Survival predictor for diffuse large b cell lymphoma
a survival predictor technology, applied in the field of survival predictors of diffuse large b cell lymphoma, can solve the problems of inferior survival with chop therapy, bcl-2 or low expression of bcl-6, and unknown molecular basis of response or resistance to this therapy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0097]This example demonstrates that significant differences were found between the survival outcomes for R-CHOP treated ABC DLBCL and GCB DLBCL patients and that survival outcome correlated with three prognostic gene expression signatures.
[0098]Pre-treatment tumor biopsy specimens and clinical data were obtained from 414 patients with de novo DLBCL treated at 10 institutions in North America and Europe and studied according to a protocol approved by the National Cancer Institute's Institutional Review Board. Patients included in a “LLMP CHOP cohort” of 181 patients were treated with anthracycline-based combinations, most often cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (CHOP) or similar regimens, as previously described (Rosenwald et al., N. Engl. J. Med., 346: 1937-47 (2002)). The remaining 233 patients constituted an R-CHOP cohort that received similar chemotherapy plus Rituximab. The median follow-up in the R-CHOP cohort was 2.1 years (2.8 years for survivors). A...
example 2
[0108]This example demonstrates the development of GCB, stromal-1, and stromal-2 survival signatures and a related multivariate model of survival for R-CHOP-treated DLBCL.
[0109]Unless otherwise indicated, patient cohorts and methods of gene expression analysis are as described in Example 1.
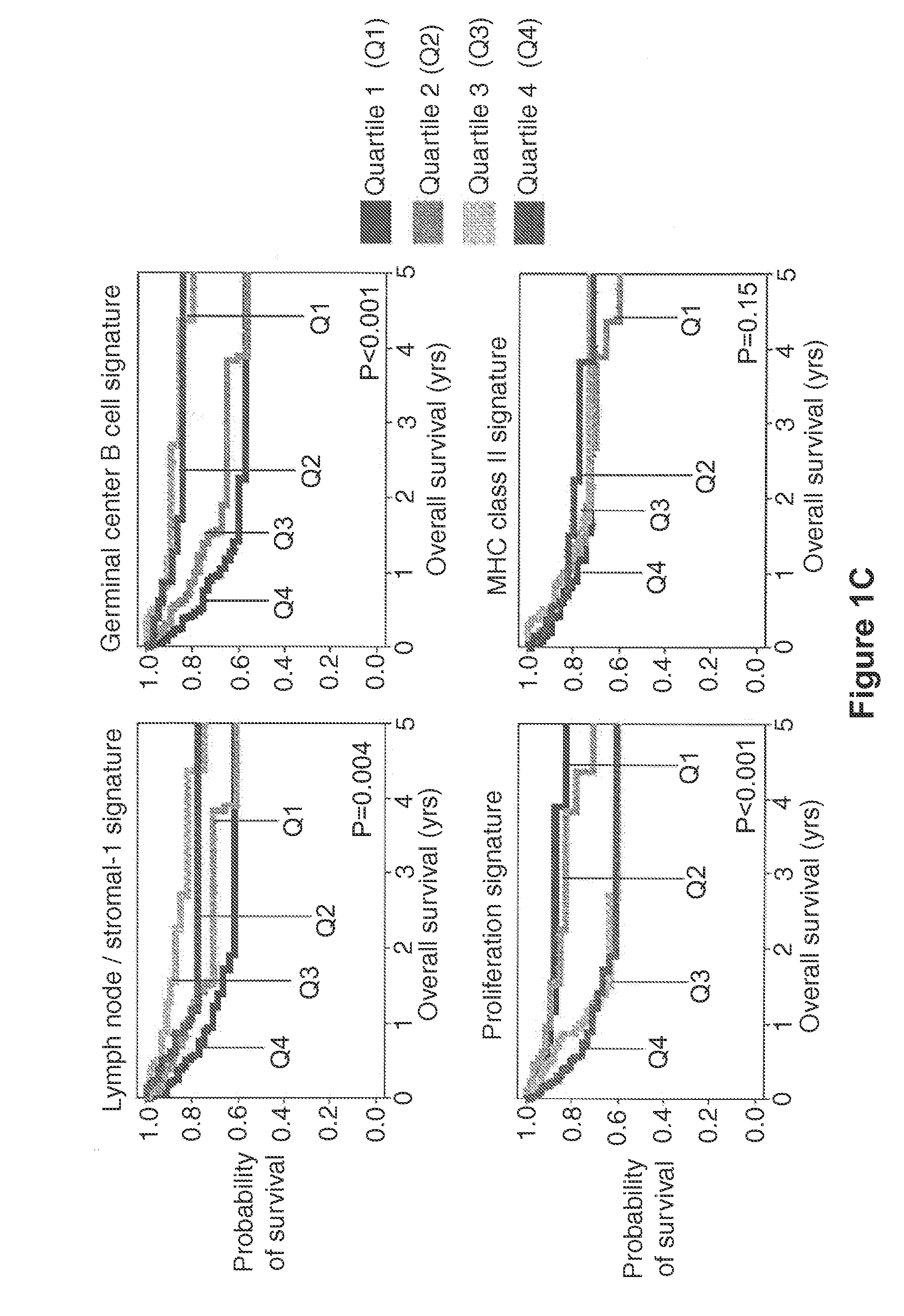
[0110]In the LLMPP CHOP cohort data, 936 genes were identified as associated with poor prognosis p0.6 and containing myc was identified as the proliferation survival signature. 1396 genes were identified as associated with favorable outcome. The largest cluster with average correlation of >0.6 and containing BCL6 was identified as the germinal center B cell (GCB) survival signature. A cluster with average correlation of >0.6 and containing FM was identified as the stromal-1 survival signature, whereas another cluster with average correlation of >0.6 containing HLADRA was identified as the MHC class II survival signature. The expression levels of genes within each signature were then averaged to cr...
example 3
[0117]This example demonstrates the use of a survival predictor score to predict the probability of progression free and overall survival outcomes at a period of time t following R-CHOP treatment in accordance with the invention.
[0118]RNA is isolated from a patient's DLBCL biopsy and hybridized to a U133+ array from Affymetrix (Santa Clara, Calif.). The array is scanned, and MAS 5.0 algorithm is applied to obtain signal values normalized to a target intensity of 500. Signal values are log 2 transformed to intensity values. For genes of interest with multiple probe sets, the intensity value of the multiple probe sets are averaged to obtain a single intensity value for each gene. The single intensity values of genes in the GCB signature are averaged to obtain a GCB signature average of 9.2. The single intensity values of genes in the stromal-1 signature are averaged to obtain a stromal-1 signature average of 8.5. The single intensity values of genes in the stromal-2 signature are aver...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| resistance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com