Omega-9 quality brassica juncea
a brassica juncea, omega technology, applied in the field of improved brassica species, can solve the problems of reducing the marketable value of oil, shortening the operation time, and not all fatty acids in vegetable oil are equally vulnerable to high temperature and oxidation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
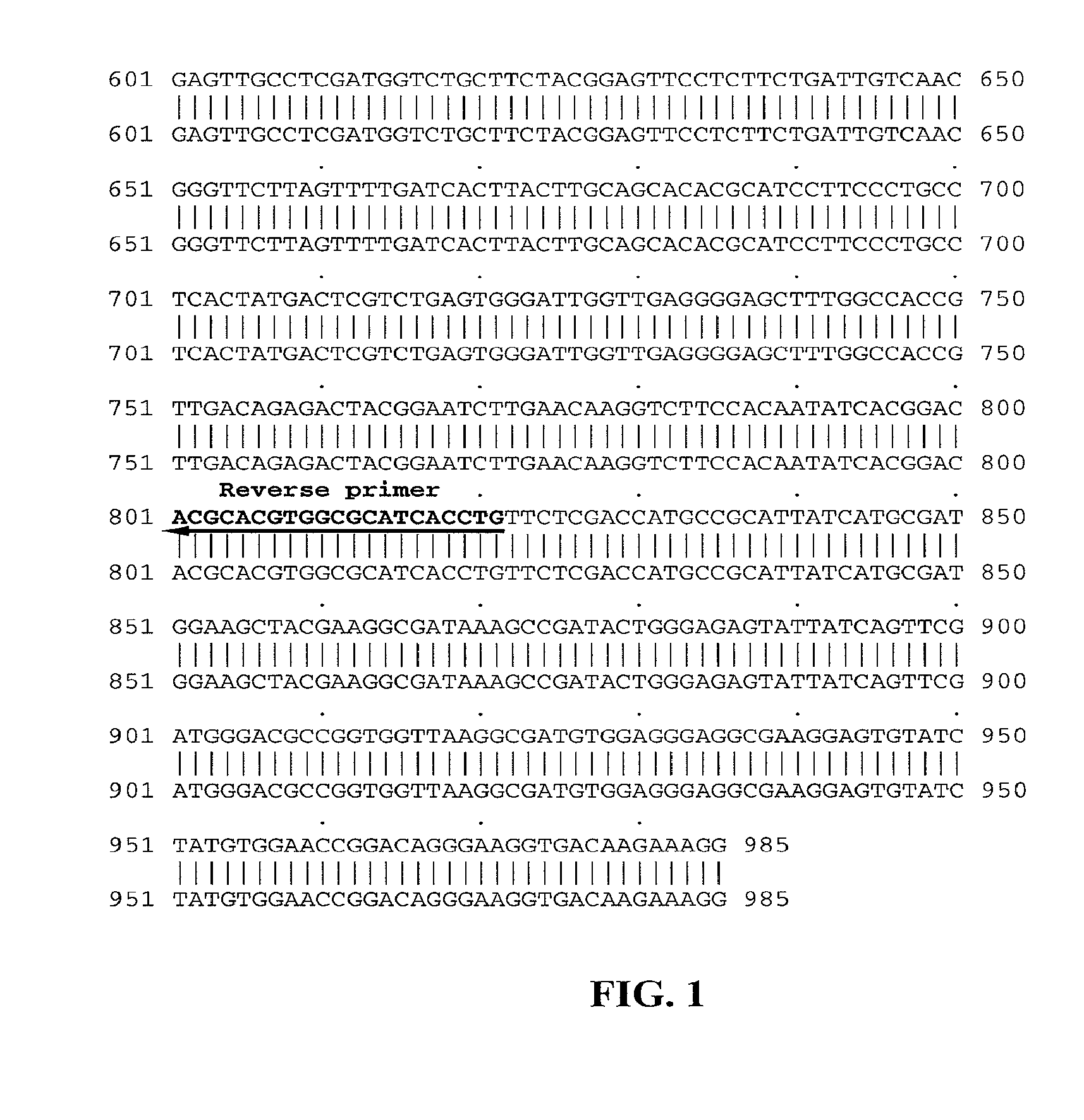
[0137]Referring to FIG. 1, one or more backcrosses (BC3 and BC4) between the high oleic—low linolenic selections and B. juncea parents (Zem1, Zem2 and ZE Skorospelka) in order to fully recover B. juncea genetic background. Only zero erucic B. juncea lines were used in the backcrossing program since this would allow for full expression of the fad2 and fad3 mutant alleles in a non competitive situation with the FAE gene(s).
[0138]After each advanced back-cross (for example BC3, BC4) and subsequent self pollination (for example BC3F2, BC4F2), progeny seed is subjected first to tissue screening for presence of fad2a and fad3a genes (using markers as described in more detail herein), then grown on to flowering to be used in the subsequent backcrosses. Harvested seed from selected lines is subjected to oil profile analysis using half seed, non-destructive single whole seed NIR analysis, or single seed NIR (FTNIR). Subsequently, samples containing increased oleic levels, and red...
example 2
Development of B. Juncea-Specific Markers
[0145]DNA Markers are developed that can detect presence of the BB genomic DNA relevant to FAD2b and other available sequences from B. nigra and B. juncea (representing the BB genome). Double haploid mapping populations are developed for marker development. In addition, DNA (SSR and SNP) markers are developed from the known B-genome sequences. These markers are able to confirm the extent of recovery of B. juncea background in the converted lines.
[0146]A total of 1931 B. napus SSR markers, predominantly containing, di- and tri-nucleotide repeat motifs, are available for parental screening. These markers are currently being screened on a panel of Brassica lines that belong to B. juncea (Zem1, Zem2 and ZE Skorospelka lines), Omega-9 B. napus, B. rapa, B. nigra, and B. oleracea. This screening provides two types of information. First, since these SSR markers were developed from B. napus genome, the screening provides information on their utility ...
example 3
Recovery and Determination of B Genome
[0151]Self-pollinated and doubled haploid plants exhibiting seed oil profile of high oleic and low linolenic acids, as previously described, are screened using the markers selected for the BB genome. The BB genome is confirmed present in the converted lines. These mutant B. juncea lines also show a decrease (or complete absence of) in the number of positive C genome markers selected for B. napus. These profiles are further enhanced by additional backcrosses and selfing techniques known in the art which improve the agronomics of the line, e.g., reduce yield drag, reduce pod shatter, alter maturity for various growing zones, increase stress tolerance, increase disease resistance, and the like.
[0152]Three different methods are used for the determination of B genome in the self-pollinated and DH progeny from B. napus and B. juncea interspecific crosses exhibiting desired seed oil profile.
A) Molecular Markers
[0153]Molecular markers capable of detecti...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| speeds | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com