Pharmaceutical Composition for the Treatment of Solar Urticaria
a technology for solar urticaria and pharmaceutical compositions, applied in the field of local anesthesia, can solve the problems of inability to establish a hypothesis, poorly understood pathogenesis of solar urticaria, and largely unknown how and why mast cells are activated in patients, and achieve the effect of low side effects and convenient patient treatmen
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
1.1. Subjects
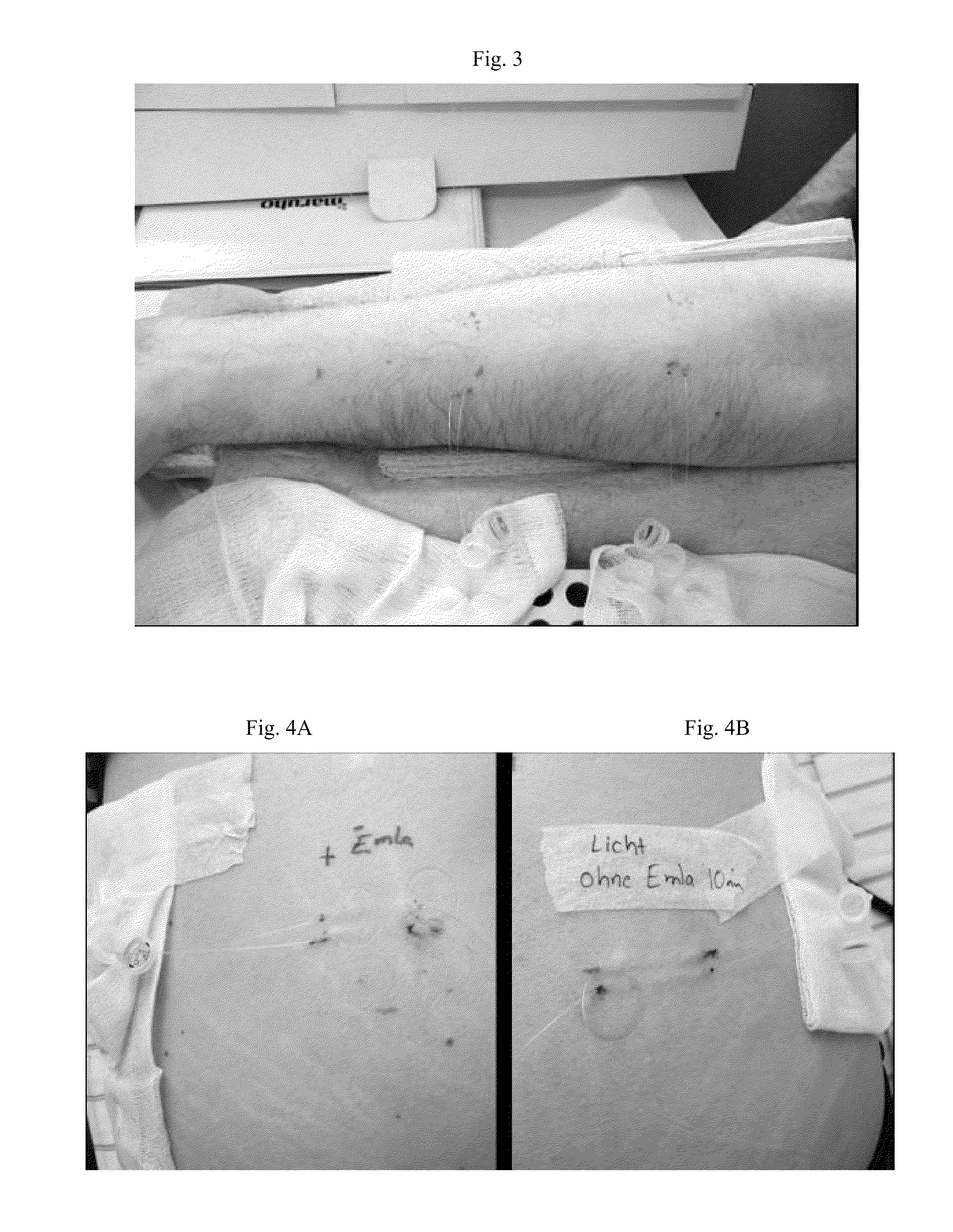
[0054]Subjects to this experiment were two solar urticaria patients, one male (aged 29) and one female (aged 36). Both patients were sensitive to UVA-radiation (FIG. 1).
1.2. Pharmaceutical Preparation
[0055]EMLA® is a topical anaesthetic cream (a eutectic mixture of lidocaine and prilocaine) widely used for superficial anaesthesia of the skin before taking blood samples or prior to superficial skin surgery. 1 g of EMLA® cream (Astra Zeneca) contains 25 mg lidocaine (i.e. 2.5% by weight) and 25 mg prilocaine (i.e. 2.5% by weight).
1.3. Experimental Protocol
[0056]The patients with solar urticaria and action spectrum to UVA underwent skin microdialysis after UVA provocation.
[0057]Microdialysis is a well-established technique for the continuous sampling of small, water-soluble molecules within the extracellular fluid space in vivo. It has the advantage over other sampling techniques in that it can be used in intact tissues to follow temporal variations in the generation and t...
example 2
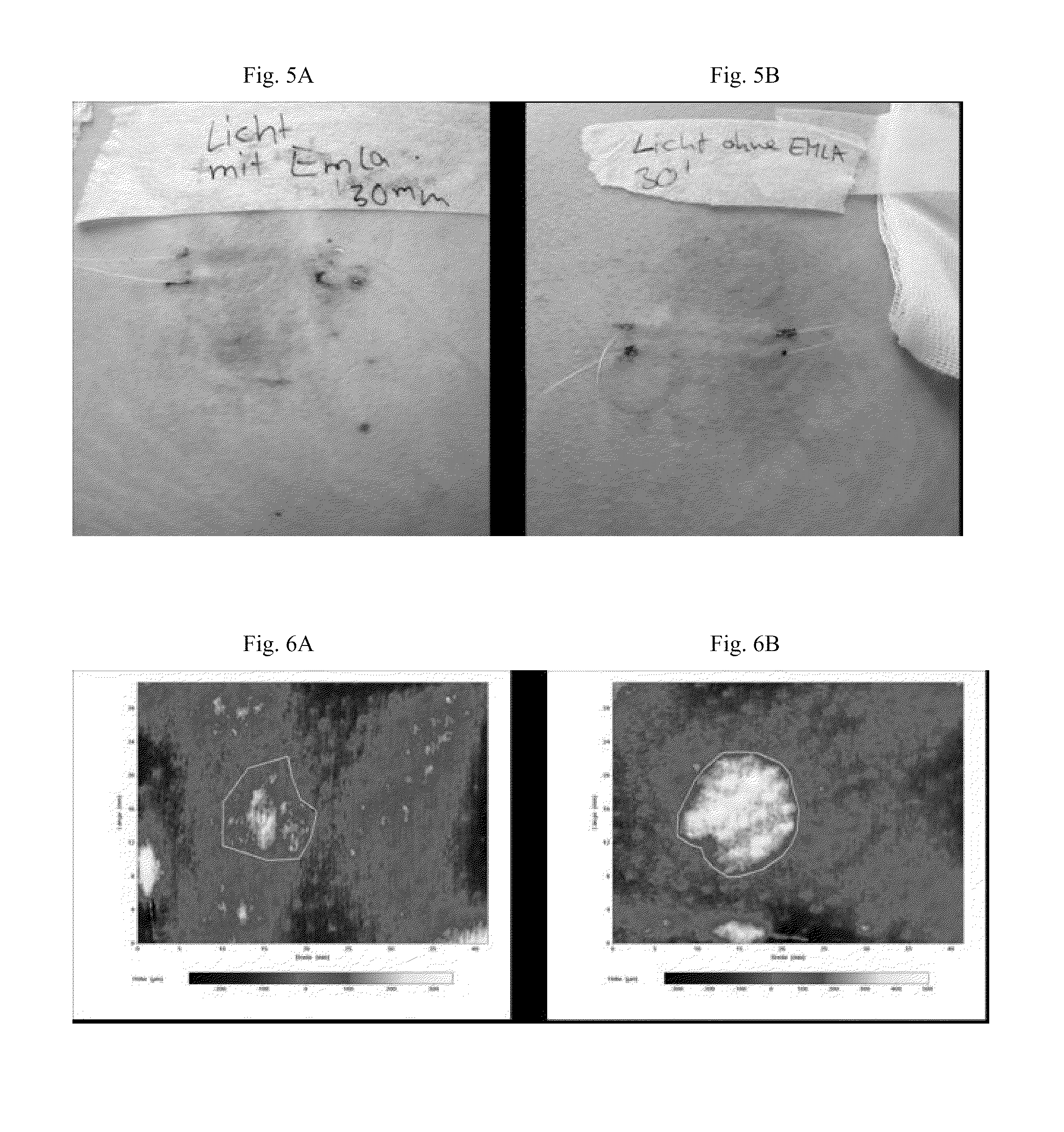
[0062]For comparison study, UV-provocation (and microdialysis) was performed a second time in skin without previous sun exposure, namely the buttocks. Thus, the female patient of Example 1 underwent the same procedure as described in Example 1 for the volar forearm again on the buttocks. A control area was irradiated with UVA but without prior application of EMLA® (FIG. 4).
[0063]Fifteen min after UVA radiation an erythema developed in both skin sites previously treated with and without EMLA®. A whealing reaction was seen after 15 min in the non-EMLA® skin site and after 20 min in the EMLA®-treated skin area, but less pronounced. After 30 min the clinical symptoms (wheal and erythema size) were much more pronounced in the non-EMLA® skin site compared to the anaesthesized site (FIG. 5). The kinetics of skin lesion development after 30 min was also documented by digital time lapse photography (FIG. 6).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| digital time lapse photography | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| provocation time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| provocation time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com