Device for filtering lubricants of a wind turbine transmission
a technology for filtering lubricants and wind turbines, which is applied in the direction of lubricant mounting/connection, machines/engines, gearing details, etc., can solve the problems of crack propagation and fracture of material, wind turbine transmissions are exposed to adverse effects of water, and the maintenance cost of hydrocarbon adsorbers is low
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
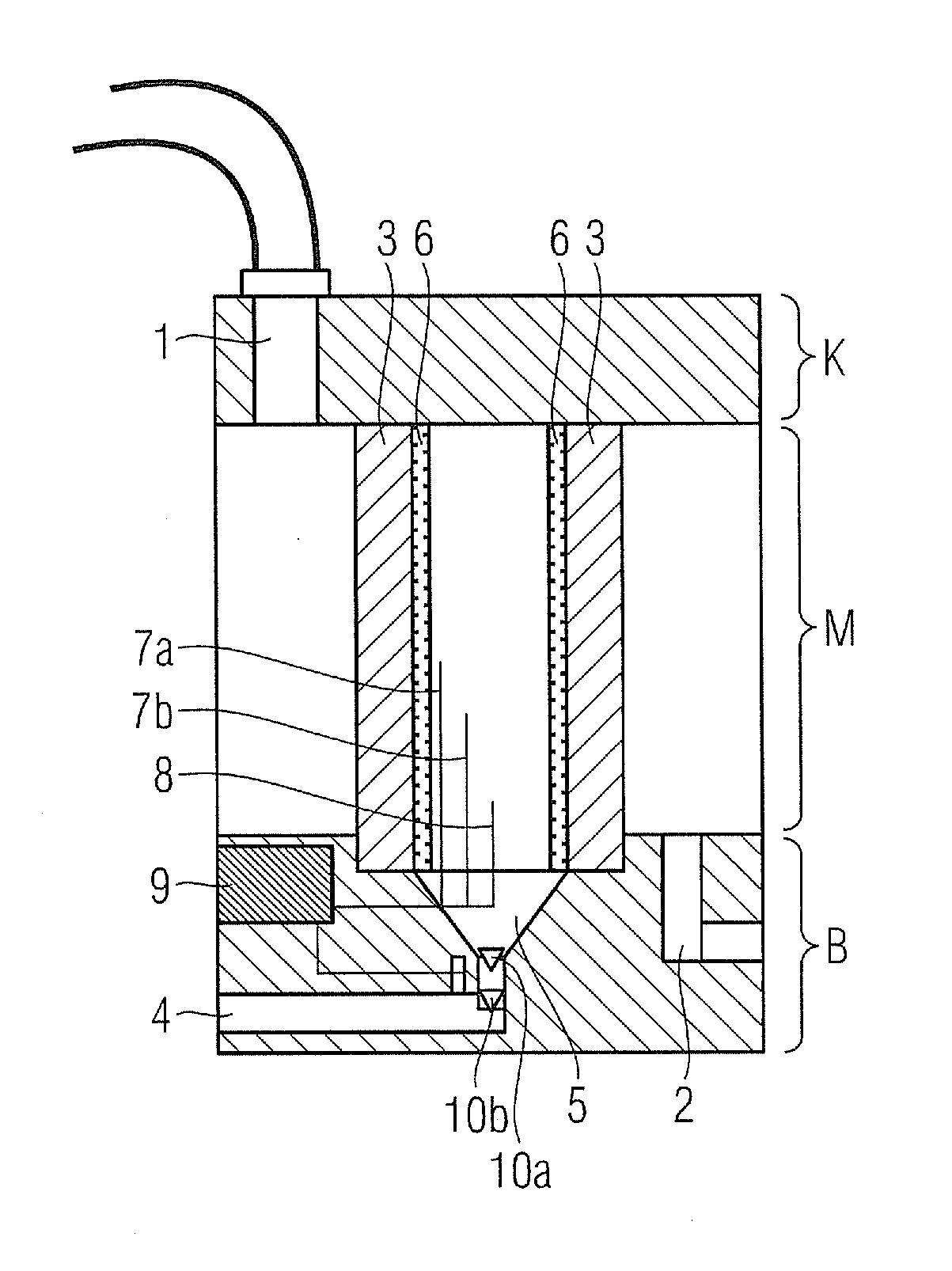
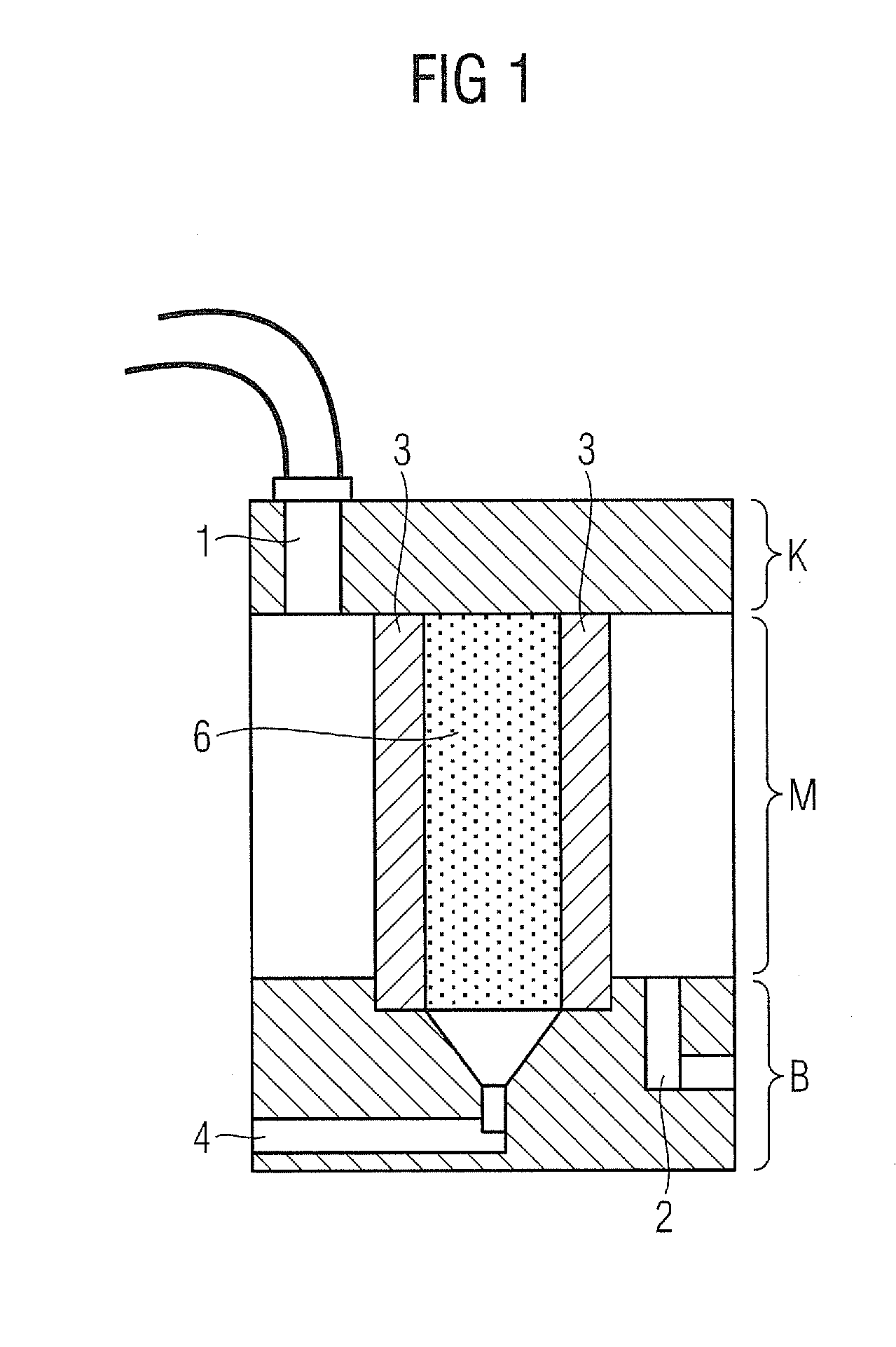
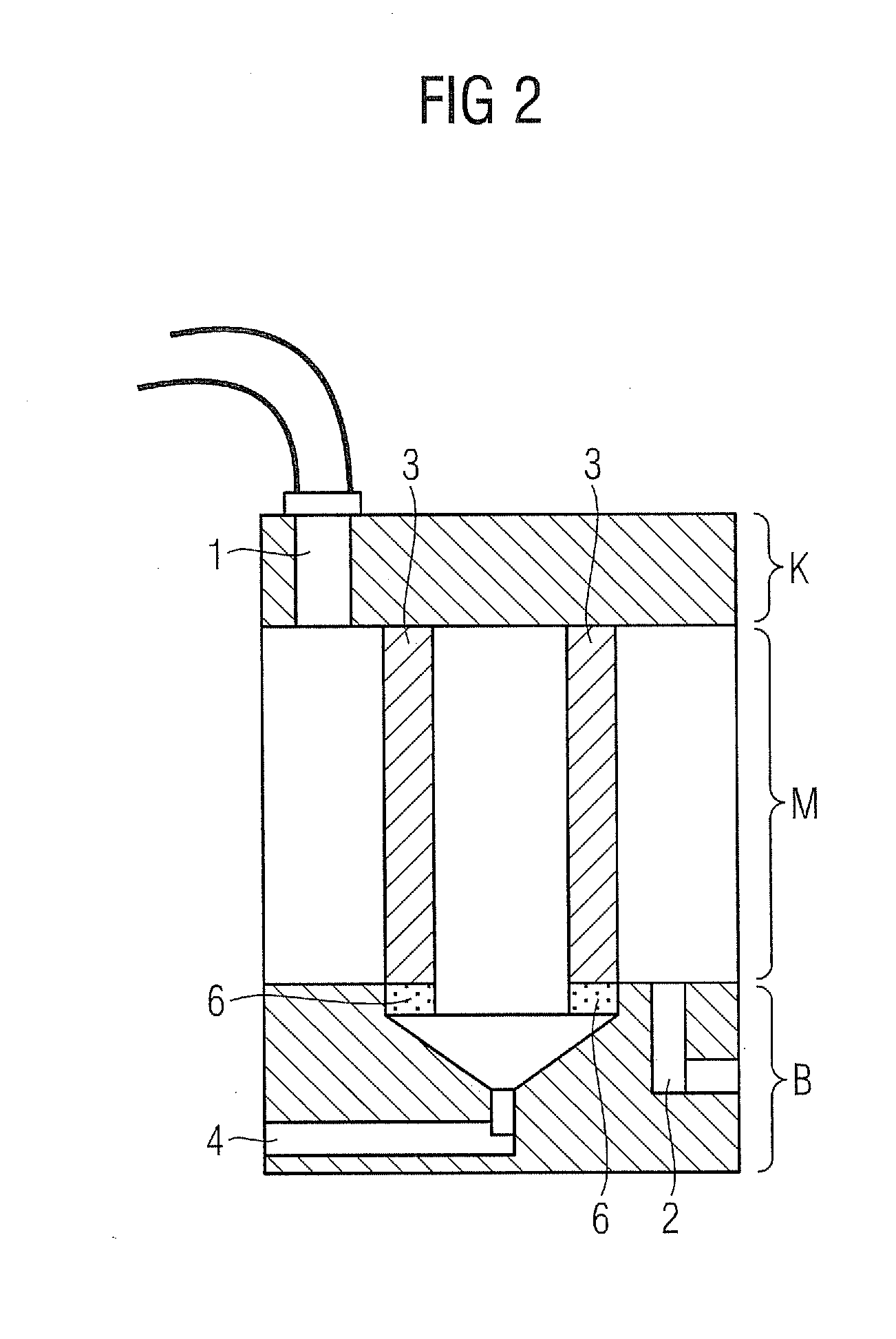
[0024]As shown in FIG. 1, the device according to the invention has a lubricant inlet (1), e.g. for transmission oil. The transmission oil that is to be filtered arrives in the device via an oil inlet connection piece or manifold (1) and is carried through the device to the oil outlet (2), which is situated downstream at the lower end of the device.
[0025]The transmission oil is preferably carried though the filter device under pressure from a pump, but alternatively can flow through the device without pressure and solely due to gravity by virtue of the relative arrangement of oil inlet (1) and oil outlet (2).
[0026]A filter element (3) is arranged between the oil inlet (1) and the oil outlet (2). The filter element (3) is designed to separate water from transmission oil or other lubricants. For this purpose, the filter element (3) features a hydrophobic fibrous braided fabric and / or a hydrophobic mesh-type material.
[0027]The filter element (3) is designed in the shape of a cylinder a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com