System and method for compensating instability in an autofocus system
a technology of autofocus and stability, applied in the field of autofocus system, can solve the problems of affecting the reliability of the measured height of the substrate, the inability to achieve environmental control to a certain level,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
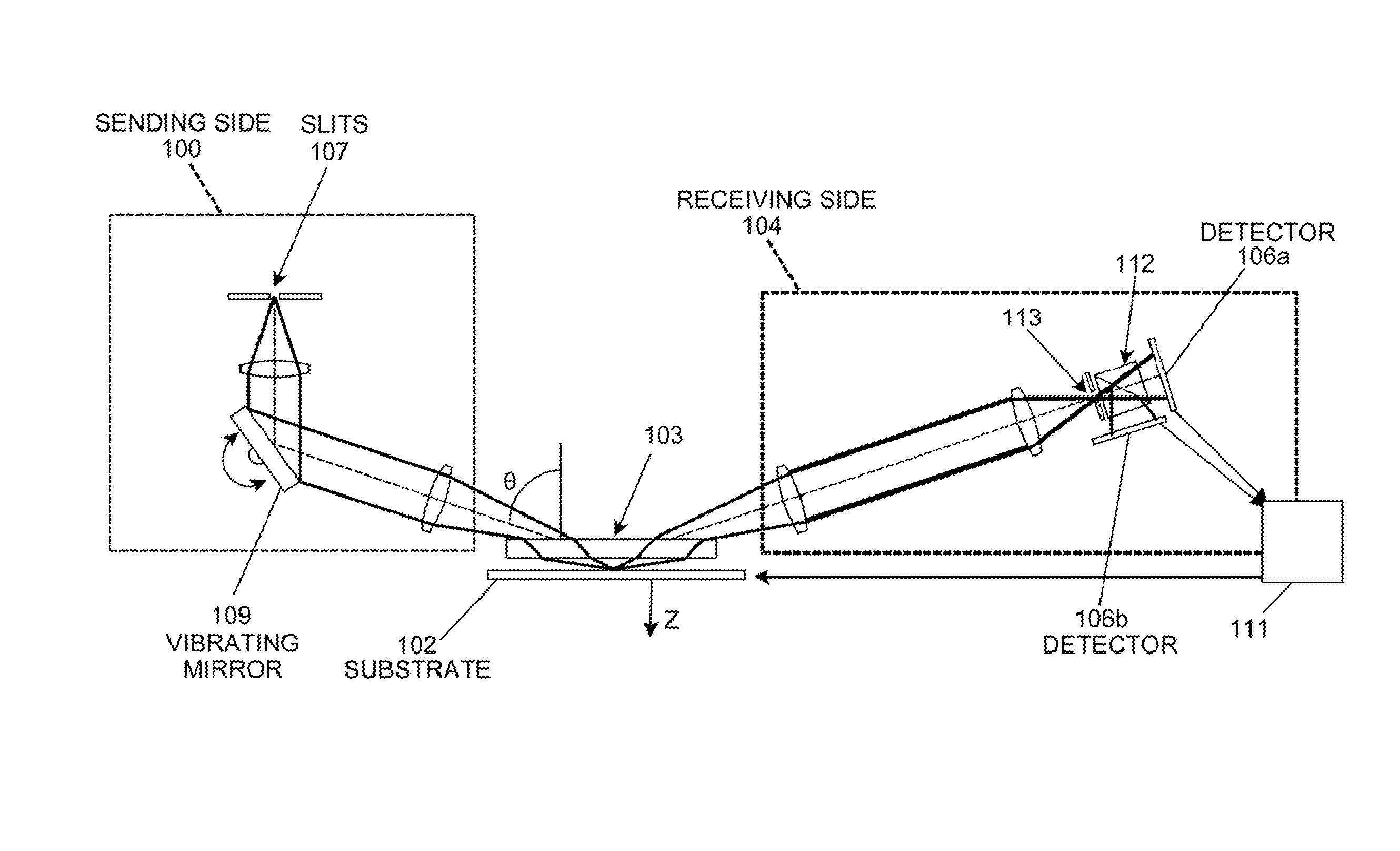
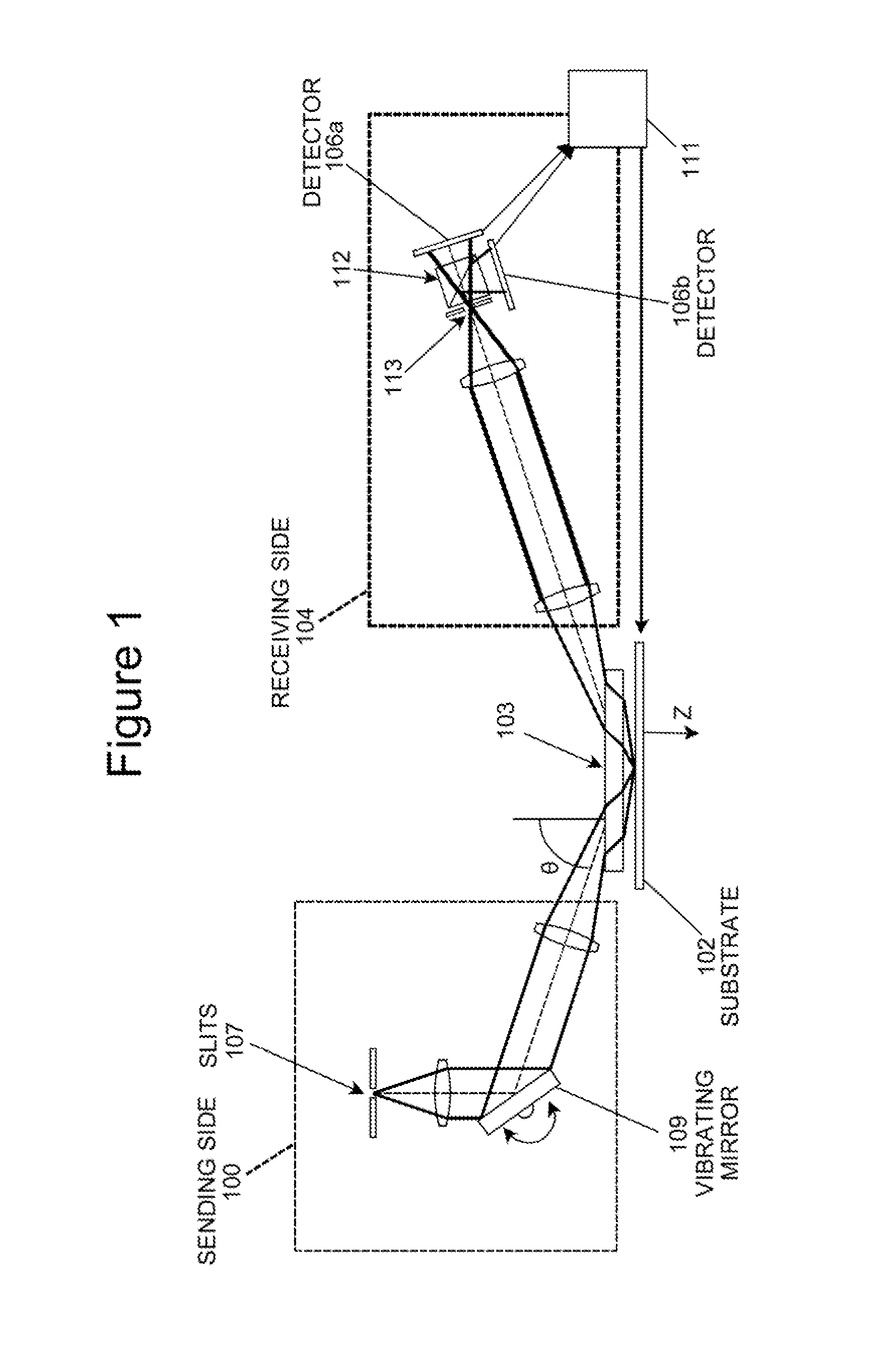
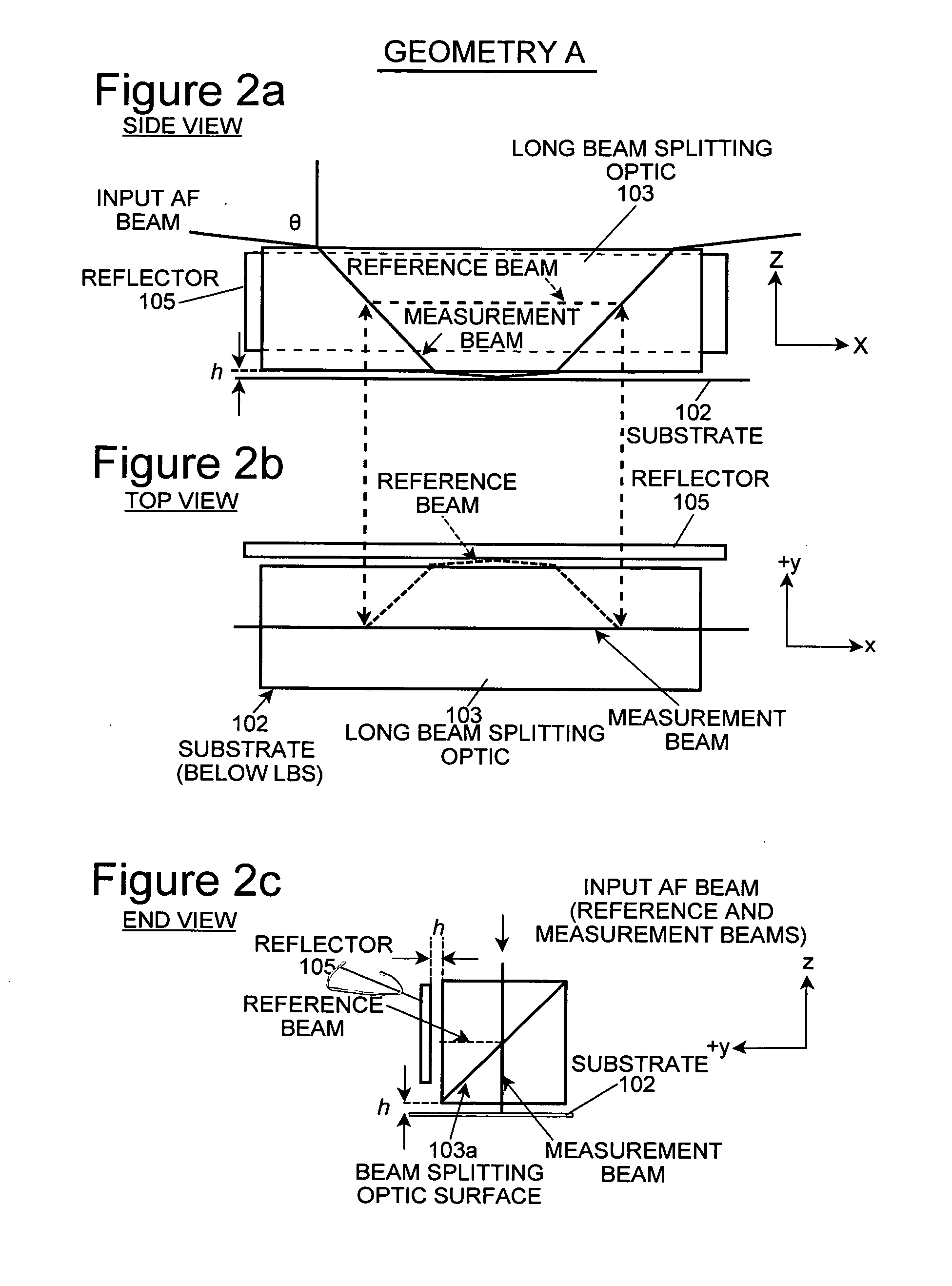
[0027]As described above, the principles of the present invention are particularly useful in an autofocus system and method of the slit detection type. The principles of the present invention are described herein in connection with a system and method of the slit detection type, and from that description the manner in which the principles of the present invention can be applied to other types of autofocus systems and methods (e.g. of the fringe detection type shown in U.S. provisional patent application Ser. No. 61 / 244,321 filed Sep. 21, 2009 and entitled “Goos-Hanchen compensation in auto-focus system by optimal spectrum or digital spectral filter”, which is incorporated by reference herein for all purposes) will be apparent to those in the art. Also, while a slit type autofocus system and method generally provides autofocus beams that emerge from a plurality of slits and are directed through corresponding slits associated with slit detectors, the principles of the invention are de...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com