Variable resistive element and nonvolatile semiconductor memory device
a resistive element and non-volatile technology, applied in the direction of semiconductor devices, bulk negative resistance effect devices, electrical equipment, etc., can solve the problems of not always employing material which can be easily used in the manufacturing process, difficult to perform the miniaturization process to provide high-integrated memory with this kind of material, etc., to reduce the variation in parasitic resistance due to process variation of the electrode, and reduce the variation in resistance change characteristics (switching characteristics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
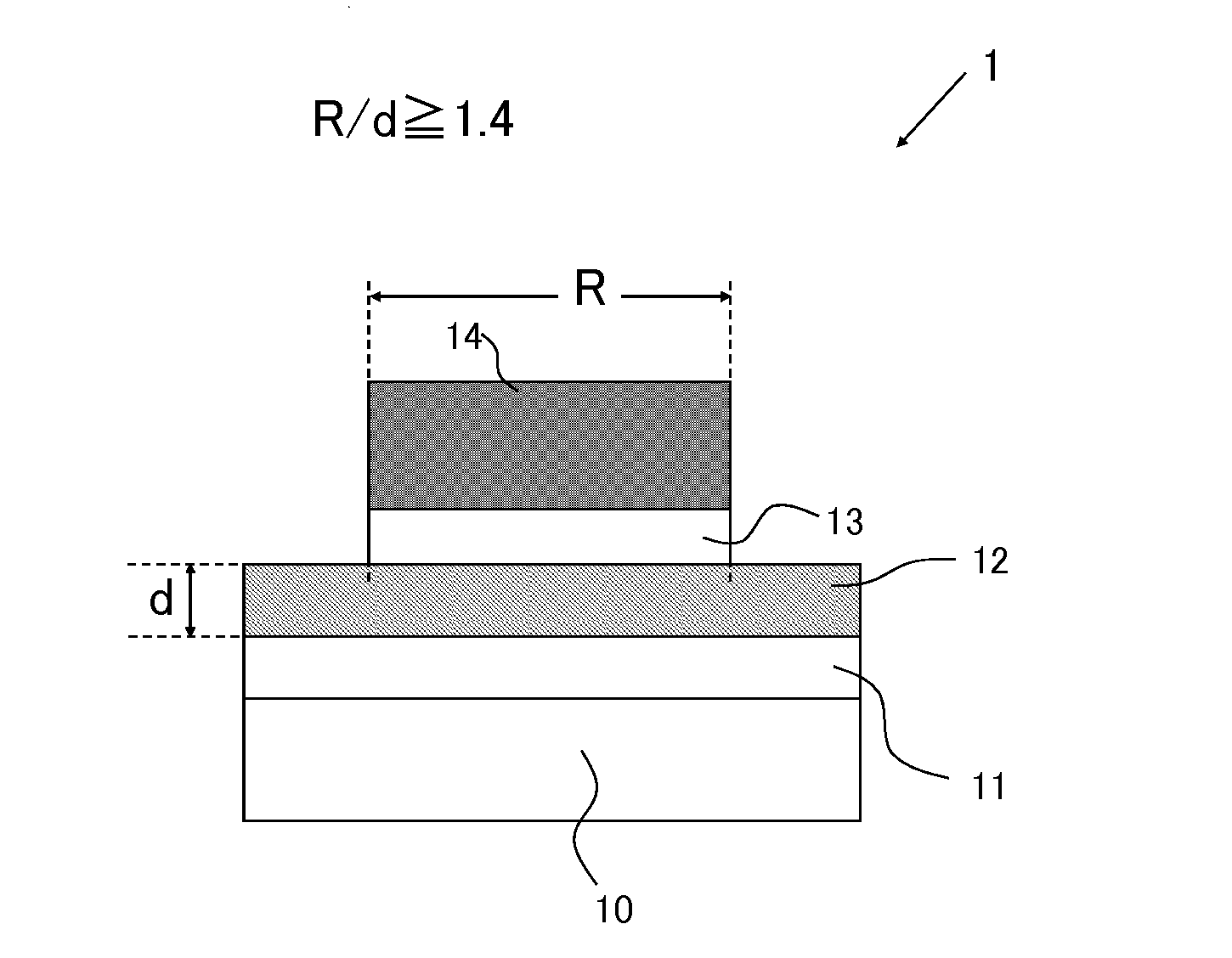
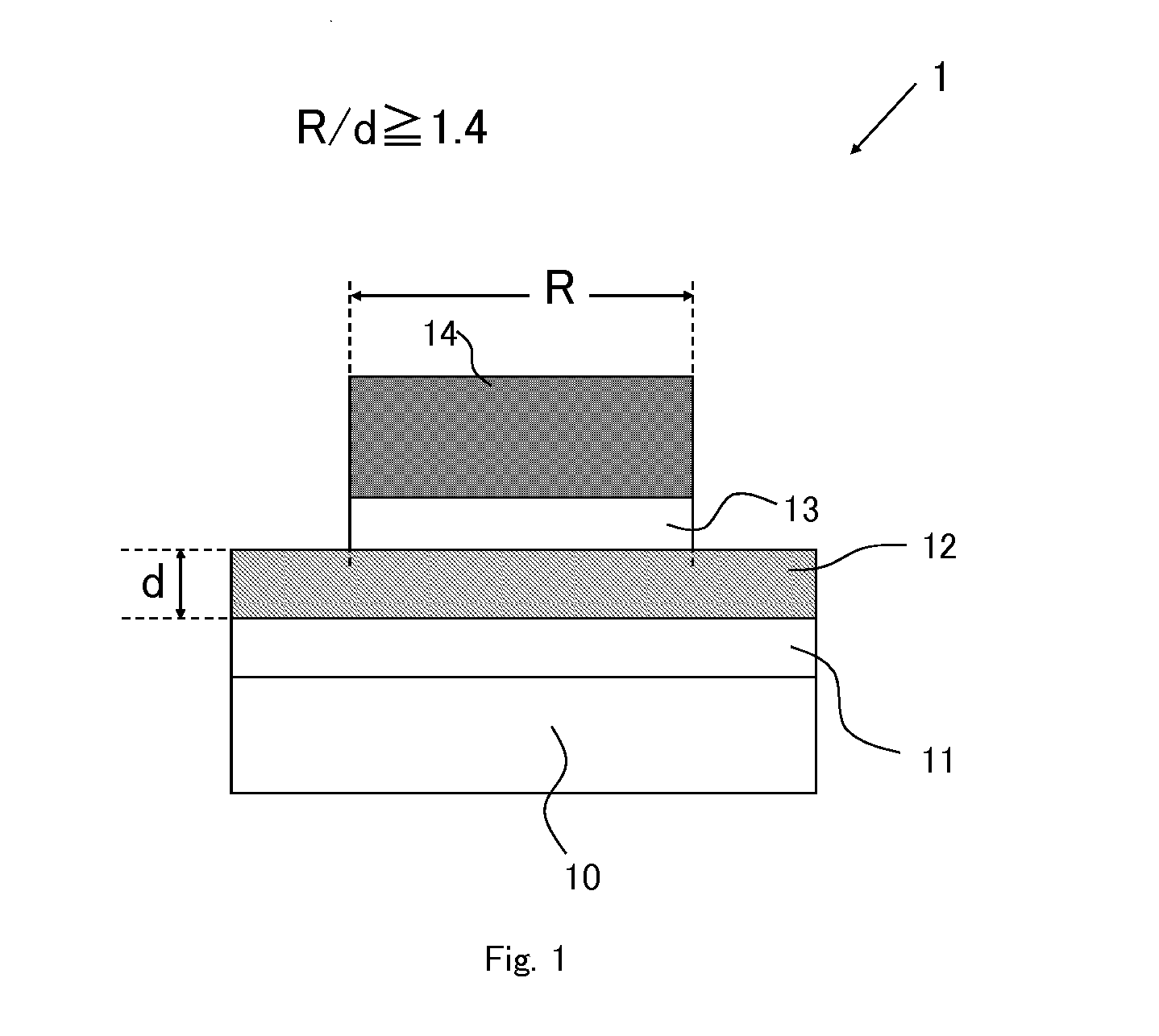
[0066]FIG. 1 is a sectional view schematically illustrating a structure of a variable resistive element 1 (hereinafter appropriately referred to as a “present element 1”) according to one embodiment of the present invention. In the drawings described below, essential parts are emphasized for the sake of convenience of description, and a dimensional ratio of each component of the element and an actual dimensional ratio do not agree with each other in some cases.
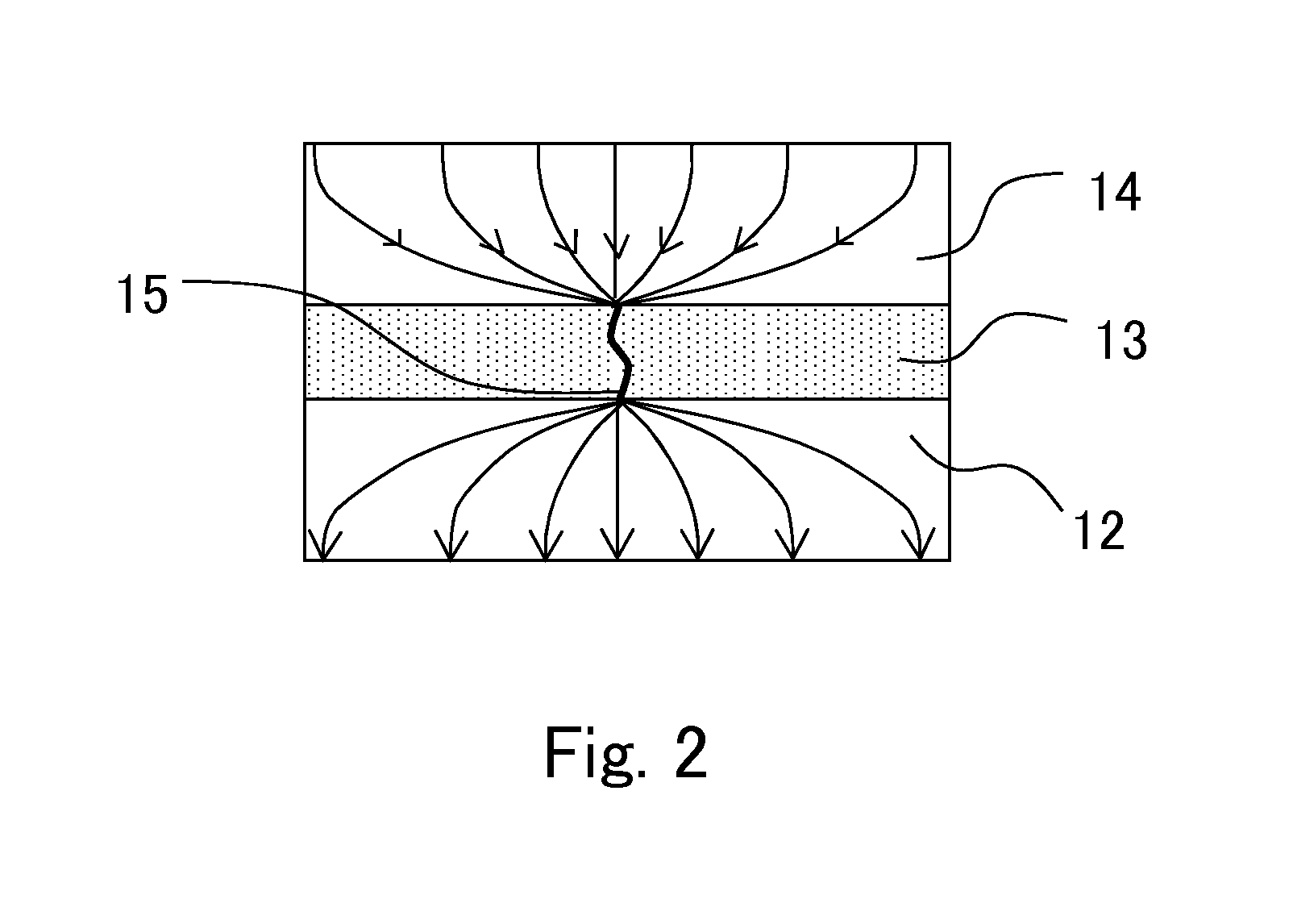
[0067]The variable resistive element 1 includes a second electrode (lower electrode) 12, a variable resistor 13, and a first electrode (upper electrode) 14, those of which are deposited and patterned in this order on an insulating film 11 formed on a substrate 10. The variable resistor 13 includes a layer which is made of a metal oxide or a metal oxynitride.
[0068]In the present embodiment, hafnium oxide (HfOX) that has a large bandgap and that is an insulating layer is selected to be used for the metal oxide serving as a varia...
second embodiment
[0098]FIG. 11 illustrates a non-volatile semiconductor memory device using the present elements 1 to 3 described above. FIG. 11 is a circuit block diagram illustrating a schematic configuration of a non-volatile semiconductor memory device 20 (hereinafter referred to as a “present device 20” as needed) according to one embodiment of the present invention. As illustrated in FIG. 11, the present device 20 includes a memory cell array 21, a control circuit 22, a voltage generating circuit 23, a word line decoder 24, a bit line decoder 25, a source line decoder 26, and a read circuit 27.
[0099]The memory cell array 21 includes a plurality of memory cells, each of which includes any one of the present elements 1 to 3 as a memory element, arranged in at least one of a row direction and a column direction in a matrix. The memory cells belonging to the same column are connected by a bit line extending in the column direction, and the memory cells belonging to the same row are connected by a ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com