Method of determining threshold for detection of peak frequency in radar and object information producing apparatus using the same
a technology of object information and threshold, which is applied in the direction of reradiation, measurement devices, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of large change in the threshold of peak detecting, instability in detecting the target object, and generation of leakage noise, so as to improve the accuracy of producing information and high precision. , the effect of enhancing the accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
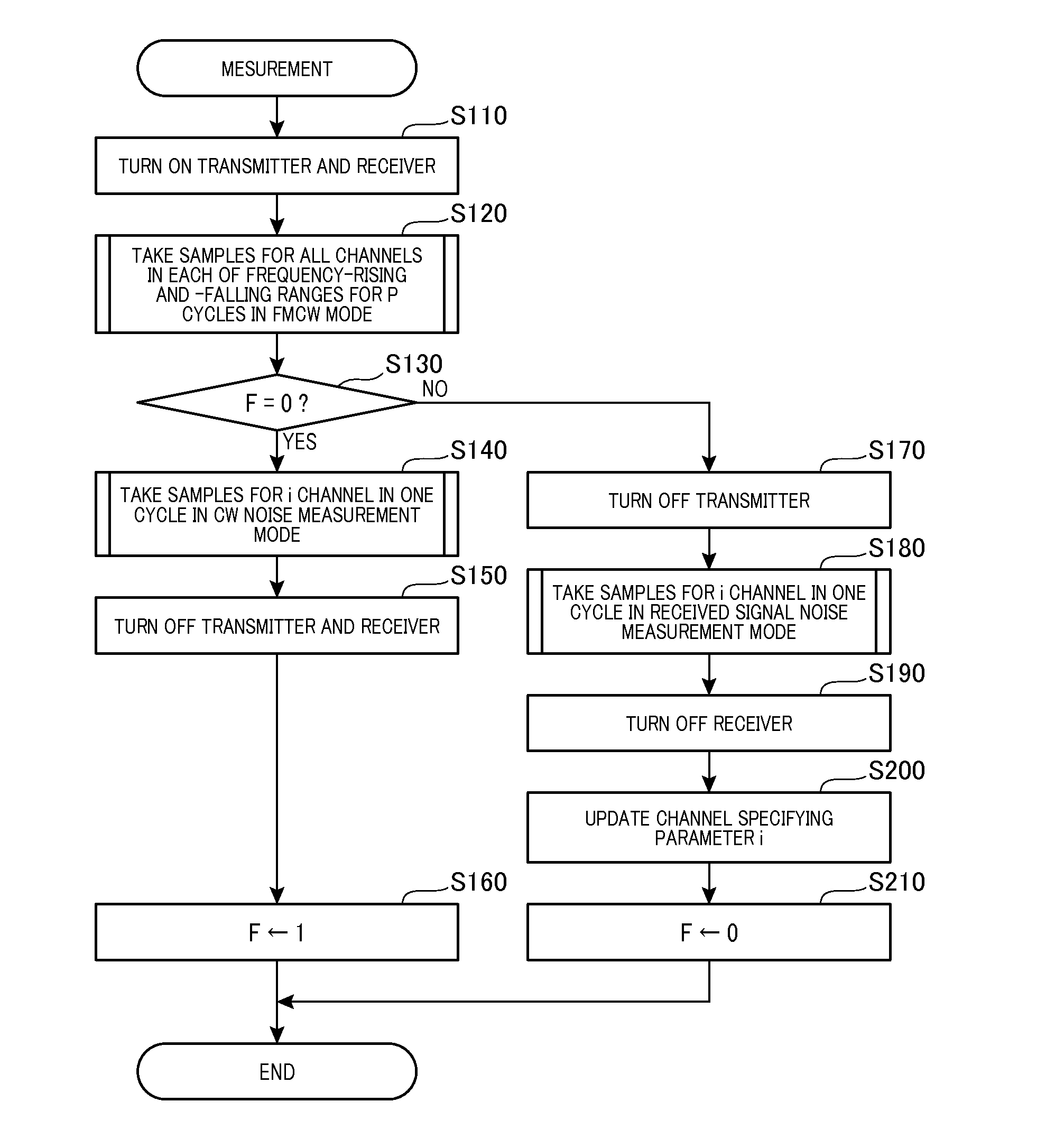
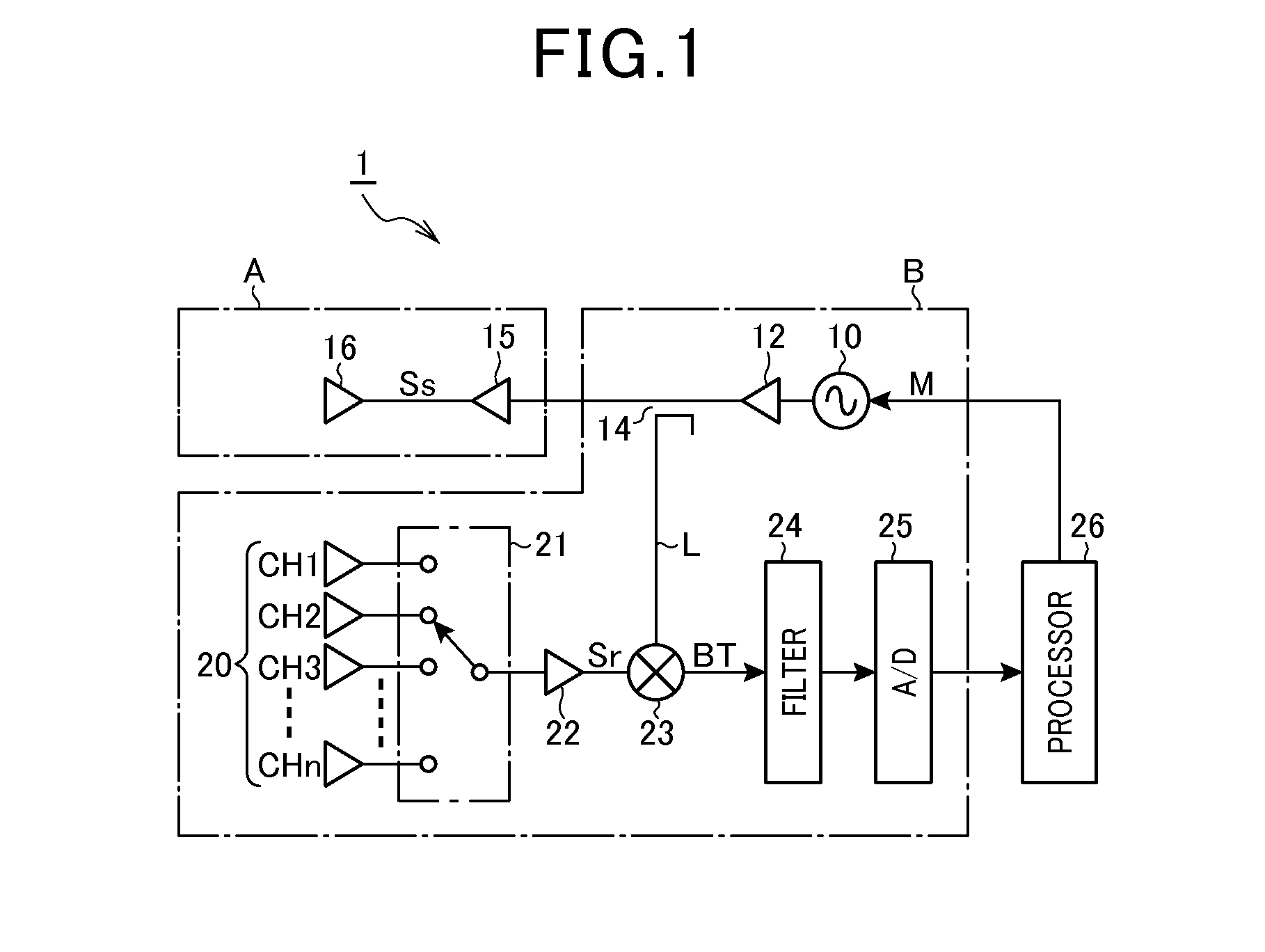
[0046]Referring now to the drawings, particularly to FIG. 1, there is shown a radar system 1 according to the present invention which may be employed in automotive vehicles to detect or track a target object present in a frontal detectable range. The radar system 1 is designed as a FMCW (Frequency Modulated Continuous Wave) type of millimeter-wave radar which transmits a frequency-modulated radar wave in a millimeter band, receives a return thereof, and identifies a target such as a preceding vehicle or a roadside object to produce information about the target.
[0047]The radar system 1 includes an oscillator 10, an amplifier 12, a divider (also called a splitter) 14, an amplifier 15, a transmitter antenna 16, and a receiver antenna assembly 20. The oscillator 10 produces a high-frequency signal in a millimeter band (e.g., 76.5 GHz) and changes an oscillating frequency as a function of the level of a modulation signal M. The amplifier 12 amplifies the high-frequency signal, as produce...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com