Semiconductor device storage cell structure, method of operation, and method of manufacture
a technology of semiconductor integrated circuit devices and storage cells, which is applied in the direction of digital storage, semiconductor devices, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of complex manufacturing process of capacitor structures and the need to refresh data values
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
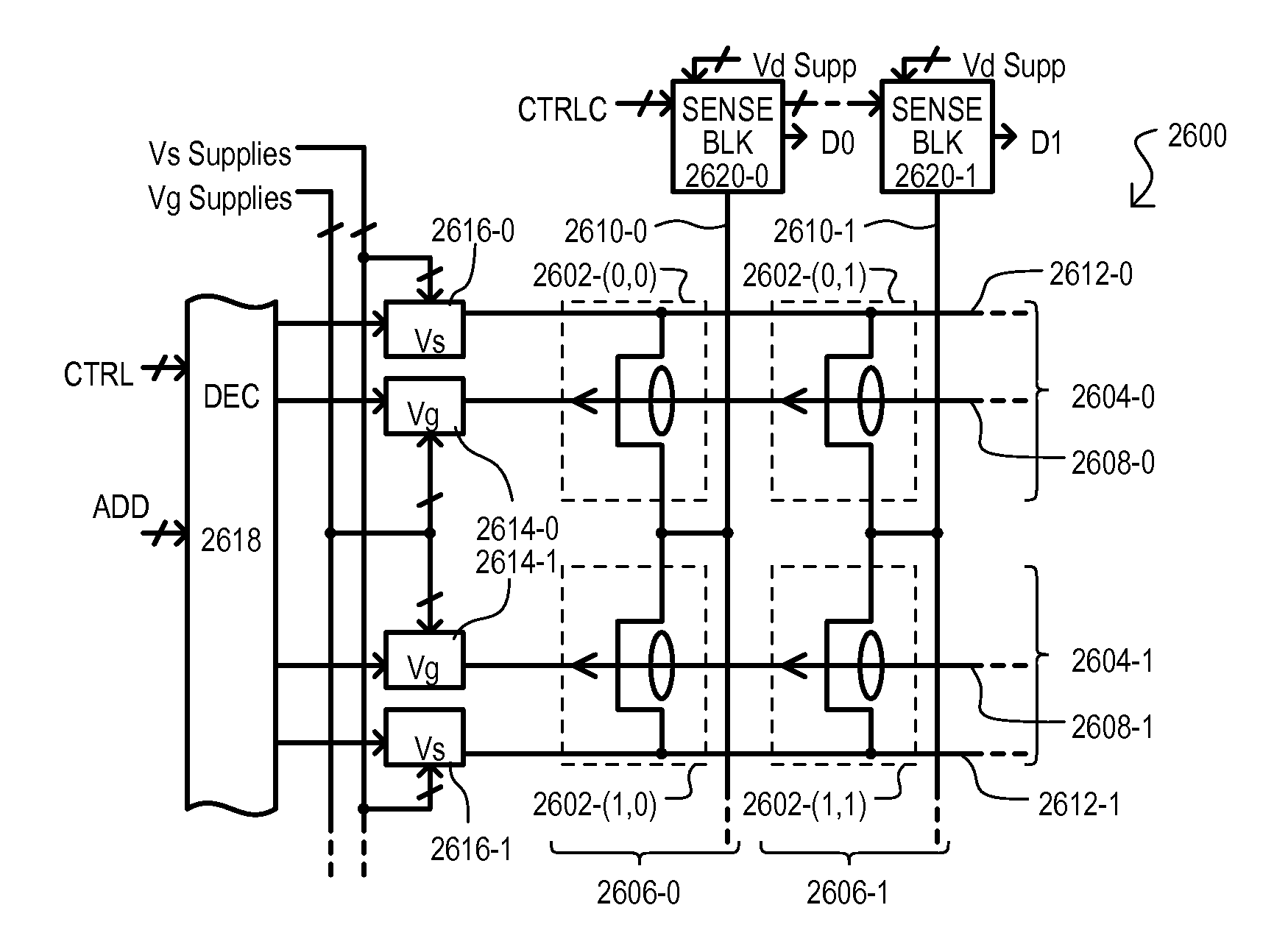
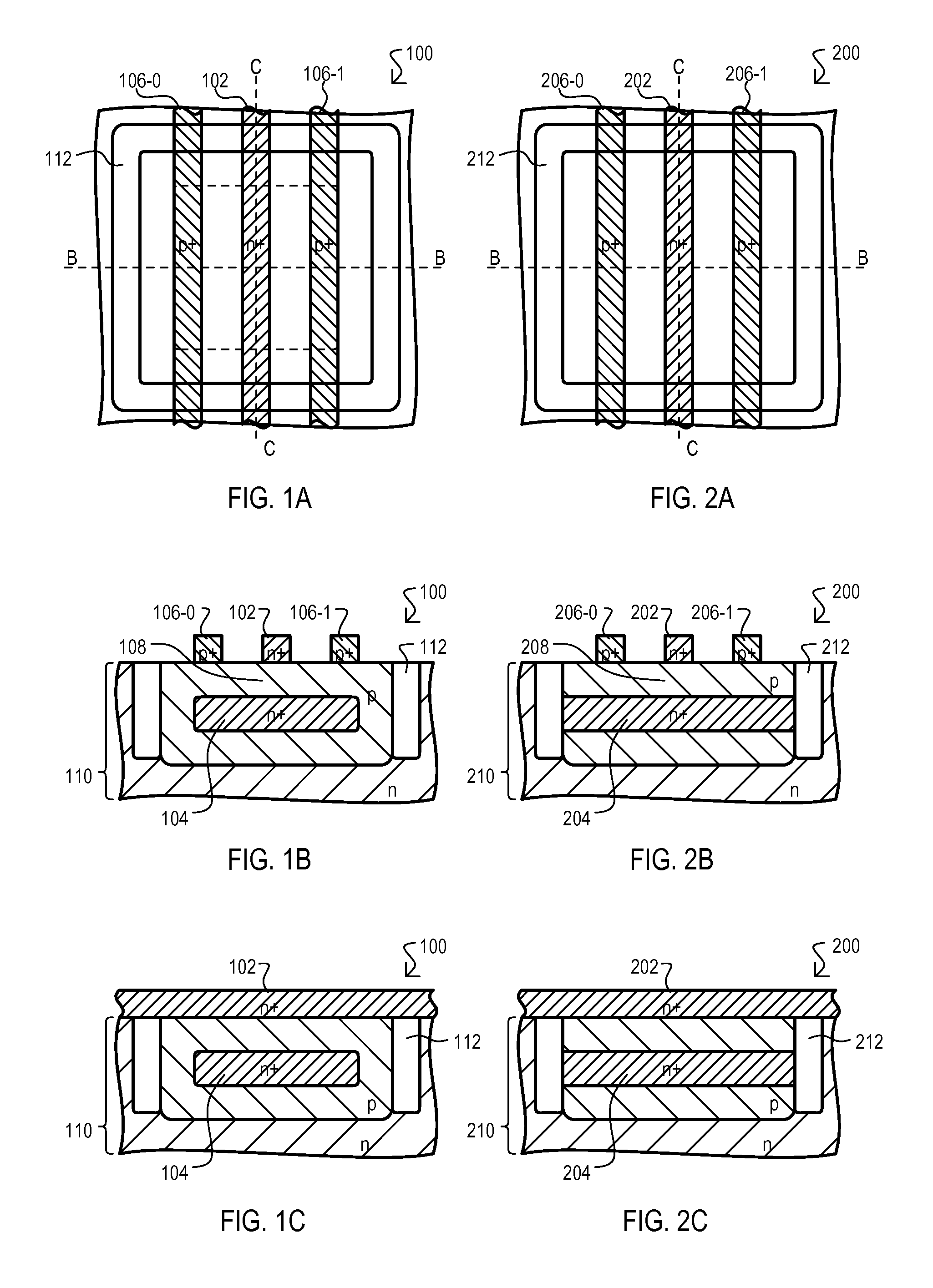
[0049]Referring now to FIGS. 1A to 1C, a storage cell is shown in a series of views, and designated by the general reference character 100. FIG. 1A is a top plan view of storage cell 100. FIG. 1B is a side cross sectional view taken along line B-B of FIG. 1A. FIG. 1C is a side cross sectional view taken along line C-C of FIG. 1A.
[0050]As shown in the various views, a storage cell 100 can include a control gate 102, a store gate 104, a first source / drain 106-0, a second source / drain 106-1, and a channel region 108. A storage cell 100 can be formed in a substrate 110, and can be bounded by an isolation structure 112.
[0051]A control gate 102 can be patterned from a semiconductor layer formed on a surface of a substrate 110, and can be doped to one conductivity type (in this example, n-type). In the particular example shown, control gate 102 can extend over, and be in physical contact with channel region 108 between opposing ends of isolation structure 112.
[0052]A store gate 104 can be...
second embodiment
[0060]Referring now to FIGS. 2A to 2C, a storage cell is shown in a series of views, and designated by the general reference character 200. FIGS. 2A to 2C show the same general views as FIGS. 1A to 1C. Further, a storage cell 200 can include some of the same general structures as storage cell 100. Accordingly, like structures will be referred to by the same reference character but with the first digit being a “2” instead of a “1”.
[0061]Storage cell 200 can differ from that of FIGS. 1A to 1C in that a store gate 204 is not completely surrounded by oppositely doped semiconductor material, and can abut isolation structure 212. Such an arrangement can result in greater charge leakage than the embodiment of FIGS. 1A to 1C, but may still provide for slower refresh rates than conventional DRAMs. In addition, a storage cell 200 may be more easily manufactured, by requiring fewer masks, or may provide more uniform performance as a storage gate position 204 may vary less according to mask al...
third embodiment
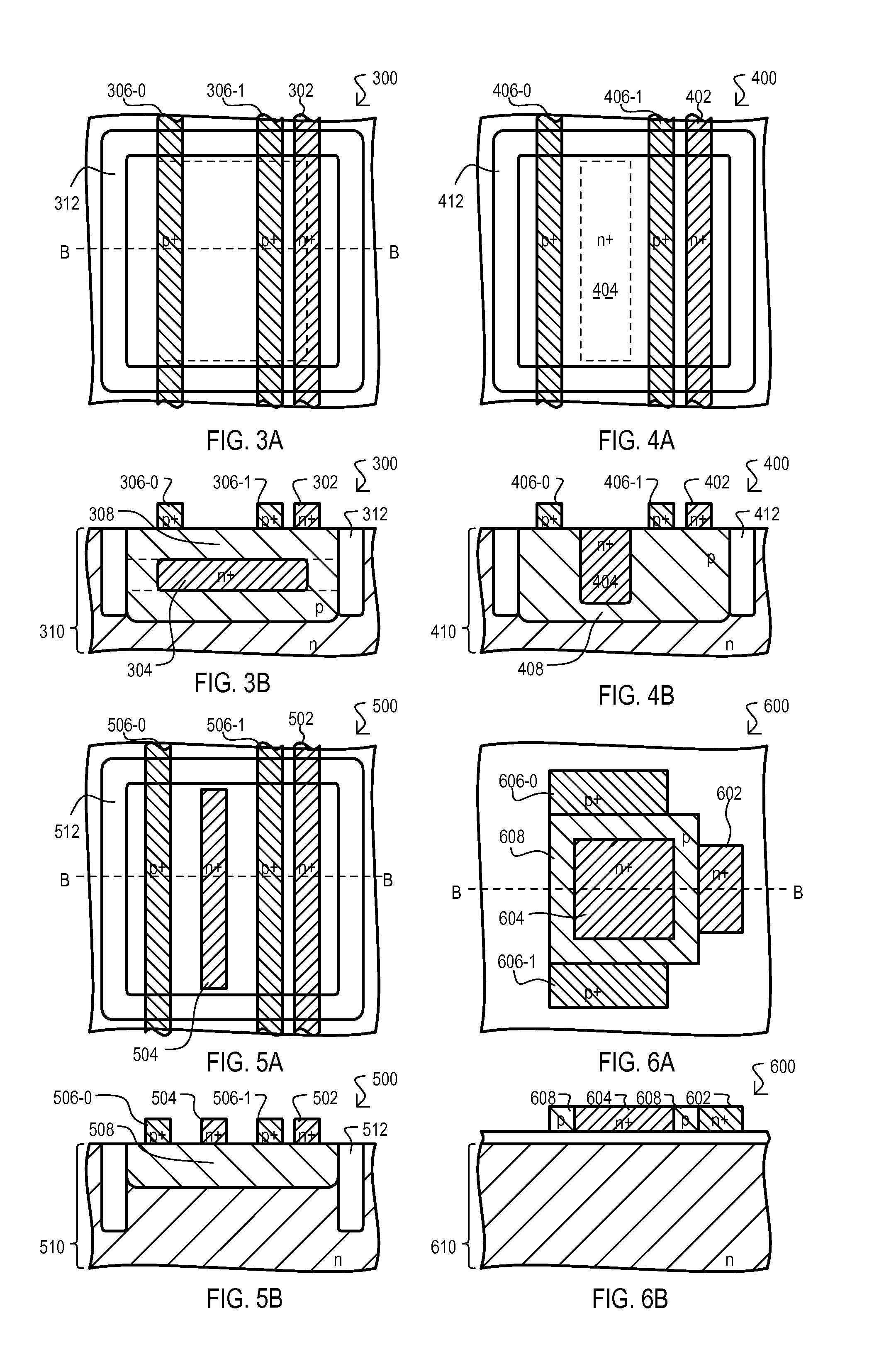
[0063]Referring now to FIGS. 3A and 3B, a storage cell is shown in a series of views, and designated by the general reference character 300. FIGS. 3A and 3B show the same general views as FIGS. 1A and 1B. Further, a storage cell 300 can include some of the same general structures as storage cell 100. Accordingly, like structures will be referred to by the same reference character but with the first digit being a “3” instead of a “1”.
[0064]Storage cell 300 can differ from that of FIGS. 1A to 1C, in that a position of control gate 304 can be different. In the case of FIGS. 1A to 1C, a control gate 104 is situated between first and second source / drains (106-0 and 106-1) in a direction parallel to a surface of substrate 110 (considered herein the lateral direction). In the arrangement of FIGS. 3A and 3B, a control gate 304 is not situated between source / drains (306-0 and 306-1), but rather to one side of both such structures in the lateral direction.
[0065]In an arrangement like that of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com