mitigated the contact coagulation pathway in a manner equivalent to inhibition by CTI and anti-Factor XI antibody. As shown in FIG. 6, increased amounts of aprotinin prolong the time to generate thrombin that or equivalent to or greater than the time to generate thrombin in the presence of CTI and anti-Factor XI antibody. FIG. 6 (lower panels) show that using the identical samples in tests that monitor the TF coagulation pathway exclusively, the thrombin generation is unaffected by aprotinin, CTI or anti-Factor XI antibody. This verifies that aprotinin exclusively suppresses thrombin formation through the contact coagulation pathway but not through the TF pathway.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com